An inconspicuous inhabitant of ponds, lakes and other freshwater bodies, a fish nicknamed rotan has a very ambiguous and controversial biography. Depending on the region of the Eurasian continent, it is called differently - firebrand, grass fireweed, Amur goby, firebrand rotan and even pensioner. It is also called a trash fish, a parasite and a restless alien, although not all fishing enthusiasts agree with these definitions. In the photo, the firebrand looks scary.
Description
The unusualness of the firebrand lies not only in how many names it has and its similarities with representatives of the goby family. This fish is worth reading its description in more detail.
Amursky
There is no information in ichthyological reference books about the classification of sleeper into any subspecies. There is an assumption where the fish got the name Amur goby. It was there, in the basin of the Far Eastern Amur River, that the original habitat of the firebrand was located. In appearance - a “cheeky” head, making up almost a third of the length, a huge toothy mouth and sharp-looking lower fins - the fish really looks like the ubiquitous goby. This could serve as a reason for aquarists in Russia and abroad to call the firebrand the Amur goby.
Main characteristics of the appearance of rotan:
- Short, dense body, covered with small scales.
- The dull color of the scales is a variation of dirty brown and gray-green with inclusions of different shapes and sizes.
- In males, as the mating season approaches, the scales darken and become almost black.
- The abdomen is usually monochromatic and gray.
- Body length with head – from 14 to 25 cm.
- Average weight – 300-400 g.
There are rumors among amateur fishermen that under favorable conditions, rotan grows to more impressive sizes. But fish with length and weight parameters that are enormous for rotans are extremely rare.
Sewer
Some fishermen call the firebrand a sewer dweller. This is due to the fact that it is absolutely undemanding to environmental living conditions. Rotan thrives both in the cleanest lakes (it has recently appeared in Baikal) and in dirty reservoirs where sewage drains are discharged. Hence its unsympathetic nickname, which causes many fishermen to doubt whether this fish is edible. Scientists consider its appearance in Baikal to be a biological contamination, although no one can say for sure how long the firebrand lives in this lake and whether it caused damage to the Baikal ecosystem.
This fish is also one of the few that can survive winter in a reservoir frozen to the bottom. Rotan has the ability to release glucose and glycerol at low temperatures, which increases the concentration of salts in its own tissues and in the surrounding water. Thus, rotan manages to disrupt the process of crystallization of water around itself and survive at the lowest possible temperatures and even for some time without water.
We recommend that you learn more about the fish that has an external resemblance to rotan - the goby.
The amazing viability of rotan is confirmed by experiments carried out on it by home-grown experimenters. For example, they keep it in the refrigerator for 12 hours in a container without water, and then release it into the pool - the fish comes to life. Or they freeze the rotan in the freezer (from 6 hours), then defrost it, and within a few hours its vital functions are restored.
Features of behavior and nutrition
Rotan is characterized by its small size and leads a daytime gregarious lifestyle, adhering to the bottom and natural shelters (rocks, vegetation, snags). The catches usually include fish weighing 200-300 g. Record specimens weighing 400-500 g, aged 5-6 years, are much less likely to be bitten. At the same time, the maximum weight of rotan reaches 750-800 g with a body length of 25-30 cm. Only individuals who have lived their entire lives (7-8 years) in comfortable and well-fed conditions can boast of such dimensions.
Rotan is an active, aggressive and constantly hungry predator that is capable of significantly reducing and sometimes completely exterminating individual populations of other fish and amphibians, for example, frogs and newts.
The favorite habitat of rotan is small bodies of water with a stagnant or slowly flowing environment and an abundance of higher aquatic vegetation. Thanks to special biological mechanisms and the mucous coating of the body, the fish can easily survive both critical drying out and complete freezing of a pond, stream, canal, or lake.
