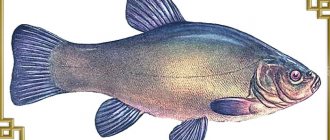
Podust is a freshwater fish that lives in Central Europe and North-West Asia. It is found in fast rivers, in the same places where grayling is found. In Russia it can be found in many places, except for the basins of the White and Barents Seas, and is rarely found in the North-Western region. The fish is schooling, lives and moves in large schools, lives in shallow water (up to 2 meters) in places with fast currents and a rocky, sandy or slightly silted bottom.
Photo: André Karwath, Wikipedia
Podusts grow to sizes of 25–40 cm in length and a body weight of 1–2 kg.
It has an elongated body, oval in cross section. The caudal fin resembles the shape of the moon and is deeply depressed. The dorsal and pelvic fins are located on the same line. The paired and anal fins are red, the caudal fin is reddish-brown, and the lower part is more reddish.
The small head, with a characteristic muzzle, has hard cartilaginous lips.
The back of the body is gray-green, the sides are lighter with a silvery tint, the crown of the head is dark, the belly is white or yellowish.
The common podust has the scientific name Chondrostoma nasus and belongs to the family of carp fish.
Pair of Common Podust, photo: lalo-asv.hpage.com
Reproduction
Podust reaches sexual maturity at 4–5 years of age. Spawns from April to May at water temperatures of 12-18 ° C. During this period, males and females become covered with a spawning rash, in the form of light spots on the head and upper body. During the spawning period, they gather in large flocks in small areas of the river, and cover almost the entire bottom with eggs. During spawning they can jump out of the water. The female, depending on the size, lays up to 30,000 eggs (sometimes up to 100,000), the eggs are greenish, protective-ocher in color, with a diameter of 1 mm. It is laid in shallow places above the gravel bottom, the eggs are sticky and stick to the stones, after which they ripen. The fry hatch in 10 to 30 days and initially hide under rocks.
What to catch podust with
70% of the diet of these fish consists of algae and other vegetation. But they do not refuse animal food, so the following baits work well:
- Boiled pearl barley or oats;
- Maggot;
- Insect larvae;
- Worms;
- Dough;
- Cheese.
You can try to make a bunch of small algae, collecting them from the surface of stones and fishing on them, but the result is usually bad, although it can rarely work.
It is very difficult to catch large pods, they can eat the bait so that the float does not even move, so it is important to have very sensitive tackle and a sharp hook.
Large specimens are best caught using caddis.
The bait for catching podust should be no more than 10 cm above the bottom, it should not lie on the bottom.
The usual bait for fish of the carp family is suitable as bait. It should be quite dense, well glued and heavy, since fishing is carried out in the current. The bait for weighting must be mixed with clay or soil from molehills. You need to add a handful of maggots or chopped worms to the bait. Blood (albumin) is suitable as a flavoring agent.
At the beginning of fishing, several balls are usually thrown, then the place is fed in small portions or after the bite stops. The bait should be thrown into places where there are shelters, stones or holes so that it is not immediately washed away by the current.
Do not use sweet flavors, use bait with neutral odors, the best flavor is blood.
Activators, flavors and other additives for the mouth
When fishing in the current, it is very useful to add liquid and dry flavors to the bait. Oils, liquids, boosters, after falling to the bottom, are carried by the current, and fragrant paths are created that are felt by the under-dusts. Along these paths they find bait.
It is very useful to add molasses to the mixture. It not only moisturizes the mixture, but makes it more nutritious. At the same time, molasses is a good activator that speeds up the digestive processes of the pod. It turns out that he does not get enough and is forced to constantly spin around at the point, waiting for more from above.
It also happens: How to catch lamprey
Molasses can be added using either cold or warm water. It is equally successfully absorbed regardless of the water temperature.
Another supplement that awakens the appetite of the mouth is hemp oil. It is sold in bottles and sprays. The oil has a characteristic odor and is added to the bait itself. The nozzles are also flavored with this liquid.
Flaxseed and sunflower oil are also used in groundbait. In general, the oil is very effective and, what is important, it flavors the bait for a long time. They are used mainly in summer, as they mix better with warm water. The oil also protects the bait from souring and prevents it from sticking together into a lump. When the bait hits the bottom, the oil begins to mix with water, and a large aromatic spot is formed, which attracts fish to the point.
Liquid liquids with vanilla, honey, barberry, melon, and other odors are also added to the bait. Anise works well. It is added both in cold and warm times. Anise drops have a persistent smell, and the bait remains aromatic throughout the entire fishing trip.
In cold weather, alcohol-based liquid additives are used. These are bloodworm, worm and maggot flavorings.
