One of the most important trophies for almost every fisherman is pike. A characteristic feature of pike fishing is that it can be done at any time of the day. For example, a large pike in most cases takes the bait in the morning, and in windy weather closer to the middle of the day. But at the same time, it is important to take into account the characteristics of a particular body of water, each of which has its own best biting hours. The weather also plays a big role in the process of pike fishing, so on cloudy days, with light rain, fishing can be more successful than in clear weather. The main methods of catching pike are using spinning rods, different types of fishing rods, mugs and other gear. However, not all of these fishing methods bring equal success. Thus, it has been noticed that on the same body of water it is sometimes better to catch pike with circles than with a spinning spoon. For example, at the end of winter she sometimes takes only lures, but not well with live bait. Therefore, when choosing a fishing method, you must always take into account the characteristics of the reservoir.
Content
- 1 Description and lifestyle of pike
- 2 Places of distribution of pike 2.1 Places of distribution of pike in Russia
- 2.2 Distribution areas of pike in the World
- 4.1 Catching pike with a float rod
Description and lifestyle of pike
The appearance of the pike is known to all fishermen: a long torpedo-shaped body with a spotted and striped camouflage color, an elongated crocodile mouth dotted with razor-sharp teeth.
Pike have large eyes that turn after their prey and have a wide range of vision - they can see well in front and to the sides. The coloring is protective: gray-green sides, alternating dark and golden stripes and spots, which allows the pike to camouflage itself for a surprise attack. It is curious that this color is very variable and depends mainly on the color of the surrounding background - the color of the bottom, the presence of plants on the bottom. In heavily shaded forest lakes with a muddy bottom, the pike is almost black, and in rivers with a sandy bottom, it becomes lighter and more elegant.
Differences in color appear even in pikes of different ages. Young pike are soft green and bluish in color (blue feather pike). And adult individuals living in deep pools are almost black. Moreover, even the body shape of this fish varies widely. There are pikes with a long body, like a torpedo, and there are short, thick ones, as if chopped off.
Based on all these characteristics, a distinction is made between the grass pike, which can be found in shallow places, in thickets of coastal grass, and the bottom pike, which lives in the depths. Whether one form transforms into another under the influence of lifestyle or we are dealing with different variations of pikes is yet to be determined by science. Pike is distributed almost everywhere throughout the Northern Hemisphere. It can be found from the tundra ice lakes of the Far North and the rivers of the Arctic Ocean to the large and small rivers of the Black Sea and Caspian basins. The American continent has its own species of pike. In the Northern States and Canada, another species is known - musky. This is a larger fish than the European one, lighter in color and heavily spotted. Black or striped pike live in the Southern and Eastern states. Finally, the sea pike, the barracuda, lives in the seas and oceans, but it has little relationship with the heroine of our story.
Depending on the time of year, pike's diet includes worms, leeches, crayfish, tadpoles, frogs, chicks and mice falling into the water. Especially large “water tigers” can swallow waterfowl chicks and water rat cubs. In conditions of fierce competition, the pike does not even allow its own young to escape!
Immoderate greed sometimes forces pikes to grab fish almost half their size. Then the tail of the half-swallowed fish sticks out of the predator’s mouth for a long time, while the head of the victim is already digested by the stomach.
It is a mistake to consider pike a harmful fish just because it destroys a lot of valuable fish: juvenile roach, bream, carp. In fact, in natural balance, a pike in water occupies the same place as a wolf on land. Exterminating weak, sick, infected individuals, the toothy one is a kind of “orderly” of the reservoir. The presence of pike, for example, in a carp pond always benefits the farm. The fish in the pond become more active and the fish stock as a whole prospers.
Pike is the number one predator in our inland waters. One might say, the main trophy of our waters, the longed-for dream of everyone who picked up a spinning rod. The unsurpassed sportiness of pike fishing is given by the strength and power of the pike's resistance on the line, its jumps and candles during fishing. In a word, this super-active predator, wise and reckless at the same time, gives the fisherman unusually vivid emotions.
