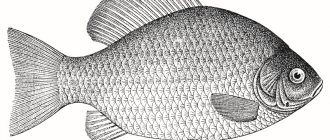
Appearance
Most representatives of trout are fish weighing 200–500 grams and a body length of up to 30 centimeters. Some specimens in the wild gain up to 2 kilograms.
Sea trout are larger than freshwater trout.
The classic color of the fish is dark olive with a greenish tint. On the sides, light transverse stripes with spots of black and crimson are clearly visible. The color of an individual depends on the habitat, time of year, food, and transparency of the reservoir. Fish living in calcareous water have a light silvery back, while in the depths where the bottom is covered with peat or silt it is dark brownish.
When there is an abundance of food in the river and lakes, spots and stripes on the sides of the trout may be absent, and after a change of reservoir they may appear or disappear. The meat of sea fish is red, freshwater fish is pink. The protein content in it reaches 18%.
The body of the trout is laterally compressed, covered with matte scales, the head is truncated, short, the eyes are large, the teeth are located on the vomer.
Trout is a commercial fish that is raised in cage farms and special farms. Norway is considered the leader in salmon farming.
Due to the genetic proximity to the species, the name “trout” is used by predatory fish belonging to three genera:
- Pacific salmon:
- "Biwa";
- "Apache";
- Rainbow;
- Gold;
- Caucasian;
- "Gila."
- Atlantic (noble) salmon:
- Amudarya;
- Adriatic;
- Flathead;
- Sevan;
- Marble;
- Ohridskiy;
- Brown trout.
- Char subfamily Salmonidae:
- Silver;
- "Malma";
- Ozerny;
- Bigheaded;
- "Palia".
Red fish spawn exclusively in clean running waters. Female trout are larger than males. They have fewer teeth and a smaller head size.
External differences
A professional can easily distinguish a sea dweller from other types. If you know the following signs, you can understand what sea trout looks like.
The color and specific arrangement of scales in this family varies depending on its habitat.
The back is olive-colored, and its yellow sides are strewn with rounded edged resinous or whitish spots. Hungry individuals do not have spots.
The pelvic fins are yellowish in color with splashes, and there are more dots on the dorsal fins.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iz6bF9WmrlA
“Color” varies from “albinos” and lighter tones to intensely dark ones.
As mentioned above, marine ones are much larger than their other “comrades” - up to 25 kg. and up to 1 meter long. It is the salinity of the sea that accelerates metabolism, helping to become larger. The average weight of sea trout is about 500 grams, and the length is about 20 - 30 cm.
All of the above distinctive characteristics vary depending on the season, region, diet, etc.
Trout (trout) of the Atlantic group live in the reservoirs of Karelia and neighboring territories. Trouts of this group live in different reservoirs, rivers, lakes and seas. Thus, trout of the Atlantic group come in three forms, sea trout, lake trout and brook or river trout. At the same time, these three forms can transform into each other, sea trout and lake trout can replenish the populations of brook trout, and brook trout populations of sea and lake trout.
Trout fish is the name of many fish from the salmon family. Trout are also classified according to their genus, Atlantic, Pacific and char. And within each genus of trout there are many different subspecies of the salmon family, for example, rainbow trout, golden trout, marbled trout and others. For example, according to the Karelian Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences in 2005, in the waters of Finland alone there were 1329 trout populations, of which 50% of trout populations are natural, 34% natural with the addition of juvenile trout from other water bodies, and 16% artificially bred.
Read How to catch pike perch using a spinning rod from the shore and from a boat
Chemical composition
The meat of representatives of the salmon family is tender, oily, bright red or milky-cream in color with a fragrant intermuscular layer of fat. Trout lends itself to all types of heat treatment: frying, smoking, boiling, pickling, stewing, steaming, spit. It can be dried and served as a snack for alcoholic drinks. Delicacy meat is baked whole or stuffed with nuts and fruits. It is used to make aromatic, oily first courses (fish soup, soups). Sashimi, tartare, and Japanese sushi are prepared from raw fish.
100 grams of trout fillet contains:
- water – 71.87 grams;
- proteins – 19.20 grams;
- fats – 2.10 grams;
- ash – 1.31 grams;
- carbohydrates – 0 grams.
The ratio B: F: Y is 80%: 20%: 0%.