Dried bloodworms, the so-called unikorm, are added over cold water. It is sold in pet stores. This supplement is easier to store than the animal component. In terms of effectiveness, unikorm is practically not inferior to live bloodworms. But this is the case specifically with podust.
Among the bulk flavorings and additives, we note food seasonings. They are most often used when fishing in cold water. First of all, there is ground coriander, which works well in cold weather. Cloves in small quantities can attract baitfish to the fishing point. Cinnamon is a very aromatic and attractive additive. It brightens the mixture and often freshens it when added while fishing.
To make the bait yellow to match the color of the bottom, add turmeric to it. It also attracts bream, roach and blue bream. It is added no more than 5% of the total volume of bait.
How to detect podust on a pond
Podusta, unlike other fish, can be tracked in a body of water, as it leaves traces of its presence. While feeding, they leave traces of eaten algae on stones and other objects. They are usually crescent-shaped, ranging from 10 to 30 mm wide. When feeding, they sometimes turn to the side to reach food in inconvenient places, at which point their silvery body reflects light and they are easy to see in the pond.
Their habitats are rivers with a strong current and a rocky bottom, but not with a rapid flow, as this prevents the growth of algae. Algae should grow on the rocks that lie at the bottom. Where the stones are clean, there will most likely be no dust.
Podust does not like very cold water, so there is no point in catching it at depths of more than two meters.
We recommend: Features of chub fishing, what it looks like and where to look, description of the fish
During the day they usually stay closer to the middle of the river and in deep places. In the evening they move to shallow water, but at this time they are very careful and are easily frightened. Closer to dawn they go deeper again.
The best time for fishing is the second half of the day.
Description of the species
The standard size of representatives of the genus Chondrostoma is 25-30 cm with a weight of 400-500 g. Trophy specimens reach 1.2-1.5 kg (40-45 cm). The largest podust weighs 1.8-2.0 kg with a height of over 50 cm. But such individuals are extremely rare, since they reach their maximum dimensions at the end of life, which is 10-12 years.
The fish got its name from the lower terminal mouth (old mouth), located under the elongated cartilaginous snout, like a sturgeon. Another common nickname is the black belly, due to the special dark film on the inner walls of the abdominal cavity.
The main distinctive characteristics of the appearance of the undermouth include:
- body flattened laterally in the shape of a pointed ellipse;
- yellowish-orange pectoral, pelvic and anal fins;
- medium, tightly fitting silvery scales with a rounded posterior edge (cycloid type);
- dark olive color of the back, on which a smoky-gray fin is located (3 unbranched and up to 10 branched rays);
- low head with a flat nose and large eyes;
- clearly visible lateral line of dark color;
- black rim on the tail.
The color pattern and tone depend on the genus taxon, specific habitat conditions in the river and the season: during the spawning period, all orange, yellow and red shades on the fins of males become an order of magnitude brighter.
Volzhsky Podust
Latin name: Chondrostoma variabile. Listed in the Red Book of the Saratov Region as a “vulnerable species.” It is distinguished by its more modest size (up to 1.4 kg) and shorter life expectancy (up to 8-9 years). The lower jaw has a sharp end. There are 52-62 scales in the lateral line. The dorsal fins are greenish in color. It lives in tributaries and rivers of the European part of Russia (Volga, Don, Ural), also found in the Sura, Moscow River, Oka and large reservoirs (Kuibyshev, Volgograd, Saratov).
To learn more:
Description of bluefish fish: habitats and fishing methods
Genoese (Western European) podust
The name in Latin is Chondrostoma genei. It lives in Italy, Slovenia, Austria, Belgium, France, Switzerland and in many rivers of the Adriatic and North Seas. The fish is distinguished by its yellow-green back and colorless fins. The lateral line runs through the entire strongly elongated body, but is poorly visible. Grows up to 35-40 cm (1.2-1.4 kg).
Dneprovsky Podust
The Latin name of the fish is Chondrostoma nasus nasus natio borysthenicum Berg. It has a moderately high body and a light, scaleless keel between the anal and ventral fins, colored red. Habitats are rivers, tributaries and reservoirs that form the basin of the Black and Azov Seas. Podust is especially numerous in the Dnieper and Southern Bug. Grows up to 1.5 kg (up to 45 cm).
How to catch podust
Podust can be caught with the following gear:
- Float fishing rod, the rod should be 6-7 meters long, the main line 0.12 - 0.14 mm, monofilament leash 0.10 - 0.12 mm (the thinner the better) 20-60 cm long (For uneven bottom you can use longer ones), bottom, hook No. 14-10.