Where does pike live?
This is a rather conservative predator. If you have found a successful pool and managed to catch several serious specimens, you can visit here again in a week. In summer she often stands near bridges. The water, running around the supports, creates reverse flow zones - predatory fish love them very much. It is worth paying attention to places where washed-out trees lean low over the water. Insects fall from the leaves, small fish prey on them, and pike feast on the small change. But be careful not to get caught on branches when casting.
To learn more:
Review of baits for catching carp in October
A type of predator, the grass weed, hides in the algae, from where it makes raids on small things floating by, but usually small specimens adhere to this tactic. In September, when the water level in the river decreases, the pike slides into deep pools and lives mainly in them. The number of fish in the bottom depressions may vary - one predator often lives in a small hole, and if it is a full-fledged pool, several trophy specimens may coexist in it. Usually the biggest bait is enough. In November, when fishing on the first ice, it makes sense to choose passages between the reeds - large specimens almost always move along “paved paths”, avoiding swimming into dense vegetation. Knowing where pike are found, you will always return with rich catch.
Pike distribution areas
Distribution of pike on the map of Russia
Distribution areas of pike in Russia
The distribution region of pike is extensive. It lives in almost all water bodies of Europe (the basins of the North, Baltic, Barents, White, Black and Caspian seas), Asia (the basin of the Aral Sea and the Arctic Ocean) and North America.
Pike can be found in small irrigation canals (polders), and in small rivers, ponds, and lakes. It is found in the largest lakes (Ladoga, Onega, Baikal, etc.) and in the bays of the seas (North, Baltic, Barents, White, Black and Caspian seas). This ubiquitous predator lives even in fast-moving, rapids northern rivers!
Distribution areas of pike in the world
Distribution of pike on the world map
Pike lives on all continents located around the North Pole. Such different peoples as the Mongols, Lapps, Eskimos and Indians noted unexpected encounters with this toothy predator. The ranges of other members of the pike family, such as grass, redfin and chain pickerel, as well as muskies and Amur pikes, are very small. Pickerel and muskie stick to specific areas of North America, and Amur pike is found only in a small area of Asia. Pike are found in a wide variety of waters, reflecting their ability to adapt to a wide variety of environmental conditions. It turned out that pike can live almost anywhere - that is, wherever the alkalinity and water temperature do not rise too high. Few freshwater fish have such a wide distribution range.
Pike habitats
Pike has fairly constant attachments to its habitat. You must understand that pike likes to sit in ambush; it will not chase prey throughout the entire reservoir, but always prefers to stand somewhere in shelter (in thickets of plants, under snags), from where it makes unexpected lunges after its prey.
Schools of fry move around the reservoir, depending on the season, gravitating, however, to the coastal zone. There is always a thriving life of aquatic invertebrates on the island, and there is always some kind of food for white fish. These two factors: the constancy of the pike and its movement after the fry, determine the presence of pike in certain places. At different times of the year, searches must be guided by knowledge of its biology.
In winter, pike stay in holes or along the edges of holes, where its main prey stands in winter lethargy. Only occasionally, and even then only during thaws, does a predator under the ice go out into shallow water for a short time. Pike hunters – zherlichniks – know this. In winter, pike girders are placed, as a rule, on dumps in pits, on edges, that is, in places of possible passage, and in thaws - in shallow water near reeds.
The spring melting of snow and ice brings revitalization to water bodies; oxygen enters the water with melt water. Pike spawn early; at the end of February - beginning of March, while still under the ice, the pike begins its movement to the spawning grounds. It often gathers near dams where the water is bubbling. It goes to bays to spawn, and the more secluded the bay is, the better it is protected from the wind by reeds, the more likely it is that you will meet pike there in the spring.