Table No. 1 “Chemical composition of trout fillet”
| Nutrient name | Nutrient content per 100 grams, milligrams |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A (retinol) | 0,019 |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 0,123 |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0,105 |
| Vitamin B3/PP (niacin) | 5,384 |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) | 0,928 |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0,406 |
| Vitamin B9 (folic acid) | 0,012 |
| Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) | 0,00445 |
| Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) | 2,4 |
| Macronutrients | |
| Potassium | 481 |
| Phosphorus | 271 |
| Calcium | 67 |
| Sodium | 39 |
| Magnesium | 31 |
| Microelements | |
| Zinc | 1,08 |
| Iron | 0,7 |
| Manganese | 0,158 |
| Copper | 0,109 |
| Selenium | 0,0126 |
The nutritional value of trout depends on the cooking method. 100 grams of boiled king fish contains 89 kilocalories, smoked - 132, canned - 162, lightly salted - 186, fried - 223.
Trout in cooking
Trout, like all red fish, is a delicacy. The average calorie content of fillet is 120 kcal per 100 grams. Some cooking methods increase the energy value of meat up to 220 kcal.
The most useful components included in the chemical composition of trout are Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, vitamins A, E, B12, folic acid, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium. When eaten regularly, fish helps normalize metabolic processes and accelerates the production of red blood cells. The benefit of trout is to improve the condition of blood vessels and activate the brain.
Features of trout culinary processing include the following:
- when cutting fish, the head is separated and not used for cooking due to the harmful substances it contains;
- Baked trout is considered the most delicious; when baking, the carcass should be wrapped in foil to preserve its juiciness;
- Citrus fruits, ginger, olives, white wine, cream or sour cream will help complement and emphasize the taste of red fish.
When buying trout, you can determine freshness by the absence of odor, transparent eyes, elastic flesh, pink or bright red color of the gills. If the carcass will not be used immediately, it must be gutted and washed inside and out. The optimal temperature for storing fish is 0-+2 degrees.
How to distinguish a female from a male trout
Trout caviar is no less healthy than meat. It is salted and used to make sandwiches, sushi and rolls. You can identify trout with caviar by the following characteristics:
| Females | Males |
| Small head and large body | The body is smaller, the head is much larger in relation to the overall size, the color is brighter |
| The jaws are the same | The lower jaw is extended and curved upward, the number of teeth in the mouth is greater than that of the female |
| Smooth body arcs | There is a hump on the back |
The female with the eggs has a dense abdomen, and the opening is widened and colored pink. Sexual maturity occurs in trout at 3-4 years, so caviar can only be found in fish of the appropriate size for this age.
Pros of trout
Red fish meat is a valuable source of omega-3 compounds, vitamins, minerals and amino acids.
Doctors recommend including trout fillet in the diet of people suffering from:
- depression;
- osteoporosis;
- oncology;
- psoriasis;
- allergies;
- diabetes mellitus;
- heart diseases.
Boiled fish has low calorie content, so it is included in the menu for weight loss.
Why eat trout?
The substances that make up red fish have a complex effect on the human body:
- Remove excess cholesterol.
- Regulate blood sugar levels, gastric juice secretion, and water metabolism.
- Improve blood circulation and keep the heart healthy.
- Participate in the breakdown of fats, amino acid metabolism, hormone synthesis, and energy metabolism.
- Reduce the risk of developing myocardial infarction (primary or recurrent).
- Activate mental activity.
- Strengthens the immune system, nervous and cardiovascular systems.
- Slow down the aging of the body.
- Prevents the formation of malignant tumors (fights free radicals).
- Improves the absorption of iron and the condition of the skin and hair.
- Increases the strength of tooth enamel.
- They break down and remove carcinogens.
- They fight stress, relieve fatigue, and have a tonic effect.
- Support reproductive function.
- Reduce blood pressure.
Thus, trout meat has a healing effect on the human body. Nutritionists recommend eating fish 3–4 times a week, 200–300 grams per day.
What do trout eat?
In terms of nutrition, trout is completely unpretentious, so it grows very quickly. She knows how to find the larvae of any aquatic insects and catch moths fluttering over the river, boldly jumping out of the water. In the spring-summer season (especially in May-June), flying “feed” allows the trout to gain fat again after the spawning period. At this time, its food consists of mayflies.
As the trout grows and ages, it begins to feed on fish, becoming a real predator. The trout diet includes everything - fry, frogs and even smaller individuals of their own relatives. In general, its menu is very diverse and consists mainly of animal food - small fish, tadpoles, insect larvae, beetles, mollusks, crustaceans. The trout also grabs pretty well all the insects that fall on the surface of the water or fly too low. She is also a hunter for fish offal and any meat waste.
Read Arapaima fish
Minuses
Trout meat does not cause serious harm to human health, since it is recognized as hypoallergenic. However, fish may contain mercury, which is dangerous for pregnant and lactating women, as it poisons the baby's body and can cause miscarriage.
In addition to their natural habitat, trout are raised on fish farms, where unscrupulous entrepreneurs use chemical additives to accelerate the growth of individuals and give the meat a presentable pink hue. Allergy sufferers should be wary of such fish, first of all, since artificial dyes can cause aggravation.