The diet of the rotan firebrand includes leeches, worms, larvae, small invertebrates, tadpoles, eggs and juveniles of other fish (bream, carp, crucian carp, gudgeon, carp, roach, loach). In addition, he is a pronounced scavenger and cannibal. The latter quality is especially pronounced in small ponds with a quantitative predominance of rotan. In turn, larger predatory fish prey on the grass. Depending on the size and characteristics of the reservoir, it can be perch, pike perch, pike, burbot or catfish.
Rotan remains active and has an excellent appetite throughout the year, which makes it possible to catch it both in open water and on ice. The fish does not stop feeding even in rain, windy weather, extreme heat and frost. The insatiable appetite disappears only during the spawning period.
Thanks to its huge mouth and wide throat, the predator is able to slowly and confidently swallow prey of the same diameter as its own body. In this case, the stomach greatly increases in size, and the belly begins to sag. Then the well-fed fish sinks to the bottom, finds reliable shelter and digests food for several days, remaining practically motionless.
To learn more:
Description and characteristics of Baikal grayling
Predator or not
Rotan is a predator, and owners of private fish farms accuse it of exterminating the population of valuable commercial fish, since it reproduces very quickly. However, experts and lovers of this fish explain the “gluttony” of rotan by the fact that it simply has nothing to eat in an artificial pond. Only juveniles of valuable fish are usually released into private reservoirs. Therefore, if a firebrand accidentally gets there, it has no choice but to destroy the eggs and fry of valuable species.
Under natural conditions, rotan encounters enemies much faster than hunting objects. Pike, minnows, tenches, perches and other predators quickly destroy rotan while it is small, preventing the population from developing.
Fishing for rotan
Catching rotan
Observations show that day and night rotan hides in the grass, under a hummock, a snag, a stump - wherever it is possible to hide. The most productive catch for rotan is with summer jig tackle. Rotan is a predator and is better caught with moving baits. It is better to catch rotan with a heavy jig, which is tied to a 0.14-0.16 mm fishing line. on a 3-4 meter rod (a long one is hard to hold). There is a guard at the end of the rod at an angle of 90 degrees to the rod.
Rotan is undemanding when it comes to tackle, so you can use a fairly thick fishing line. It is better to take hooks of a fairly large size with a long shank. The rotan has a huge mouth, and it swallows a large hook without any problems. And a small rotan hook can become so swallowed that surgery is indispensable.
The technique for catching rotan is as follows: having lowered the jig to the bottom, you need to lift it slowly up, shaking or rocking the rod. A sharp and reliable bite is noted by the guard and is even transmitted along the rod. At this time, cutting should follow.
If rotan is caught using a float rod, then you need to play with the bait, shaking the rod. The attachment is a dung or earthworm.
In winter, rotan is caught well on the first ice. They catch rotan using a jig with a bloodworm or a worm, or even just with a red thread. Rotan is also well caught using the vertical lure method. In the middle of winter, rotan does not bite.
Benefits and harms
Among fishing enthusiasts, there is ongoing debate around the potential harm and benefits of rotan fish. Some consider it a truly “weedy” inhabitant of fresh water bodies, displacing more valuable species or reducing their numbers. For pond farming, rotan clearly appears to be an enemy that can cause harm to fisheries and huge losses to pond owners.
Others justify rotan, saying that with proper management of fisheries, it is possible not only to preserve populations of valuable fish in its presence, but also to improve their condition. According to the observations of experienced fishermen, in natural ponds where rotan has settled, the populations of other fish are noticeably enlarged. That is, the individuals that survive as a result of natural selection grow to larger sizes than in the absence of such a “nurse” as rotan fish. Rotans get along especially well with crucian carp, since they are not competitors in nutrition: crucian carp feeds on plant foods, and rotan eats small freshwater animals.
This version is followed by connoisseurs of the taste of rotan. Its tender, white-pink meat has a dense structure; when cooked, it separates well from large bones, which are not so abundant in the body of this unusual fish. It tastes like crucian carp. The pulp contains all the macro/microelements and vitamins that river fish is rich in: phosphorus, calcium, potassium, molybdenum, vitamins PP, A, D, E.