As soon as the water warms and aquatic vegetation rises, the pike disperse along the river. Now it can be found in its permanent habitats and ambushes. Such places are any zones where there is a current boundary, any natural obstacles, the mouths of tributaries, places in the shadow of any pile structures, borders of edges and falls into pits, the edge of aquatic plants and water lily fields. The toothy predator does not really like fast-flowing water; it always looks for calmer zones, or more precisely, the border between the stream and calm water. This has its own calculation: the stream brings prey to the pike (weakened fish), and the shelter allows it to wait for a long time, without wasting energy.
The statement that pike loves calm water is not entirely true. In musty, stagnant bays there are no pike in summer. It should be taken into account that in summer the “mistress of the reservoir” always prefers colder water, so it can often be found near underground springs, where the water temperature is lower. It is for this reason that pike avoids shallow waters that are too warm in the summer, and if they appear there, it is only at dawn and in the morning hours.
In summer, pike activity also depends on the weather. Namely: in hot sunny weather with high atmospheric pressure, it is mostly passive, but if a cyclone comes, the pressure drops, and all this is accompanied by light rain, then real “pike weather” sets in, when the pike will bite all day.
A few more words about searching for catchable pike spots. Along the edge of the grasses, in the coastal zone, you can always catch small squints, but these trophies are unlikely to please anglers. Large pike prefer deep, snagged areas, whirlpools, and riffle holes.
Grass thickets are also a place for constant ambushes of the river robber. As a rule, algae and aquatic plants grow until the first drop in depth. Forage fish usually accumulate in such a place; pike hang out on the edge of the algae. And if the algae does not reach the dump itself, pikes can hide near bottom structures: snags and driftwood, elevations and bends of the bottom. Our predator also loves whirlpools and “returns” behind fallen trees, and loves cliffs with bottom changes, especially if there are trees bent over the water above such a cliff.
At the beginning of autumn, water renewal occurs, cool water from cold air and rain mixes with warm water, and the thermocline disappears. The activity of forage fish decreases. But since pike is a “cool-loving” fish, its activity, on the contrary, is on the rise. The period of autumn cold water creates excellent conditions for the “river wolf”. But the question arises: where to look now for the toothy predator? As the weather gets colder, as a rule, pike, along with forage fish, move to deeper areas. As always, you need to look for bottom anomalies - snags, edges, ridges, stones.
On small and medium-sized rivers, we look for pits and barrels, and fish the edges of overflow pits. Somewhere here, on the border of the depths, on the edge, there should be a pike in the fall, grazing white fish standing in the hole. However, on warm, sunny autumn days, when peaceful fish come out to feed in small bays bordered by reeds, pike naturally move there too. The peak bite, as in early spring, shifts to daytime, when the water has warmed up well. In shallow water, the pike still adheres to familiar tactics - looking for bushes of grass, the edge of reeds, some clues on the bottom. Sometimes you can fish in shallow water until the freeze-up.
Predator feeding and spawning
Any small living creature that finds itself in the predator’s field of vision can become its prey: perch, roach, minnows, ruffs and other fish. On occasion, he does not refuse small bream, silver bream, ide, small pike. More than once, villagers noticed that large predators attacked birds and small animals living in the water. Ducklings, mice, frogs, and muskrats can become targets of attack. There are no restrictions for her - she will happily feast on any living creature that is smaller in size.
To learn more:
Rating of the best wobblers for pike
Pike spawning begins soon after the final ice melts, when the water warms up a little. Early spawning is observed in small pikes; large specimens spawn several days or weeks later. Females begin to throw at the age of four, and sometimes three years, males mature a little longer. A shallow place is chosen as a spawning ground - 50-100 cm, where the water warms up faster, which means that the fish will be more active. Here the female lays eggs and the partners fertilize them.
