Behavior of fish in troubled waters
Any rise in water in a reservoir leads to cloudiness. This usually happens because the current erodes the banks, from which most of the dirt comes. In spring, the water also becomes cloudy due to the melting of ice and snow. In such conditions, underwater inhabitants become uncomfortable - a large amount of turbid suspension forms in the water column, which clogs the fish’s gills, and it tries to move to areas with cleaner water. In addition, the current in rivers noticeably increases, which also leads to the migration of fish from the main channel to shallower areas with slower flows. In such places, the fish do not have to spend a lot of energy.
The behavior of the fish also changes. Pike and pike perch rely more on vision; in poor visibility conditions they have to change their hunting tactics - look for places with a large concentration of juvenile fish. Peaceful fish species, such as bream, roach, crucian carp, and carp, rely more on their sense of smell, so poor visibility is not as critical for them as for predators.
Water level and fish bite
The water level in the reservoir significantly affects the fish bite. The depth of the reservoir and the hydrostatic pressure on the fish’s body depend on it. Every 10 meters of water depth is equal to one atmosphere or 760 mm of mercury. A difference in water level one meter higher or lower is equivalent to a change in atmospheric pressure of 76 mmHg. pillar We talked earlier about how atmospheric pressure affects fish bite.
The water level is affected by the amount of precipitation or its absence (drought), intensive melting of snow and ice, water intake for human needs, and the operation of hydroelectric power plants (HPPs). In winter, the water level in reservoirs is on average lower, in summer it is higher. The most significant change in water level, its increase, we can observe during the spring flood - the time of fish spawning.
Sharp changes in water level are inherent in regulated reservoirs. The water in such reservoirs is either profitable, then stops, or decreases. The fish, to some extent, get used to such fluctuations in the water level, but according to observations, it is better for the fish to bite when the water level increases (the water is used for profit). There are exceptions.
Changes in the water level in regulated reservoirs are associated with the current, which also affects the fish bite.
Where to look for fish on the river and in still water
Fish, as a rule, do not stay in one place for a long time, so to catch it you need to run a lot. On large rivers, as the water level rises, the relief is difficult to read, but promising places can still be identified. Such places are:
- River bend.
- Confluences of streams or small rivers.
- Water meadows.
- Places with little current.
- Places located below the dam.
In reservoirs with stagnant water there are no problems with the flow, as well as with finding fish. The most promising places on reservoirs are the mouths of tributaries, places with shallow depths, snags and various bottom vegetation.
Fishing methods
Fishing in muddy water on a river in the spring has its advantages - the fish does not see a person and relies on its lateral line and sense of smell. She behaves less carefully than in clear water. Therefore, the thickness of the fishing line and the size of the hook play a small role. Before the water level rises, it is good to fish with a float rod. At this time, the fish stays close to the shore, where there is no current. With the onset of the flood, it is better to switch to bottom gear (feeder, regular bottom) - they allow you to fish in places where you can no longer reach with a float rod.
On the eve of spawning, many representatives of the carp family - roach, bream, ide - work up a good appetite and feed actively. Fish gather in large schools and enter small rivers or channels, moving upstream to their spawning grounds
On large rivers, as the water level rises, the current intensifies and fishing on the riverbed becomes extremely difficult. It even carries loads weighing 120–150 g without much difficulty. In addition, fish leave the riverbed because, along with melt water, the stream carries with it an abundance of various debris. Water with a strong current is the dirtiest in the entire river. The fish tries to stay in areas of the reservoir with a slow current. It is better to fish near steep banks, in pools, in places with reverse flows, at the confluence of small rivers.
Various animal baits are used as bait - worms, maggots, bloodworms, bark beetle larvae. Vegetable baits are not popular with fish at this time of year.
Large fish are well caught on crawlers, which are not difficult to catch at this time
Bait must be used carefully, as during this period it is very easy to overfeed the fish. On small rivers, during the spring fish run, you can do without it. But if the fish path is a little to the side, then a small amount of bait can attract a school to the fishing point.