Contraindications for use: diseases of the liver, kidneys, digestive organs in acute and chronic form, individual intolerance.
Due to its low calorie content, fish is not recommended for people doing heavy physical work and athletes. Otherwise, loss of strength, loss of vigor, and lack of energy may occur. To avoid exhaustion of the body, combine trout intake with vegetables, grains, and beans.
Trout habitats
The favorite habitat of the river predator is areas near seething rifts.
All types of trout love clean, cold water, however, it is found, albeit infrequently, in fairly warm layers of water. This happens on large, deep-water lakes, where the surface layer of water is constantly saturated with air due to wind and waves. It will not be possible to find this fish in shallow, warming lakes and swampy lowland rivers.
The favorite habitat of the river predator is areas near seething rifts. There the fish finds comfortable conditions for itself and picks up food brought by the current. On flat sections of the river it often chooses cluttered areas - large stones, fallen trees, uneven terrain.
On warm, clear days, trout become inactive. The onset of light bad weather awakens the predator. This is the best time to catch it both on the river and in reservoirs without a current.
The natural habitats of trout are North America, Northern Asia and Europe. Several species of trout, introduced by fishing enthusiasts to Australia and New Zealand in the 19th century, have practically displaced and threatened some native species of fish living in mountain reservoirs. Introduced species included lake trout from England and rainbow trout from California.
The rainbow trout was a species native to the Pacific coast of North America and is believed to have originated from Sonoma Creek. Rainbow trout from New Zealand still have the habit of entering rivers in winter to spawn. The closely related trout, simu or "cherry salmon", and other trout species can be found in the Himalayan region of India, Nepal, Bhutan, Pakistan and the Tian Shan Mountains of Kyrgyzstan.
The favorite places of rainbow trout are not much different from the places of brook trout. She also loves bottom layers, hiding behind riffles, snags and underwater rocks. She is most active in cloudy weather, and stands almost motionless in clear and sunny weather.
As for lake trout, you already know that they live at a depth of 100 meters. If during spawning it is only at the bottom, then in other months it can be found on any horizon. In summer, in warm weather, lake trout can be found in coastal areas.
Watch fishing movies for free online
The best educational films on Spinning Fishing
This fish can be found both in the fresh water of rivers and lakes, and in the salt water of the seas. Many varieties are classified as anadromous. This family is distinguished by the fact that its representatives can change their habitat.
Read Fishing for perch with a spinner and top best luresThis fish belongs to the predatory fish, because feeds:
- zooplankton;
- insects and their larvae;
- small fish.
The stream species is anadromous, because Its habitat includes both fresh and salt water bodies. Some species still prefer to live in fresh waters. These include brown trout: they do not leave their usual habitats.
Adult trout, which spawn in the autumn-winter period, can go to depths where they find clean, oxygen-enriched water. There she lives until spring, hunting for small fish.
In Kabardino-Balkaria and Khakassia, golden-amber trout are bred (where other varieties of this fish live).
White trout is found in the USA and Norway. In Europe, it lives in mountain and forest rivers and streams, the waters of which have a fast flow.
Rainbow trout live near the Pacific coast of North America, where there are many bodies of fresh water. This species is valued for its taste. It is artificially grown in countries such as:
- Australia;
- New Zealand;
- Japan;
- countries of South Africa and Madagascar.
The fish have taken root well in these places. It is also bred in Europe (in paid reservoirs). This type of fish loves temperatures of 15... 20°C, does not tolerate direct sunlight, trying to hide from it under snags and between stones. It is most active on cloudy days, especially in the morning and evening hours.
This species cannot live in bodies of water that are covered with ice in winter. This happens because she needs to rise to the surface from time to time in order to fill her swim bladder with oxygen.
Interesting Facts
The spicy taste of trout is emphasized by ginger, herbs and lemon.
In the Caucasus, red fish meat is usually served with pomegranate sauce. In oriental dishes, it is used to create sashimi, rolls, sushi, stews, and soups.
Salted fish goes harmoniously with strong alcoholic drinks, and smoked fish goes well with dry wine and beer.
It is interesting that in Japan trout is not subjected to long-term heat treatment, but in the West it is customary to thoroughly boil and fry the product.
In European countries, spicy fish meat is baked with nuts and fruits, marinated in spices, vinegar, lemon juice and cooked on a barbecue or grill.
Lifestyle
This fish chooses exceptionally clean habitats: fresh, cold springs with a transparent rocky bottom. Once a reservoir becomes polluted, trout are the first to die of all the underwater fauna. It follows that trout meat is environmentally friendly, and therefore healthy.