One pike per season can spawn from 20 to 200 thousand eggs - the specific number depends on age and size. Large (up to 3 millimeters in diameter) fertilized eggs have a slightly sticky surface, making them easily stick to objects. But after a few days, the stickiness decreases and they fall to the bottom, where they subsequently grow. The process goes through several stages:
- the egg is not active, develops due to the supply of nutrients;
- The larva hardly moves. It receives everything it needs for life from the yolk sac attached to the stomach;
- The fry swims confidently, feeds on the smallest organisms, gradually turning into an adult.
During spawning, the predator develops a strong hunger, but fishing is not allowed - fishing is poaching and is strictly punishable by law.
Pike fishing methods
Pike can be caught in many ways. Some of them are traditional - passive, and there are also more active - modern.
Live bait fishing rod equipment
Catching pike with a float rod
Recommended reading: Fishing for pike with live bait in spring
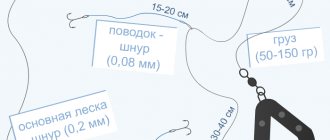
This method, the most accessible to any angler, is applicable mainly in reservoirs, lakes, ponds and rivers with weak currents. The tackle consists of a rod of the greatest possible length with a strong end; fishing line with a diameter of 0.3-0.4 mm; a float (made of cork, foam plastic or bark) egg-shaped and of such a size that it can hold live bait; sinkers; a metal leash and a single hook (double, tee) No. 5-10 with a nozzle. The rod can be medium-sized, or even short, if it is equipped with guides, a reel and a sliding float, which allows you to make long casts. The best bait is live bait: roach, ruffe, perch, gudgeon, char, loach, bleak, crucian carp.
Live bait is released 40-60 cm from the bottom and higher. It is attached by the lip or the back, less often by the tail. Some anglers put two minnows or loaches on a double. In general, it is more effective to use two single hooks, passing one through the gills into the mouth and hooking the other bait on the back. This, by the way, allows you to hook a pike immediately as soon as the float disappears under the water, rather than waiting for it to swallow the bait. As you know, pike in most cases does not immediately swallow its prey, but swims with it for some time, holding it in its teeth. That is why, when fishing for doubles and trebles, the angler is in no hurry to hook, but hesitates to give the pike time to swallow the prey.
At depth, fishing with a float rod is mostly done from a boat installed on anchors. The rod can be short, but preferably with a reel and a sliding float. The live bait is placed behind the back on a tee or two single hooks, one of which is passed into the mouth through the gills. However, a large single hook hooked to the back of a live bait also works well. An interesting tackle of his own invention was recommended by L.P. Sabaneev. It consisted of “a small hook No. 5 (according to the old numbering, corresponds to modern No. 7 or 8), to which was attached a thin copper wire bent in half, about an inch (4.45 cm) long with a single or double hook at the ends.
Fishing for pike with a spinning rod
When catching pike with a spinning rod using artificial bait, anglers often encounter a situation where the pike chasing the fry does not want to take any of the baits. Various types of bait wiring do not help either. In this case, you need to try to catch pike with live bait. It is better to catch pike with live bait that lives in the reservoir where you are fishing. As live bait for catching pike, you can use ruffe, small perch or crucian carp, roach, bleak and other fish. Moreover, it is better to use live bait to catch fresh bait, which with its movements attracts pike, stimulating its appetite and provoking a bite. Depending on the size of the live bait and the diameter of the leash, hooks, tees or doubles No. 6-8, single hooks No. 8-12 are used. It is necessary to place live bait on the hook carefully so as not to injure the bait and leave it alive and lively. Casting a spinning rod with live bait must be done to places where pike are chasing fry, without allowing the fishing line to weaken. Feeling the tension in the line and the jerk, you need to make a hook. If a large pike is caught on a spinning rod, in order to prevent the line from slipping or breaking, the pike must be tired by slowly pulling it towards its shore, without allowing it to go into a snag.
Live bait methods of catching predators are not humane; for this reason, in some European countries, live bait fishing is prohibited. The height of skill is to seduce the spotted beauty with artificial baits. This requires knowledge of bait animation techniques, the ability to cast and cast it correctly. Spinning fishing also requires precise hooking, the ability to tire with relatively light tackle and reel in large prey. Finally, such fishing is spectacular and exciting. Let's look at spinning fishing in more detail.