Feeding with mixtures consisting only of plant components is an unpromising activity. The bait must include animal components - bloodworms, maggots, worms. If there is a current, you should add a little earth to the bait.
What is the best way to fish?
Experienced fishermen in weak currents prefer to fish with a summer jig. Since fishing is complicated by poor visibility in muddy water and sometimes deep water, it would be better to choose a fishing rod with a side nod, with which you can reach even inaccessible coastal places.
Although the shallow water and the shore are covered with various vegetation, there is no current here, which creates conditions for the water to settle and the mule to settle. Therefore, the water in such areas becomes clearer and the fish direct their movements in search of food here.
If the current in the river is strong enough, it is necessary to use larger and heavier jigs, and when the current is weak or completely absent, for fishing in muddy water it is better to take a jig that is smaller in size and weight. There are also options for using a fly rod and even a plug in cases where the current is strong and the bait is small in size.
Which tackle is better
When going fishing in muddy water, an angler must choose gear depending on the current and water characteristics of the reservoir. Basically, he will have to choose between the gear mentioned above and a fishing rod with a half-bottom rig. It is necessary to remember that a significant part of the mass of the jig is contained in the bait, but in the float equipment the mass is, on the contrary, contained in its load. If the angler chooses a float rod, he will have to hold the bait in the fishing area in muddy water.
Fishing with a float rod in muddy water
Catching predatory fish
Before the spawning ban begins, you can catch not only peaceful fish, but also predators - pike, perch, pike perch. Fishing at this time is quite unpredictable and you can often end up with nothing. The bait must be given literally under the fish's nose, otherwise it will not react to the prey.
In troubled waters, predatory fish should be looked for in the same places as peaceful fish. A promising place needs to be fished carefully, making a large number of casts; often the result is achieved by changing the bait. The wiring should be as slow and delicate as possible. You can use any type of spinning bait:
Silicone baits. The weight of the jig head should be as small as possible (2–5 g), despite the increasing strength of the current. It is the smooth lowering of the bait to the bottom that attracts a passive spring predator. If the current is weak, then you don’t have to surround the silicone bait at all.
Spoons. Large oscillating and spinning lures are great for fishing in muddy water. At this time, they are the most effective baits, along with silicone.
Mepps Aglia Long is one of the best baits for catching predators in muddy spring water
Wobblers. Wobblers with active play and sound effects give good results. Mostly cranks and shads work. Sometimes minnows are also fired, but the wiring must be done smoothly and slowly, with pauses of 10 seconds.
Along with spinning baits, it is also effective to catch predators using live bait. A small roach or gudgeon is suitable as bait.
As you know, pike perch and pike rely more on vision than on smell, so in turbid water conditions they should be caught with brightly colored lures. Both acidic colors - red, yellow, orange - and less bright but contrasting ones - black, white work well.
“If there are no bites, it is useful to change the type of bait, for example, change a twister to a vibrotail.”
Factors affecting fish activity
- Fish always spend a lot of energy during strong currents in order to stay in place during high water periods. After this, their appetite increases, and they become more active in search of food to restore strength and energy during the period of low water. Of course, predatory and more aggressive fish will begin to bite more intensely, which is why it seems that the bite has intensified.
- Muddy water provides a chance for anglers to get closer to their prey. In conditions of poor visibility, fish are less timid.
- When the current is strong, the fish always tries to stay closer to the bottom. Therefore, you don’t have to stand on ceremony here: put out rough and heavy gear with large hooks and thick leashes. This will increase the fishing area, simplify contact with prey, and also increase the overall sensitivity of the gear.
Grayling is caught very well in spring
On the jig
In the spring off-season, a fishing rod with a side nod is a good alternative to float and bottom tackle. Often, fish in troubled water come close to the shore and it is even easier to catch them with a jig than with a float or feeder. The oscillations of the jig in conditions of low transparency are more noticeable to the fish than the bait lying motionless on the bottom. You can catch any white fish with a jig - roach, white bream, silver bream, crucian carp, and often perch is also caught.