After spawning, the fish move down to the river beds and stay closer to the bottom. It feeds on minnows (small fish).
In summer, when the water warms up by more than 15°, schools stay at the mouths of rivers and springs, since the water temperature there is much lower.
Article on the topic: Fishing for carp and grass carp
Individuals that have not reached half a kilo in weight are not predators and parasitize at the expense of their older relatives, feeding on their eggs. In addition, they feed on earthworms, which are washed out of the soil with rain.
Breeding
For the food industry, for industrial purposes, trout are artificially grown in clean ponds and fish farm pools.
The species most suitable for breeding fish of the salmon family: brook (river) or rainbow.
It takes 1.5 years to grow trout weighing 500 grams. Larger specimens are bred as mother stock in order to obtain red caviar, which is subsequently processed (salted) for sale.
The fish becomes sexually mature in the fourth year of life. In one female, the number of eggs does not exceed 3000 eggs. Because of this, the product is classified as a delicacy and is highly valued.
The difference between rainbow trout and regular trout
Rainbow trout
Outwardly, mykiss is a little similar to ordinary sea trout; formally, it also belongs to the red fish, but in culinary terms it is very different in taste. Its flesh is a cross between salmon and river fish. The color is always paler than that of marine rocks, sometimes even without red tints.
The main differences between rainbow trout and sea trout:
| Differences | Marine | Rainbow |
| Carcass size | 3-5 kg | 1-2 kg |
| Flesh color | Mostly bright red or bright orange | Pale, sometimes almost white with a creamy tint |
| Scale size | Large scales | Smaller |
| Color of the skin | Silver, homogeneous | Two reddish stripes on the sides. Sometimes they shimmer in several colors |
Catching
For the sports fisherman, the following types of trout are of greatest interest: brook trout (speckled trout), sea trout (trout), and lake trout. Salmon spend the main part of their lives sedentary, with the exception of small movements to search for spawning areas (rifts). Trout spawn during the cold season, when the water temperature drops to 1 – 6 degrees Celsius (from October to February).
Fishing gear
The choice of devices for catching a skilled predator depends on the planned fishing location. For river fishing you will need a compact fishing rod or spinning rod. When fishing for trout in a lake or pond, give preference to a medium-class telescopic fishing rod, 5 meters long with a safety reel. Fly fishing is also used.
When fishing for trout, take off your bracelets, wristwatches, and shiny objects, as they reflect glare from the sun and scare away the underwater inhabitants.
To lure fish, it is recommended to use a two-legged rod, with a length of 1.80 to 2.30 meters, with a spoon weight of 4 to 15 grams. Fly fishermen use artificial flies (dry and sinking).
For trout fishing, high-quality hooks No. 6 - 10 and fishing line for tackle 016 - 018 are used.
Fishing methods
The traditional method of catching trout using a float rod is used in calm parts of mountain rivers and streams. The ideal place for catching red fish is the opposite side of the rocky shore of the reservoir. In this case, the bait is thrown upstream, so it slowly floats, swimming near the hidden individual, and a bite occurs immediately.
As with whitefish fishing, the “Drazkovic method” is widely used, which involves catching fish with dead bait.
For the best bite on a spinning rod, it is recommended to choose sinking braid of dark green or gray color.
When hooked, trout behave aggressively, putting up strong resistance as they take the bait. It makes powerful jerks downward, jumps out of the water sharply, and tries to stop behind a stone, which often leads to the tip of the rod bending and the line breaking.
Trout can be caught well all year round, however, luring and fishing for it requires a lot of endurance and skill. During the cold season (winter), the fish’s caution increases. Despite the fact that during this period the trout is in an inhibited state, it instantly reacts to the slightest sound and movement of the angler. When danger is detected, the individual hides in the depths of the reservoir and lies to the bottom. To catch trout, they drill fresh holes, since they are not found near the old ones.
With the thaw and the appearance of the first thawed patches on the surface of rivers, lakes, and seas, its activity intensifies.
In the spring, the fish remain in “wintering pits” or move to the rifts, where the water is more quickly saturated with oxygen. In summer it rarely appears off the coast. The most likely places where it can be found are spring rivers with tributaries and streams. The optimal water temperature for trout is 18 degrees Celsius. On hot days, fish come out to bite at night, when the reservoir cools down.
In the fall, spawning begins, and she is constantly on the move, actively feeding, and gaining weight. At this time, different baits work: tadpoles, spinners, wobblers, juveniles.
Trout's favorite bait: larvae, fish eggs, crustaceans, insects, minnows.
How to feed fish?
Mix eggs, milk and pour into a heated frying pan. Don't add oil! Stir the mixture until the liquid evaporates. Cool a third of the “omelet” to 50 degrees.