Can it be eaten?
The question of whether rotan fish is eaten can be answered in the affirmative. The meat of this fish has a pleasant, delicate taste. It is believed that it contains vitamin PP, which is necessary for the synthesis of enzymes, lipid metabolism and stimulation of regenerative processes in the body.
The disadvantages of rotan meat include the abundance of bones and the smell of mud. Therefore, the fish is prepared, like crucian carp, by frying in a frying pan in flour and spices. This way you can enjoy the taste while eliminating the unpleasant smell. Rotan meat can also be added to the fish soup, combining it with other types of fish.
Having found its way into many reservoirs by accident, rotan has adapted well to local conditions. Due to its unpretentiousness, it can be found in places where other species cannot survive.
The question of the benefits and harms of rotan fish has not yet found a consensus among researchers. At the same time, it is recommended to eat it only if the fish was caught in a clean reservoir.
Like other predators, this species accumulates elements found in water in its body. Therefore, fish caught from a dirty river or swamp is not beneficial for a healthy diet.
Where is it found and what does it eat?
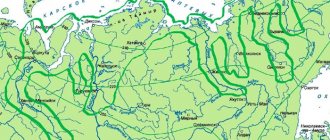
Rotan fish is found in rivers and lakes in northeast China, northern Korea, and northwest Sakhalin. At the beginning of the 20th century, the “Amur goby” appeared in reservoirs around St. Petersburg, after which it very quickly spread throughout the northern part of Eurasia, including most of Russia.
Photo. Habitat of rotan. The places where rotan originated are indicated in green, and the places of settlement in pink.
Rivers in whose basins rotan are caught:
- Ob is the largest river in Western Siberia;
- Styr is a tributary of the Pripyat, flowing through the territories of Ukraine and Belarus;
- Ural - flows in Eastern Europe through the territories of the Russian Federation and Kazakhstan;
- The Irtysh is the left tributary of the Ob, the waters of which pass through China, Kazakhstan and the Russian Federation;
- The Danube is the longest river in the European Union;
- Dniester - flows through the territories of Moldova and Ukraine;
- Don is a large river in the European part of the Russian Federation;
- Dnieper - ranks 4th in length among European rivers;
- The Volga is the largest river in the European part of Russia.
Due to its dark, dull color, rotan is almost invisible in the water, which serves as good camouflage for it when hunting. Firebrands feed on:
- small fish, often of their own species - cannibalism flourishes among them;
- fry, tadpoles, invertebrates;
- crustacean larvae;
- newts, leeches;
- caviar of other fish.
Ichthyologists have established that rotan practically does not feed on aquatic plants; no traces of food of plant origin are found in the caught fish. Its diet consists of small specimens of river fauna that live in the waters and at the bottom of fresh water bodies.
Lifestyle
In addition to the fact that rotan is an active and quite dangerous predatory fish, it is characterized by cannibalism. The diet of firebrands consists not only of fry and eggs of other representatives of the ichthyofauna, but also of their own relatives. Adult fish eat almost everything that moves - even leeches and tadpoles. The fry menu includes plankton and zoobenthos.
Look - Eel fish - habitat, habits, lifestyle, hunting and 125 photos of river and sea species of eel
Despite the small size of rotan fish, its appetite is terrifying. She does not know a sense of proportion, so she can cause the disappearance of other species of fish in a single pond. It is not for nothing that the firebrand is considered a trash fish, and the reservoirs in which it swims are considered biologically polluted.
Rotan is also food for larger predatory fish, such as pike and perch. Fishing for it is quite an interesting event, especially if it happens in winter.
Lifespan
If rotan were not edible, its lifespan could be 7 years. But usually rotan lives no more than 4-5 years. At 2 years of age, individuals reach sexual maturity and go to spawn. The female rotan lays about a thousand eggs, which attach to plants, pebbles or other objects at the bottom of the reservoir. Rotans prefer to spawn in stagnant waters - quiet river backwaters, lakes, where higher aquatic vegetation is well developed.