Lightweight carbon-fiber rods with a length of 5 m or more are ideal for side-nod fishing. They are equipped with either a regular reel or a small wire reel. The weight of the entire set plays a primary role, since you have to constantly keep the tackle suspended and play with it. Longer nods are used than for ice fishing. Jigs also have more impressive sizes, but their shape remains the same:
- Devils.
- The pellets.
- Uralki.
- Nymphs.
First of all, you should fish coastal thickets, snags, bushes hanging over the water, and backwaters with a reverse current. Although there are bites on a naked jig, there are fewer of them than on a baited jig.
Standard animal baits are used as bait:
- Worm.
- Maggot.
- Bloodworm.
“In the spring, you need to fish only with bait of animal origin; the fish ignores plant baits.”
You need to approach the fishing spot as quietly as possible - although the fish in muddy water cannot see the fisherman, they can hear sounds perfectly. Stomping and loud conversations can alert underwater inhabitants
Gear used in troubled waters
In ancient times, when there were an order of magnitude more fish in the rivers than now, the best gear for high water and floods was considered to be a net (as well as others based on it - muzzles, venter, tops, etc.). Actively walking fish in conditions of poor underwater visibility were perfectly caught in all this.
But over time, the most conscious people realized that it is blasphemous to use this method of fishing in the spring - during the spawning period, because it massively destroys caviar individuals, and therefore undermines the population of the entire fish stock.
There has never been such monstrous damage from amateur gear, and if we take into account the increased complexity of fishing conditions, then it generally tends to zero.
Theoretically, you can fish in muddy water with any gear, but those where the bait attracts fish purely visually will be very limited. And the cloudier the water, the more pronounced this will be. Therefore, during high waters and floods, those tackles and baits where fish are attracted by smell or vibrations come first.
Donka
This is probably the very first tackle for high water. Donki, or zakidushki, are the biggest catches of fishermen during floods.
Animals are usually used as bait: worms, bloodworms, bark beetle larva, caddis fly larva, live bait, fish meat. Plant-based ones are not so popular at this time; they are more suitable for summer. Nevertheless, anything can happen. There are known cases of catching fish in the bottom spring using canned corn, bread, dough, peas, etc.
The spring donka has proven itself very well in catching fish such as chub, ide, bream, crucian carp, carp, tench, and burbot.
Float rod
It is slightly inferior in effectiveness to the previous gear, mainly due to the fact that fishing takes place close to the shore, and on rivers you have to look for areas with no current. However, it is no less popular, especially when catching those fish that stay close to the shore and whose bite you don’t have to wait long for (bleak, roach, dace, perch, ruff, grayling).
On a float in high water, the same baits are used as when fishing with a donk.
Summer jig (rod with a side nod)
If in fishing with the two previous tackles the fish are attracted mainly by smell, then the nodding tackle provokes it to bite due to the vibrations that the jig makes. Regardless of whether it is a true baitless bait, or whether there is something attached to the hook. Vibrations in water travel faster and farther than smell.
But the range of action of a nodding fishing rod is even more limited than that of a float fishing rod. Therefore, it can only fish the coastal zone. However, on small rivers, it can prove to be many times more effective than the two previous gears.
You can catch any fish with nod tackle, except perhaps outright predators. Summer jigs perform very well when catching spring grayling.
Spinning
In muddy water, this tackle does not lose its catchability, although the radius of attracting fish is noticeably reduced. Those baits that actively produce vibrations and noise begin to work best: spinners, spinners, twisters and vibrating tails. Especially with all sorts of “rattles”.
In spring, the brightness of the color of the bait plays an important role, especially if visibility in the water is at least half a meter. Spoons and wobblers of the most acidic colors will work right now.
Fishing in high water with a spinning rod is quite a risky business, because due to the turbidity it is completely impossible to see what is under the water. Planting valuable bait at this time is a matter of one minute.
Surface tackle (boat, drag, balda, fly fishing)
In troubled waters, fishing with this gear often turns out to be a very, very dubious adventure. But when the turbidity settles a little, the level begins to drop and visibility under water will be about half a meter (this happens towards the end of the spill) - fishing with surface gear begins to make some sense.