Grind shrimp, squid, fatty and salted canned herring, add to the mixture, and stir. Trout loves salt, so you can provide complementary foods with it.
A traditional component for winter fishing is canned corn. Drain the liquid, grind the grains into a homogeneous mass, add the starting materials to the mixture. Wrap the resulting mass in a plastic bag and place it in the refrigerator overnight. Ready-made complementary food has a uniform taste and pronounced aroma that attracts fish. Transfer the required amount of the mixture into a thermos in the morning, and place the rest in the freezer, where it can be stored for a month from the moment of preparation.
Fish seed material
Broodstock development
Aquacultured trout do not reproduce naturally, so eggs are obtained through the artificially induced spawning of mature females from the broodstock. Although two-year-old trout can already spawn, females are rarely used for breeding before they are three or four years old. The number of broodstock individuals depends on the number of fry required for production on the farm. It can be calculated based on the survival rate at different life stages and the fertility of the broodstock females. As a rule, one male is enough for three females of the broodstock. Males and females are usually kept separately. Broodstock maintenance is expensive and labor-intensive, so some farms purchase eye-stage eggs from third-party producers; the latter must have certificates of freedom from disease, otherwise they are treated with iodine (100 mg/liter for 10 minutes) and the water temperature is gradually increased to the temperature of the incubator. Broodstock are selected for rapid growth and early maturation (usually after 2 years). One commonly used method is to use an all-female sex-reversed broodstock to produce all-female offspring that grow faster. Functional males are produced at the fry stage by oral administration of 17-methyltestosterone. This male hormone is introduced into the food.
Collection and fertilization
The process and technique of raising rainbow trout is well studied and developed. The most common is the dry method of egg fertilization. Eggs from females are removed manually (under anesthesia) by applying pressure from the pelvic fins to the anus or by air spawning, which causes less stress on the fish and produces cleaner, healthier eggs. Air is injected with a hypodermic needle (about 10 mm) under pressure (2 psi) into the body cavity near the ventral fins and thus expels the eggs. Air is removed from the body cavity by massaging the sides of the fish. Up to 2,000 eggs per kilogram of body weight are collected in a dry pan and kept dry for better fertilization.
The semen of males is collected in the same way as that of females, in a bowl, avoiding contact with water and urine. Semen from several individuals (for better fertilization, they are taken not from one, but from several males) is mixed with caviar. To reduce the likelihood of inbreeding, it is recommended to mix the reproductive products of three or four males before fertilization. Water is added to activate the sperm and increase the volume of the eggs by about 20%, filling the perivitelline space between the shell and the yolk. This process is known as "water curing".
Rainbow trout caviar at the eye stage (ikra-dabie.pl)
After fertilization of trout eggs and washing (de-sticking), an active process of crushing and compacting the shell occurs. Fish farmers call this period “spawn swelling.” The eggs lie in running water for at least 6 hours after fertilization, in the dark and with water changes.
Eggs can be transported 6-12 hours after fertilization, for 3 days, then only at the eye stage. At the “eye” stage, or stage of eye pigmentation, the eggs are resistant to mechanical stress.
To increase productivity, a technique has been developed that uses the culture of unisexual females or triploids. Triploidy is induced by pressure or heating of the eggs. Same-sex individuals are obtained by fertilizing normal female eggs (XX chromosomes) with the sperm of masculinized females with a sex change (XXX chromosomes). Mature testes of sex-changed individuals are large and round, but do not have an exit hole. Therefore, the testes are removed from the abdominal cavity and torn to drain the milk into a container. An equal volume of swelling fluid is added to make the sperm motile and ready to fertilize normal eggs. One of the advantages of this method is that only the broodstock consists of sexed individuals and these can be reared separately, while the fish sold are not treated with hormones.
Incubation
The eggs in the incubator are not disturbed until the eye stage is reached. They can be in setter trays, vertical flow incubators or setter tanks. The trays are usually 40-50 cm wide, 20 cm deep and up to 4 m long. They contain 2 rows of eggs placed in wire baskets or screened trays, fixed 5 cm above the bottom, where water passes through the tray (3-4 l/min). As they hatch (4-14 weeks), the fry fall through the net into the bottom chute. An alternative to such trays are vertical incubators, in which up to 16 trays are stacked on top of each other. Water flows from one source (3-4 l/min) through the eggs, flows from above and pours into the pan. This aerates the water, allowing large quantities of eggs to be incubated in a minimum amount of space. The prelarvae may remain in the trays until they begin to swim, approximately 10 to 14 days after hatching.