Tackle. A good spinning tackle is a real work of fishing art, in which all elements are balanced and matched to each other.
Over the long history of the development of spinning rods, a huge variety of fishing methods and techniques has appeared. Since various spinning techniques require their own gear, let’s talk about them.
Jig fishing
Jig fishing - or jig fishing with silicone baits mounted on special hooks with a lead head. A complex action rod, braided line and a medium-class reel are required.
Twitching
Twitching - fishing in a jerky style with driven twitching wobblers. A rigid rod and non-stretchable braided line are used.
Jerking
Jerking - fishing with bladeless wobblers - very large jerks. Requires a special powerful rod with 80-100 grams of dough and an appropriate reel, preferably a multiplier.
Trolling
Trolling is fishing using a motor boat, when wobblers are pulled behind the boat. Lures are most often large and deep-reaching. Trolling is used to catch fish in large rivers and reservoirs. The tackle is quite powerful, again with “multi” reels, because very large trophies are caught. A little about spinning lures for pike. Each fishing method requires, of course, its own baits. But the general rule applicable to pike baits: they should be large, bright, clearly visible, even in muddy water, and preferably with an acoustic effect.
Oscillating spoons
Oscillating spoons are traditional lures for pike fishing. Pike “spinning spoons” are large, wide spoons, like DAMM Effzett, KUUSAMO Professor, ABU GARSIA Atom. These lures must be able to glide in the water, that is, vibrate attractively and play when falling.
Spinners
Spinning spoons remain attractive to pike, but of course, you have to use large numbers, starting from No. 3 and higher. The best spinners are known: French MEPPS, Swedish MYRAN, Finnish BLUE FOX. There are special pike “spinners”, such as the very large MEPPS Pike killer. Spoons with two petals also attract pike, and not some other fish. The color of the spinners depends on the time of year and the transparency of the water; pike often prefer “acid” colors, noticeable in muddy water.
An attractive pike lure includes a spinnerbait - a combination of a rotating blade mounted on a rocker with a hook in a furry “skirt”. A spinnerbait is used to fish in shallow water, among the grass.
Jig lures
Jig baits are soft plastic baits that are attached to a hook with a lead head - a jig. The most common are vibrotails - baits in the shape of fish and twisters, more like a plump worm with a tail. The tails of jig baits oscillate under the influence of water pressure and create an attractive vibration.
The best companies producing silicone baits: MANNS, RELAX, MISTER TWISTER, STORM, BASS ASSASSIN, PROFI BLINKER, BERKLEY, GARRY YAMAMOTO. Recently, passive baits have become increasingly popular; these are plastic baits that do not have their own game in the water: worms, slugs, frogs, crustaceans. And, nevertheless, pike takes passive baits well, if, of course, they are revived correctly.
Fishing with wobblers
Fishing with wobblers is a whole chapter in the book about pike fishing. There are a huge number of different classes of wobblers (surface, medium-depth, deep-going, sinking, floating and neutral buoyancy - suspenders). Here are the most famous companies that produce the best wobblers in the world: MEGABASS, RAPALA, DAIWA, YO-ZURI, ZIP BAITS, JACKALL, SALMO, BOMBER. Each type of wobbler requires the ability to animate it and know when to use it. Take, for example, surface baits of this class – poppers and walkers. You can put them into action when the pike strikes in the thickets of water lilies, in grassy bays. Special classes of wobblers include twitching and jerking baits. They have one thing in common - a jerky style of wiring. Read more about fishing with these baits here.