I know fishermen who successfully catch chub with ide at this time (end of May - beginning of June) using a boat and dragging. A dragonfly larva is used as a nozzle.
You can also use artificial baits like flies. At the same time, the largest of them and the most “poisonously” colored are beyond competition.
During summer rainy floods, the situation is the same with surface gear - the success of fishing directly depends on how cloudy the water is and on how visible the bait is in it.
Burbot fishing
Techniques for catching crucian carp in spring (video)
In early to mid-April, the ice breaks up on the rivers and an interesting period of open water burbot fishing begins. In muddy water, burbot is more active and it is best to catch it during this period of time using donks and baits. If in the fall it bites mainly at night, then in the spring it can be caught throughout the day. But the main thing here is to choose a suitable place, otherwise you may not get any bites. Good places at this time:
- Braids.
- Coastal dumps.
The simplest tackle for catching burbot is a hook. It is a piece of thick fishing line (0.5–0.6 mm) with a retractable leash, a hook and a flat sinker at the end. The length of the fishing line is selected for the specific fishing location, but, as a rule, 20 meters or less is enough. In general, the thickness of the fishing line does not affect the number of bites in any way - you can use very coarse tackle and always have a catch. Animal bait is placed on the hook:
- A bunch of worms crawling out.
- Live bait (minnow, ruff).
- Chicken giblets.
The tackle is thrown into the intended stopping place of the burbot. The fishing line is attached to a wooden peg stuck into the bank.
To detect a bite, hang a bell on the line
Burbot, as a rule, is spotted on its own, and such gear does not require constant presence from the angler. Therefore, the number of tricks can be quite large - 10 pieces is not uncommon.
Catching bleak
In early spring it is interesting to catch bleak. Although this fish is not large in size, it is very tasty when dried and in spring it is especially fatty. To catch it, no special gear is required; a regular Bolognese or fly fishing rod will do. You need to hang the equipment on it:
- Line with a diameter of 0.12-0.14 mm. You can use a thicker one, but thin lines flutter less in the wind.
- Lightweight float with a load of up to 1 g. The smaller the load of the float, the better - bites from such a small fish as bleak will be more noticeable.
- Loaded pellets.
- Leash with a diameter of 0.08-0.11 mm.
- Hook size 16–20, according to international numbering.
It is necessary to fish with bait. It allows you to attract fish from long distances. But unlike other white fish, bleak is not demanding on the composition of the bait, so you can use any purchased mixture - for bream, raft, carp. The main thing is that the bait has a strong smell. A prerequisite is that the bait should be crumbly, easily disintegrate in the water and create a cloudy cloud of particles, and it should not fall like a stone to the bottom. You need to feed often and in small portions, i.e. the lumps of bait should be the size of a walnut.
Bleak is shy and may not come to the bait right away - you need to take this into account during the fishing process
To obtain additional suspension, it is useful to add dry milk to the bait or mix the mixture not with water, but with diluted kefir.
The best bait for this time is maggot. Due to its density, it is more difficult for bleak to pull it off the hook.
Bleak lives in the middle and upper layers of water; catching it at the bottom is a futile task. The float should be lowered in the area of 0.5–1 m.
“When the bite is capricious, it is useful to slightly increase the descent of the float and raise the sinker up. A hook with a nozzle will sink more slowly and, as a rule, this technique provokes a bite.”
Fishing for crucian carp in the river
As the water rises, crucian carp also enter the river. Moreover, crucian carp is large; fishermen often trophy fish weighing more than 1 kilogram. You need to look for it in creeks, with snags and bushes. The depth at the fishing site is often shallow - up to 3 m, the water here warms up the fastest, and as you know, crucian carp is a heat-loving fish.
They catch crucian carp with a regular float rod without using bait. Given the large size of the fish, thin summer rigs are not recommended. After hooking, the crucian carp tries to go into the snags and often you have to force the landing, but this cannot be done with a thin fishing line.