Rotan spawns in May-June. The eggs are guarded by the male until the fry hatch. Sometimes at the cost of one’s own life, because its meat is liked not only by people, but also by numerous river predators who control the number of rotan in nature. True, a new father can eat his offspring himself if there is no other food nearby.
Where does it live?
Initially, as described above, rotan lived in the Far East and China. Then it was launched into the reservoirs of central Russia. It prefers reservoirs with stagnant water and rich vegetation, so it is almost impossible to find a river species of these fish.
Now it is distributed almost throughout Russia. Such rapid dispersal is due to the fact that the “firebrand” is very unpretentious, and waterfowl carry the eggs over long distances and they survive well.
The largest in the world
Fishermen love to tell stories about huge fish of different species that they “caught in the old days.” Rotan also began to appear more and more often in stories, despite the fact that, according to ichthyologists, the maximum weight of an adult is 400 g. And yet on fishermen’s forums there are stories about 800-1000 gram rotans with a huge mouth and sharp teeth ready to bite the hand of a gaping fisherman. True, all these stories are not accompanied by photographs or other documentary evidence. The largest rotan that was captured in the photo was 550 g, according to its catcher.
Keeping in an aquarium
Lovers of original pets have long learned to breed rotan in an aquarium. This does not require any special skills, the main thing is to feed it correctly so that it does not eat other inhabitants of the home “reservoir”. According to aquarists, this “monster” is capable of swallowing up to a dozen female guppies in a few days. For this reason, they try to keep rotans in a separate aquarium.
Firebrands eat everything that is protein food of animal origin:
- worms, flies, moths;
- larvae and bloodworms;
- pieces of frozen fish;
- minced meat or fish.
Even not very careful aquarists can take care of firebrands, since these fish:
- do not need frequent cleaning of the aquarium, the water can not be changed for more than 2 weeks;
- do not suffer from a lack of oxygen, aeration of the aquarium is practically not needed;
- tolerant to changes in temperature of water and ambient air.
Both at 0 and at 400, rotan feels great, grows well and reproduces in captivity. Aquarium rotans differ from those found in nature by the golden color of their scales. Only in males it darkens slightly on the eve of the mating season.
Watching these active fish is quite interesting. Although many call them lazy, they constantly fight for territory and start fights among themselves.
The only thing that can happen to a careless rotan owner in an aquarium is attacks of cannibalism if they are not fed on time. In the absence of food, large individuals will certainly eat smaller ones.
Rotan fish - an environmental disaster?
Indeed, many scientists and fishermen are sounding the alarm. When rotan gets into a body of water, it begins to eat everything it gets:
- Caviar
- Fry of other fish and your own fish
- Insect larvae
Some reservoirs were assigned the status: “Biological contamination by rotan”
Because of this, the population of peaceful fish is significantly reduced. But if there is another predatory fish in the reservoir, such as:
- Pike
- Perch
Rotan no longer feels so good and its numbers are much smaller. That is, the number of these fish can be controlled, which means there is no catastrophe.
Moreover, many fishermen are glad to see this predator in water bodies. The fact is that by destroying the fry, rotan naturally reduces the number of fish. This means that the food supply for others increases and, as a rule, there are fewer fish in these reservoirs, but they are larger.
Read, interesting: Chub fish photo and description. Fishing tips
Goby and rotan - what is the difference
Despite the similarity, rotan does not belong to the goby family. This fish belongs to the genus of firebrands of the firebrand family, being its only representative. An important difference between the firebrand is that it is an inhabitant of freshwater bodies of water, in contrast to different types of gobies that prefer salty and slightly desalinated waters. These fish also have external differences:
- a spine characteristic of perciformes, located on the gill covers; in fish the firebrand is soft, while in gobies it is quite hard and prickly;
- the dorsal fins of the firebrand are also soft, while the gobies have hard rays protruding on one of the fins;
- the pelvic fins of the firebrand are paired, disproportionately small and located near the head; in gobies they are fused into one fin, more reminiscent of a sucker;
- some types of gobies (for example, whip goby, or martovyk) grow up to 50 cm in length and weigh up to 1.5 kg, and the maximum recorded weight of a firebrand is 550 g;
- the classification of gobies includes 186 genera (31 species are found in the Black Sea alone), and rotan is the only representative of the genus of firebrands.