The time taken to hatch varies depending on water temperature, taking 100 days at 3.9°C and 21 days at 14.4°C (about 370 degree days). In incubator vessels (Weiss apparatus), commercially available or made independently from a 40-liter drum and PVC pipe, water enters from the bottom and flows upward. In such a flow of water, without large financial costs, it is possible to mix up to 50,000 thousand eggs and keep them suspended. A necessary condition for proper operation is filling the vessel no more than 2/3 with eggs and raising the eggs when stirring to no more than 50% of their height in a static state.
In all the above methods, dead eggs are removed regularly to prevent fungal infection. Prevention of fungal infection is carried out with formaldehyde (37% formaldehyde solution). It is added to the supply water in a ratio of 1:600 for 15 minutes daily, but not within 24 hours after hatching. Once the eye stage is reached, weak and undeveloped eggs are removed.
As a rule, hatching reaches 95% of the total number of eggs. Rainbow trout larvae and fry have a supply of nutrients in the yolk sac, which lasts for 2-4 weeks. Hatching of one batch usually takes 2-3 days, during which time the shells of the eggs, as well as dead and deformed fry, are regularly removed. The eggs are incubated separately from the hatching trays and transferred to them after hatching. After hatching, the trays are removed from the tray, while the depth remains shallow (8-10 cm), and the strength of the water flow is reduced until the fry reach the active swimming stage, absorb the yolk sac and begin to actively search for food.
1. Expressing the female’s eggs; adding sperm to caviar. 2. The fertilization rate can be increased by mixing a saline solution (NaCl 90.4g, CaCl2 2H2O 3.4g, KCl 2.4g per 10 liters of water). 3. Placement of fertilized eggs in incubators. 4. This type of incubator is traditionally used in South Korea. 5. This type of growing system is traditionally used in South Korea. The optimal water temperature for incubating fertilized eggs is 10 degrees, at which the eggs mature to the eye stage on the 16th day, the larvae appear by the 32nd day and begin to swim by the 60th day. During incubation, physical impact and light exposure to the eggs should be avoided. 6. Rainbow trout larvae have just hatched. To prevent infection, 100 ppm formaldehyde is added to the water. Dead eggs are regularly removed (www.lib.noaa.gov/retiredsites/korea/main_species/rainbow.htm)
Feeding the fry
Trout fry are traditionally raised in fiberglass or concrete tanks, preferably round in shape, which ensures even flow and distribution of the fry, but square tanks are also available. Pools usually have a diameter of 2 m or, if it is a square, 2x2 m with a depth of 50-60 cm. Water is supplied using an elbow pipe or a sprayer, which circulates the water. The drain, protected by a strainer, is located in the center of the tank. This position ensures that the water forms a whirlpool so that the waste is concentrated in the center and can be easily removed. The sump or drain pipe, which is used to regulate the water level, is connected to an elbow pipe on the side of the tank.
Indoor culture of Rainbow Trout fry (left). Traditional trout culture channels in South Korea (right) (www.lib.noaa.gov/retiredsites/korea/main_species/rainbow.htm)
Rainbow trout fry are fed special juvenile feed starting when approximately 50 percent have reached the active swimming stage. Use automatic feeders. When most of the fish begin to feed actively, feed should be fed daily at a rate of 10% of the fish's weight for 2-3 weeks, preferably continuously, using a clock feed mechanism. Pelleted feed made from a mixture of fishmeal (80%), fish oil and grain provides balanced nutrition, promotes growth and product quality. They contain approximately 50% protein, 12-15% fat, vitamins (A, D and E), minerals (calcium, phosphorus and sodium) and pigment to produce pink meat (if necessary).
High-energy commercial feeds and proper feeding regimens provide a feed conversion ratio of 0.8:1. When the fry reach 15-25 mm, feeding is carried out according to tables that are based on data on the temperature and size of the fish. Automatic feeders are convenient, but in the early stages it is better to feed by hand to avoid overfeeding. Automatic feeders are more effective for larger fish. During the process of growing trout, the content of dissolved oxygen is controlled. To reduce density, fish are moved to larger tanks.
Rainbow trout feeding methods
Diagram of canals and ponds
When the fry reach 8-10 cm in length (250 fish/kg), they are transferred to reservoirs for feeding in the open air. These can be concrete channels, flowing Danish ponds or cages. Individual canals and ponds are usually 2-3 m wide, 12-30 m long and 1-1.2 m deep. The canals supply oxygenated water. Oxygen concentration can be increased by increasing the speed of water flow; however, trout are vulnerable to the quality of incoming water, and environmental temperature has a significant impact on their growth rate. The number of channels or ponds in rows varies depending on pH (a low pH of 6.5-7.0 reduces the concentration of non-ionized ammonia) and the slope of the ground (aeration requires a 40 cm drop in ground level between channels). In terms of hygiene, water quality and disease control, a parallel design is preferable since any contamination flows through a small part of the system. In both systems, fry are stocked at 25-50 fry/m², which should provide up to 30kg/m² of adult trout with proper feeding and water supply, although higher production is possible.