The bait is a dung worm. You can also use a regular worm, but a dung worm has a stronger smell and is more noticeable to fish in turbid water conditions.
To catch crucian carp in the river, it is better to use a float rod rather than a bottom one.
Tips for fishing in troubled waters
- Avoid places with strong currents - catching fish here during the peak of the flood will be problematic.
- The best places for fishing in muddy water are small rivers and stream mouths. The water here is cleaner than on large rivers.
- When catching a predator using a spinning rod, use bright, contrasting baits. They are more noticeable to fish than lures of natural colors.
- When catching bleak, use bait. It will attract fish from long distances and keep them in place.
- If there are no bites, then do not sit in one place - in the spring the fish actively move around the water area of the reservoir. This rule does not apply to catching predatory fish. In this case, you need to fish each place as carefully as possible.
- The worse the weather (rain, strong wind), the better the burbot bite.
- To catch white fish, use bait of animal origin. At this time of year, the bite on them is better than on plant baits.
- In the spring, the most catchy baits for catching predators are spoons (oscillating and rotating) and jig baits.
Fishing in murky water conditions is not the easiest. Unpredictable bite due to constantly changing water levels makes such fishing less interesting than in other periods. But by following certain principles, you can still have a stable catch.
How do high waters and floods affect fish?
Photo 2. The height of the flood.
In almost any river area, a sharp rise in water level is accompanied by a very noticeable turbidity. This is due to the fact that the river bed, regardless of the rocks composing its bed, is usually “designed” for the average spillway value, and with an increase in water mass, it begins to erode. Dirt is also added to the water by temporary flows that always occur during rains and massive melting of snow - they wash away soil from the surface of nearby lands.
Photo 3. Temporary watercourse - melt stream. It carries its muddy waters into the big river.
This moment is not the most favorable for fish, because three factors begin to act against it at once:
- Solid particles suspended in water settle on the gill rakers, which significantly impairs breathing.
- In muddy water, visibility is greatly reduced - down to several centimeters.
- As the level rises, the river flow accelerates. This is especially felt on the main jet. The fish have to spend a lot of energy to overcome the flow.
But the underwater inhabitants “fight” these negative manifestations of the flood in their own way. And, as a rule, they emerge victorious.
The fish simply leaves from the suspended matter that clogs the gills. Where the water is cleaner, or where the turbidity settles faster. In rivers, the only way is to rise to the upper reaches, or go into tributaries. After all, the smaller the watercourse, the less water passes through it even at the very peak of the level, and accordingly, less soil will be washed out from the bottom and banks. And indeed, during high waters and floods, small rivers are always noticeably clearer than medium and large ones.
Pond fish act in a similar way, moving into the main and subsidiary tributaries, but can also concentrate away from the flooded channel - closer to the banks. The dirt settles there faster.
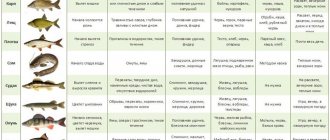
Different fish species react differently to reduced visibility. Those of them who mainly rely on their sense of smell and (or) the lateral line when searching for food are not at all embarrassed by this circumstance. These fish include: ruff, carp, crucian carp, tench, bream, roach, catfish, burbot.
Photo 4. Visibility in completely muddy water. The picture was taken using a camera hermetically sealed in a plastic bag and submerged to a depth of about half a meter.
The same species that rely heavily on vision have to change their tactics for finding food. These are active fish, or ambush predators: pike, asp, dace, chub, ide, pike perch, perch, grayling. In clear water they usually “stand” in one place and wait for the food object to be in the visibility zone, but in muddy water this zone is very limited. Fish have to constantly move, “comb” their hunting grounds, “listening” and “sniffing” the situation.
The fish generally tries not to get involved with the third negative factor of the flood - a strong current, because it is energetically unprofitable to spend energy on it. It rarely goes out onto the main stream and mostly huddles closer to the shores and quiet backwaters. And, again, it rises into smaller tributaries, where the current is weaker.