- Spinning rods, but it is very difficult to catch them. The spinning rod and its equipment should be from the ultralight series; small aggressive wobblers, no larger than 4 cm in size, work best as artificial bait. Podust attacks from behind, so the wobbler must be equipped with one rear hook. Natural colors should be used, the bait should imitate small trout, bleak and other small fish that live in this reservoir. In clear water it is best to use dark wobblers; in the late evening and in cloudy water, use light-colored wobblers.
- Feeder - the optimal length of the rod is 3.60-3.90 meters, the weight of the feeder is 40-60 grams. Main line, monofilament with a diameter of 0.16-0.20 mm, leader 0.12 - 0.14 mm, hook No. 16-18.
When fishing for bait, wear polarized glasses, they make it easier to notice the glare from the fish and the bite
Fishing for undermouth in the fall
In autumn, podust is caught in deeper areas than in summer.
In this case, it is better to use a match or Bolognese fishing rod, adapted for long casts. Donks and feeders work, but worse because of the weight and feeder, noisily falling into the water. In autumn, the dust concentrates in local zones with a depth of 2.5 to 4.5 meters. Areas behind the rifts, near holes and in the lower part of the edges, as well as behind the coastal dump are considered promising.
Podust are often caught in the same places as ide. Moreover, the emphasis is on fishing from the bottom. There he still finds the remains of plant food, and subsequently switches to plant food. For this feature, the under-dust is also called a “scraper”. It scrapes vegetation and other food from the bottom with its mouth.
At the beginning of autumn, podust is still caught using bottom rigs, and then a float rod is used. Fishing is carried out by wire. It has been established that the colder the water, the slower the wiring should be. Since the bait takes the bait decisively, you can use heavier floats that will slow down the movement of the equipment. It is effective to make small holds during postings. The nozzle either drags along the bottom or is 5 cm higher.
The most effective baits for fishing underwater in the fall are granny - a mayfly larva and amphipod, which can be found under stones, near dams and bridge supports. Place one or two pieces on the hook. It has been noticed that larger specimens are caught on amphipods and grandmas. Walnut worms are also a success among podusts. They live in hazelnuts that have fallen to the ground. The length of such a worm is 5-7 mm. Its body is yellow with a black head.
They are caught using maggots, bloodworms and pieces of worms. But smaller specimens bite on these baits.
In autumn, podust is caught using the thinnest gear. Hooks use Nos. 16-20 according to international numbering, fishing line with a cross-section of 0.14-0.18 mm. When fishing with a feeder, it is better to feed immediately and then use small feeders. When fishing at long distances, the priority is a fence with a cross section of 0.1 mm. At a distance, bites will be visible very clearly on braided line.
On the autumn fishing page there is information about fishing for all river fish in the fall.
Despite the unoptimistic forecast for catching podust in winter, it makes sense to fish from the hole. You just need to know the places. Promising areas will be quiet backwaters and coastal areas where the current slows down. Sometimes the podust gets out of the wintering pits and visits these places. They catch it with bloodworms, painted udders and steamed wheat.
The main thing is to hook at the right time and not miss the bite. Sometimes he can fiddle with the bait for a long time, and in other cases single bites follow. They feed the mouth with dump trucks of steamed wheat, rolled oats, crackers and add bloodworms
In the sections: ice fishing and winter fishing you will find a lot of useful information about fishing during the period of cold weather and frosts.
On our website - Fishing - there is a detailed description of how to catch podust with various gear. You can read how to catch certain types of fish depending on the time of year on the fisherman's calendar page.
Good fishing online stores will allow you to purchase any fishing goods at competitive prices!
Podust prefers sections of rivers with clay and rocky bottoms with clear water and moderate currents. The bottom may contain dense clay, gravel and stone. Podust can be located near dams, bridges, dams, behind rifts, on the border of slow and fast currents.
In early spring, podust is successfully caught in pits. At this time, the water level rises significantly. It becomes cloudy. Podust prefers to sit in the pits at this time. Then, in about a month, schools of fish will leave their usual places and go up the river to lay eggs.
In some reservoirs, podust prefers calmer areas with a depth of 2 to 4 meters. These can be stretches, places behind a dump, or a riverbed zone. In any case, you should look for podust where there is clay and stones at the bottom. There is no point in catching it on the muddy bottom. He ignores such places.
At the beginning of fishing, each feeder scans the bottom, determines its structure, relief and depths in different areas. How can a beginner distinguish a clayey, silty or shell area on the bottom? The easiest places to identify are shells and rocks. When pulling the weight, the tip trembles slightly. When the load goes over stones, the tip rattles a lot. It is not difficult to distinguish a shell from a stone. Just a little practice is enough.