Catching pike with mugs
Circle for pike
The success of this method of catching pike depends primarily on the correct choice of place, which poses considerable difficulties. After all, it is necessary that a confluence of circumstances such as a slow current, the desired wind direction, sufficient (4-7 m) depth, and a flat bottom over a long distance be favorable. If they fish in a reservoir, they look for the beds of flooded rivers, shallow reaches, bays, and “patchlets” (areas of a slightly elevated bottom). It’s a good idea to find an area with a flat bottom. Otherwise, on some mugs the live bait will go too high, while on others they will cling to the ground and various underwater objects. Steering a boat requires solid skills, which in the wind and waves will certainly drift and spin. The rules of amateur fishing allow fishing for no more than 10 circles. They are released 4-6 m from one another, sometimes in a checkerboard pattern, in two rows. Live bait is released approximately 60 cm from the bottom. On rivers with a slow flow and a flat bottom, the descent may be greater. Half-water fish let in live bait on hot days, when the pike stays in the middle layers of the water. Having launched the mugs, the fisherman holds the boat in such a position that each of them is in his field of vision. The best position is behind or to the side. The fisherman carefully watches the circles, separates those that have floated down, returns to their place those that have drifted far to the side, and frees those that are caught on the ground. But the main thing for him is not to look at the inversion. An inverted circle can spin slowly or quickly under the action of the reeling line. We must hurry here. The fisherman approaches the circle against the wave and hooks. Reversals can also be false. One of the reasons for this is the large baitfish. In this case, the line is removed from the upper cut of the stick and wound around its base (two or three turns). A false reversal occurs when a pike or other fish grabbed the bait, but for some reason did not swallow it. Live bait that has been in the teeth of a predator must be replaced.
Catching pike on a running donk
In the old days, this method was called floating fishing and was widely used by Russian fishermen. It can be compared to a lure, only not a metal likeness of a fish, but a real live bait. A walking rod consists of a fishing rod usually up to two meters long (you can use a one-handed spinning rod), a fishing line with a diameter of 0.4 mm, a soft wire leash, a sinker weighing up to 50 g and a tee No. 7-9. The best live bait is the minnow. Of course, in the absence of it, they use fish and other species, frogs. A walking bottom is effective in deep holes where there may be snags and sunken logs, which eliminates or at least makes it difficult to catch fish with a spinning rod or a line. It is caught mainly in the fall with a running bottom, when pike, following small fish, goes to deep places in reservoirs. It is more convenient to fish together, when one rows with a stern oar, and the second, sitting in the bow of the boat, periodically lowers and raises the live bait. Some anglers fish without a partner, steering the boat with one hand and jerking the rod with the other. In this case, you need a small oar with a short handle, for example from an inflatable rubber boat kit. Anglers do not have a consensus on where to place live bait when fishing with a running bottom. Some argue that it should go 50-70 cm from the bottom, others - that the live bait along with the weight should drag along the bottom. Maybe the second option is preferable, but how to protect the tackle from snagging? Apparently, the choice will depend on the angler’s knowledge of the nature of the bottom. Live bait on a running bottom often indicates an approaching bite. Seeing a predator, it begins to rush, and its energetic movements are transmitted along the fishing line and fishing rod to the angler’s hand. The pike, having grabbed the bait, tilts the tip of the fishing rod down. There is no need to rush into hooking, remembering that the predator does not immediately swallow its prey. It’s not superfluous to lower part of the fishing line, or even lower the fishing rod into the water and only then jerk it sharply.
Catching pike on a girder
It cannot be called such a great art to catch pike with live bait, especially in a passive way, for example, by setting up girders at night. Zherlitsa is an old way of catching pike, one might say ancient. The zherlitsa is called a postavusha, also a flyer, because it is a flyer cut from a tree, with a fishing line wound crosswise on it in a figure of eight. At the end of the line there is a sinker and a leash with live bait. After setting the descent depth, the fishing line is secured into a split at the end of the flyer. The zherlitsa can be placed by tying it to tree branches bent over the water or snags sticking out of the water. Well, in shallow water, they do this. They take a pole, stick the pointed end obliquely into the bottom, and hang the pole itself to the pole. A pole with a pole can be stuck into a steep river bank, above a pool. Usually they place the girders at night, inspect them in the morning and remove the prey. Gear fishing can be productive in some places, but it cannot be called sporting.