Firebrands and gobies are actually very similar, although they belong to different families.
There is another version why rotans are sometimes called gobies or confused with them. Or, on the contrary, the bull is called ratan. This is because of the Latin name of one of the Black Sea gobies, Ponticola ratan. The Black Sea “ratan” is one of the smallest representatives of the goby family, it grows only up to 10, rarely up to 20 cm in length, and its weight does not exceed 100 g. Fishermen call it the Black Sea goby.
Unusual in all respects, but very interesting and tasty rotan fish, no matter how much they talk about it as weed, insatiable and dangerous, is becoming a popular object of fishing. Fishermen are attracted by the active bite of rotan, its taste and the absence of small bones.
Rotan recipes
Fried firebrand. Select large specimens. Gutted carcasses can be cut into pieces, but it is better to fry them whole. The fish is well dredged in flour and fried on both sides until golden brown. Use vegetable or butter. To get a crispy crust, cover the pan with a lid 5 minutes before the end of cooking.
Firebrand omelette. The roasted carcasses are cut into pieces and placed in a frying pan. Beat eggs with milk. The resulting mixture is poured into a frying pan. You can add finely chopped green onions and other greens to it at your own discretion. Prepare in the same way as a traditional omelet with the lid closed.
Fish under marinade. The carcasses are boiled in salted water until cooked. Separate the bones by placing the meat pieces in a deep dish. Prepare the marinade. Finely chop the onion, grate 2 carrots. The vegetables are transferred to a frying pan and fried, tomato paste is added to them, about 3-4 spoons, and 1 spoon of vinegar and spices. The fillet is poured with marinade and allowed to brew for several hours. Suitable as a cold snack.
Fish salad with egg and cucumber. The carcasses are boiled or stewed until cooked. Disassemble into pieces, separating the bones, crush with a fork. Add chopped boiled egg and pickled cucumber cut into small cubes to the minced meat. Season with mayonnaise or special dressing. For dressing, take mustard, vegetable oil, a little salt, add pepper as desired.
Firebrand soup. Chop the potatoes and carrots into cubes in a saucepan of cold water. It is better to add dried dill and parsley to boiling water instead of fresh herbs. Add bay leaf and black peppercorns. Place the prepared fish pieces into the broth and cook for 20 minutes. You can add butter and sour cream to the finished dish.
Ear. Whole processed carcasses, turnips, carrots, parsley and celery roots, a medium onion, bay leaf, and black pepper are placed in a cauldron with cold water. After boiling, add diced potatoes. Cook for about 60 minutes. The finished dish is sprinkled with finely chopped parsley and dill.
Fish ears. Belarusian dumplings are called ears. Minced fish is prepared from pre-boiled fish. Fry onions. Add 1 cup of boiled mushrooms and onions to the minced meat. Pepper, add salt and mix. The resulting filling is used to fill dumplings.
Baking in the oven. Prepared headless carcasses are rubbed with a small amount of salt. Let them sit until they are salted. Rinse off the salt and dab with a paper towel. Preheat the oven to 200⁰. Pour vegetable oil into a glass baking dish, spreading it over the bottom in a thin layer. Place the fish and cover it with vegetable oil so that the fish does not dry out or burn. Cover with foil and bake for 30-40 minutes. Then remove the foil and bake until golden brown for about 10 minutes.
The firebrand is considered a universal fish. You can prepare almost any dish from it: cutlets, casseroles, canned fish and pies. There are many recipes for experienced cooks and those who do not know how to cook rotan. The fish is combined with a side dish and can be used as an independent holiday dish.