Rainbow trout fingerlings
Rainbow trout usually grow to market size (30-40 cm) in 9 months, although some fish take more than 20 months to grow to a large size. Individuals are usually sorted 4 times (2-5 g, 10-20 g, 50-60 g and more than 100 g) in the first year of production. During this period, it is necessary to reduce density to ensure faster growth, adjusting the feed supply to obtain the same size of individuals. Assessing the number and size of individuals (twice a month) allows you to answer important management questions: assess and calculate growth rates, feed transfer, production costs and proximity to maximum load.
Alternative nursery systems for rainbow trout include cage systems (6 x 6 m to a depth of 4-5 m) in which fish (up to 100,000 fish) are kept in floating cages in freshwater and marine environments that provide a good water supply and sufficient dissolved oxygen. This method is technically simple as it involves natural bodies of water at lower capital costs, as opposed to using flow-through systems. However, here the fish are vulnerable to predators (rats and birds), to water quality, and growth rates depend on the ambient temperature. In such systems, high stocking densities are achieved (30-40 kg/m²), and fish transferred to sea cages have higher growth rates and larger sizes. In less than 18 months, fry weighing about 70 g reach 3 kilograms.
Pickling
Most often, trout is sold salted or frozen. At the same time, the cost of these products differs significantly. To save money, you can salt fish yourself at home using a dry or wet method.
Regardless of the cooking technology, pre-wash, dry and cut fresh fish into thin slices. Place the fillet in a ceramic or enamel bowl.
For dry pickling, mix granulated sugar and table salt in a 1:2 ratio, add seasonings, pepper and carefully sprinkle each layer with the resulting mixture. Place the container with fish in the refrigerator. After a day it can be consumed. If desired, add lemon juice or vegetable oil to the marinade.
To get rid of the taste of raw fish, increase the salting time. To do this, sprinkle the trout carcass with salt and sugar, observing the indicated proportions, and wrap in a damp towel, then in plastic wrap and wrapping paper. Place in the freezer for 5 days.
Interesting facts about trout
- The largest trout species is the lake trout, found in the Great Lakes (USA), Alaska and Canada. This type of trout can reach a weight of 45 kilograms. Rainbow trout are capable of spawning at 3 years of age and typically breed every 3-5 years.
- Rainbow trout are considered endangered in some regions of the United States.
- If rainbow trout migrate to the ocean as adults rather than remain in streams and rivers, they are called steelhead trout. Her body is almost entirely silver in color.
- The average lifespan of rainbow trout is 4 to 6 years in the wild.
- The spawning season for rainbow trout is spring.
- Rainbow trout are farmed on all continents except Antarctica.
- The color of rainbow trout meat will vary depending on the fish's diet and environmental conditions.
- Man began breeding rainbow trout in 1870. The largest producer of trout is Chile.
- During the spawning season, one trout can spawn anywhere from 200 to 8,000 eggs.
- Rainbow trout are an indicator of water pollution because they can only survive in clean waters.
- This fish spawns in the waters where it was born.
"Royal" recipes
Baked trout with vegetables
Ingredients:
- onion – 1 head;
- carrots – 1 piece;
- broccoli;
- trout fillet – 600 grams;
- white wine – 200 milliliters;
- lemon – 0.5 pieces;
- fresh tomatoes – 3 pieces;
- salt;
- a set of spices (rosemary, savory, oregano, mustard seeds, allspice, cardamom, paprika, fennel).
Cooking principle:
- Cut the fish meat into portions.
- Mix salt and spices. Generously provide the trout with the fragrant mixture and cover with lemon rings.
To ensure that the fish is saturated with spices and acquires a pleasant aroma, leave it in the marinade for 30 minutes.
- Prepare the vegetables. Peel them, cut the carrots into strips, onions into rings, tomatoes into slices.
- Preheat the oven.
- Line a baking sheet with foil (15 x 15 centimeter squares). Place a vegetable bed in portions, on top of which place pieces of trout and a slice of lemon.
- Pinch the edges of the foil so that the juice does not leak out, and the fish will be baked in its own marinade.
To enhance the taste and add piquancy to the dish, pour 50 milliliters of wine into the resulting “pockets”.
- Place the pan with the fish in the preheated oven for 30 minutes.
This dish is recommended to be served with white wine (dry or semi-sweet).