How to choose a spinning rod for pike fishing
The choice of spinning rod for pike fishing will be influenced by a number of features, primarily related to the fishing method. You will fish from the pubes or from the shore. If from the shore, then what is the size of the reservoir, how overgrown is its shore? So, on a small body of water, especially with an overgrown bank, or for fishing from a boat, a one-handed spinning rod of short length is suitable.
If the area of the reservoir is large, especially when fishing from an open bank, it is better to take a two-handed rod up to three meters long. The length, test and action of the spinning rod will also be influenced by your fishing method. When fishing with a uniform or intermittent retrieve, you can use any spinning rod.
For twitching or jigging, you need a rod with a fast action and light or medium cast. The spinning test will also be influenced by the mass of baits you use, lighter in summer and heavier in autumn.
Optional video
How to catch pike with a spinning rod
Catching pike with a spinning rod is simple and difficult at the same time. To catch it, you need not only to know how to choose the right fishing time and place of bait. It is necessary to have a good grasp of fishing techniques, and, in addition, to know many nuances that come with experience and ultimately determine its capture.
The time for catching pike undoubtedly depends on the time of year, but mainly it is the morning and evening dawns, when it is actively feeding. She is an ambush predator, so she almost does not move around the reservoir, you need to look for her.
To do this, moving around the reservoir, all promising places are fished, in each of which up to a dozen casts are made, in order to check the presence of pike at different depths, at different points, passing the bait at different speeds. There is no need to stay in one place for a long time.
Important! Since the location and bite of pike is influenced by many factors, to successfully catch it, you need to actively move, change baits, methods and depth of fishing.
It is better to start catching this predator with baits that have a more natural color and style of play, and only if there is no bite, move on to experiments.
Fishing techniques can be different and there is no one that is the most catchy or universal. Sometimes simple smooth wiring gives better results than the most sophisticated twitching. You can start with slow, even movements, gradually introducing additional elements such as jerks, nods, stops, trembling of the bait and changing its speed.
It is fashionable to use stepped wiring, pulling the bait with periodic pauses, during which it smoothly sinks to the bottom. Pike usually bite during a pause on a falling bait.
Twitching wiring: perch (left) and pike (right)
Twitching is used when fishing with wobblers, making horizontal twitches or jerks with the tip of the rod during continuous retrieving. In this case, the wobbler will rush from side to side, increasing the chance of a bite.
Important! When performing a retrieve, remember that a pike, when attacking from an ambush, attacks the weakest prey, so the more attractive and catchy the bait will be, the more its manner of movement resembles a wounded small fish.
Separately, it is worth mentioning some features when fishing for pike from the shore. When choosing fishing spots, such as coastal holes, edges, and algae thickets, you should also take into account factors affecting the landing of fish.
Consider the depth near the shore, the presence of thickets and underwater grass, snags and other causes of possible failures. Pay attention to the branches of bent trees, they can interfere with casting. When wiring, take into account the change in depth and the presence of algae in the strip along the shore. For fishing through the grass, you can take baits with wire hook protection.
Another way to avoid underwater snags is to fish with surface lures. These are wobbler baits with high buoyancy, such as poppers, propbaits, stickbaits, etc. In addition to the ability to fish in overgrown reservoirs, these baits allow you to visually observe the bite, which has a good effect on their catchability. When casting such a bait, the retrieval begins immediately at the moment of fall, preventing it from sinking.
Surface baits
Another factor influencing the fishing result is hooking. The pike has a rather bony and hard mouth, so the hook must be quite strong. For spinning rods with a fast action it is short and sharp, with a slow action it is longer and more powerful. If you are hunting for a large specimen, after the first hook you can make a couple of additional ones.