How to distinguish a muddy bottom from a clayey one? The simplest method is to cast a weight onto a muddy or clayey area located directly on the shore or a few meters from it. After a lay cast, pull, look at the tip and remember how you feel. The main thing here is the sensory perception of how the weight goes along the bottom.
Podust loves places with differences in depth, so-called steps. There he finds plant and animal food for himself. It collects food equally well on the bottom and dumps. At the same time, it doesn’t really matter to him what kind of surface: inclined or flat. It is more convenient for feeders, of course, to fish on tables so that the bait is concentrated in one spot.
When fishing in weak currents, we will use a medium-class rod with a weight of up to 100 grams. When fishing in the middle current, a heavy fish with a dough weight of up to 120 - 140 grams is suitable. The action of the fishing rods is medium-fast, length – 3.6 meters. Rods with a length of 3.9 are suitable for fishing at distances of more than 60 meters.
It also happens: Catching medicinal leeches - Development || Methods for catching leeches
We will use the reel with a front or rear clutch with a spool capacity of 3000 to 5000. When tightening the spool, we adjust the clutch once. This fish itself is not very big. Rarely do you come across specimens of 500-700 grams. Therefore, we adjust the clutch as for a bream up to 1 kg. Still, the underdust provides significant resistance when playing.
We wind a wattle with a cross section of 0.12-0.16 mm onto a reel. When fishing at a distance of up to 35 meters, you can use fishing line with a cross-section of 0.22-0.25 mm. Breaking load 3 kg. quite enough for this kind of fishing.
For summer fishing, any feeder rig is suitable. In autumn and early spring it is better to use an asymmetrical loop. It is best suited for fishing in a stronger current. Asymmetrical is more sensitive. Weak bites will be visible more clearly than with the same paternoster. When fishing in calmer areas, you can use any installation, even method.
We use a medium volume feeder with a metal body if the depth at the fishing spot is more than 4 meters. You can also use bullets. They reach the bottom faster and do not bury themselves in it. We don’t need to lose bait and create a cloud of turbidity in the water column, since the mud sticks to the bottom.
When fishing in areas with a depth of up to 3-4 meters, you can use feeders with a plastic body. They float better and won't fall for as long.
First we set the leash with a length of 50 cm. Then we look at the activity of the fish. If the hook swallows deeply or eats the bait and no bites are visible, then shorten the leash. And if after reeling out we see an untouched bait, then we extend the leash.
The diameter of the leash may vary. If we fish on a rocky or clay bottom, but with shells, then we use a fly with a cross-section of 0.14 mm. If the bottom is clean, then we use thinner leashes. In autumn we use leashes with a cross section of 0.1 mm. When fishing on thin leashes, you can use a feeder 5 - 7 cm long. It will help deliver heavy fish and protect the leash from breaking.
We use hooks No. 12-16 when fishing in warm water and No. 14-20 when fishing in early spring and late autumn.
Mixtures that include grains, flour, crackers and store-bought bait are suitable for subdus. You can use the classic composition for the river, which has long been used by donors: ground boiled peas with breadcrumbs. This bait works well in warm and cold weather and is very easy to prepare. Peas can be cooked in a slow cooker without even monitoring the process. It is better to grind it in a meat grinder. It is better to mix peas with breadcrumbs while fishing.
A more complex recipe includes the same crackers, ground sunflower seeds or ground rolled oats, semolina, barley and boiled millet. This composition is adapted for fishing on the current. You can add chopped worms, bloodworms and maggots to it. An animal component is added when fishing in cold water.
It is advisable to pass fine-grained components through a fine sieve with a mesh size of 2 or 3 mm. And it doesn’t matter what kind of bulk it is: a store-bought mixture or an additive, crackers, ground flour or bran. We sift all these components, crush the large remains or set them aside.
The color of the bait plays a certain role. For catching undermouth, it is better to use mixtures that match the color of the clay, light brown. They will not stand out at the bottom and will not scare away potential clients from entering the fish tank.
Among store-bought baits you can use roach and bream with the scent of vanilla, coriander and bloodworms. There are baits with dried bloodworms. They are suitable for fishing in cold water. In stores, such compositions are usually black. These are not always suitable for our conditions. It is better to mix black bait with the lightest one and get a neutral, gray color, which will look more natural on a clayey and rocky bottom.
A few words about attractants for feeder groundbait. It is useful to add liquid flavors and molasses to bait compositions. In summer, vanilla, caramel, garlic, barberry, melon, raspberry and chocolate liquids work well. In cool water, it is better to use hemp oil, add ground coriander, cloves, black pepper, turmeric, and cinnamon to the bait. Cinnamon, by the way, colors the bait well, making it yellowish.