Fish pie
Ingredients:
- trout fillet – 2 kilograms;
- yeast dough – 1 kilogram;
- butter – 50 grams;
- onions – 2 heads;
- parsley – 1 bunch;
- Bay leaf;
- allspice peas;
- salt.
Cooking sequence:
- Divide the dough into 3 parts. Connect the first two and roll out an oval 1 centimeter thick. Make a small circle from the third part.
- Wash and cut the trout into pieces. Salt and pepper it.
- Chop the greens and mix with the fish.
- Peel the onion and cut into rings.
- Place the dough in a baking dish, spread the fish and herbs on top of it, then the onion rings. Raise the edges of the oval with a “side”.
- Grate the butter and place it on the filling.
- “Close” the pie with a small oval, pinch the ends of the dough with the sides.
- Use a fork to make holes in the center to allow steam to escape.
- Preheat the oven to 180 degrees.
- Place the pie pan in the oven for 60 minutes.
Before serving, cut the hot fishmonger into portions.
Trout species
The name trout is a collective name common to several species of salmon fish:
- char;
- noble, Pacific salmon.
In numerous reservoirs of Russia you can find three varieties of trout:
- stream;
- lake (other names: trout, Karelian);
- rainbow trout.
Brook trout are a freshwater form of sea trout, an anadromous fish. However, the habits of brook trout are different - they do not migrate from their native reservoir.
brook trout
For a comfortable existence of brook trout, fast rivers and streams with clean, cold water are necessary. The standard weight of freshwater trout is 1-2 kg.
Individual individuals, under particularly favorable conditions, can grow up to 12 kg.
Lake trout, also known as brown trout, Karelian trout prefers to live in deep-water lakes with cold water. The ideal place for it is the lakes of Karelia, the Kola Peninsula, Lake Onega, and Lake Ladoga.
lake trout
This is a solid-sized fish (up to 1 meter in length), flocking in schools and most often spending time at a depth of 100 meters.
Rainbow trout are Pacific steelhead. This species is most common in Russian waters. Many fish farms engage in industrial breeding of rainbow trout.
Rainbow trout
This is a predator that inhabits paid water bodies (ponds); amateur fishermen catch it using a spinning rod.
Appearance of fish
All trout species have a similar body shape. The beautiful fish has a dense, powerful body that resembles a spindle. Her head is small and truncated in shape.
The trout's eyes are small, light, almost transparent, its vision is excellent, it is perfectly oriented in the depths of the water. There is one more nuance regarding trout vision.
She vigilantly looks out for prey, simultaneously focusing with both eyes, that is, she looks simultaneously in different directions.
Trout is a beauty and cannot be confused with any other fish. Countless motley spots give its body an extraordinary decorative appearance.
The dorsal fins of the fish are covered with dark dots, the ventral fins are slightly yellowish in color.
The body of the fish is covered with a layer of mucus and small scales. On the abdomen the scales are denser.
The trout's body is somewhat flattened laterally and has more than 60 vertebrae. The fin on the back is long, narrow, consists of several ordinary rays and many branched ones.
Behind the dorsal fin is an adipose fin, its edge is often dark. This fin is the identifying mark of all salmon fish.
The pectoral and pelvic fins of trout are composed of 100 rays, the anal fins have 300, and the caudal fins have more than 20 rays.
A characteristic feature of trout is its iridescent color. The back of the fish has an olive tint, the sides are greenish with some yellowness, decorated with black, red, white spots with a bluish halo.
The ventral part is light, with a yellowish tint. The gill covers are characterized by a golden color; the gills themselves are pink or red.
The color of this fish depends entirely on its living conditions - the quality of water and food. In reservoirs with clear water, trout acquire a silvery color.
If the bottom is muddy or peaty, the body of the fish darkens. Trout also change color during spawning.
It becomes much darker, spots on the sides may appear and disappear.
Brook trout is distinguished by a brownish color; its head and back are often dark black in color.
The body of brook trout is decorated with red and black specks, for which it received its second name - speckled.
Rainbow trout is much lighter in color and has a red-violet stripe on the sides of its body, reminiscent of a rainbow.
Female trout look more respectable and larger than males. The lifespan of this fish is 12-20 years.
The most well-fed trout are found in the Caspian Sea; amateurs have managed to catch specimens weighing 50 kg.
Rainbow trout: features, calorie content and cooking methods
Among trout varieties, rainbow trout remains one of the most popular: this fish has light pink, tender meat, which, when cooked correctly, is not too fatty and not too dry. Also, the medium size of rainbow trout makes it convenient both for baking whole and for portion cooking: it is convenient to make steaks from the fish. There are a lot of recipes for trout dishes - find the best option for yourself or regularly surprise with a variety of dishes.