Description of the Verkhovka
This small fish, which is called the redhead, oatmeal, and in some places chikoy, belongs to the ray-finned fish from the carp family. Verkhovka has some similarities with a small bleak , with which it is often confused. But the difference between the verkhovka and the bleak lies in the slab body and larger head. Bleak is a somewhat flat fish.
The crown is distinguished by a short lateral line, attributable to 2-12 scales, compared with the head with large eyes, an upper mouth and, of course, small size. This fish never grows more than 9 cm, and most often its length is about six centimeters.
The color of the top has a light green tint, the back is slightly darker, and the sides have a silvery tint. In the water, flocks of crowned moths sparkle like sparkles. In the sun, the scales of these fish become dazzling silver. The fins are transparent, matching the color of the water. On the sides you can see something like a bluish stripe. Depending on the color of the water and other conditions in a particular reservoir, the color of the top can change, be a little lighter and darker. The life of this small fish is also short - no more than four years.
Winter fishing for topwater
Our reservoirs are inhabited by a small fish called bleak – the top-finning fish. This name comes from the fact that it floats mainly in the upper layers. There are also bystryanka and verkhovka, which are similar to it, but in the bulk it is bleak that predominates. For many fishermen, this fish is not of particular interest. Only in vain.
It’s not known how others are, but I’ve always been willing to compete with bleak. So this fall we went out specially to catch the wonderful topwater fish. As soon as I throw it in, there’s a bite right away; in a whole day you can pull in a whole bucket. In winter, it’s especially exciting to fish for topwater, when nothing else bites except it and small perches. This is what I want to tell you about.
In February, when it is impossible to predict the bite due to frequent changes in weather, bleak surprises with its stability. You just need to find it and set up the necessary gear. Often, the topwater fish stays in deep areas of lakes and eriks. If there is a current, it chooses backwaters or holes with a weak current and always stays at the very edge of the ice or halfway through the water.
It also happens: Fishing using the herabuna method
It is easy to detect visually; all you need to do is drill a hole, clear it of ice shavings and pour bait into it. If there is a bleak nearby, it will not be afraid of daylight and will quickly reveal itself by collecting food particles. If this fish is not there, you need to equip a fishing rod and fish up to two meters below the ice. But if bites are not observed within 10 minutes, you need to change the place.
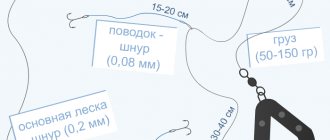
Powdered milk can be used as bait, which slowly settles, creating a cloud of attractive turbidity. It’s hard to get enough of this kind of fish bait, but it’s easy to keep it near the hole. You need to constantly add a small pinch of the mixture so that the flock does not swim away. The rod should be light and sensitive, the fishing line on it should be as thin as possible (up to 0.1 mm).
If you fish with a float rod, then hooks should be set to No. 18-19 according to the international system of standards. The gear you need is simple, a small float for two short leashes, a small sinker that can sink a fishing line with bait to 1 m depth. It is best, of course, to fish with a jig, whose size should also not be large.
Other fishing articles on the topic:
- Winter fishing for pike in shallow waters As we have already noted, during the first ice the pike clearly gravitates to the shallows, where the ice is just beginning to form, where it is thinnest. And this is where you should start fishing. During the first ice, be sure to remember to be careful when moving along...
- Winter bream fishing and the importance of professional experience Winter bream fishing always begins with a sea of emotions and excitement. Fishing, like love, is suitable for all ages; young winter fishing enthusiasts began to appear in more and more water bodies. Moreover, not only guys, but also girls appear on the ice. ...
- Winter fishing for perch with spoons. The spoons shown in Fig. 46-18, work very well and have the following feature: their pause is longer than that of spinners with a hard-soldered hook. The length of the pause when flashing is determined at home, in advance. So, we flash in the bathroom and...
- Winter roach fishing Winter roach fishing is fundamentally different from summer fishing and is similar to ruff fishing. Strangely enough, it begins in October, with the arrival of cold weather. At this time, they are usually caught with fillies, they are placed either on the bench of the boat or on its side. The filly's sinker...
- Winter fishing for perch in snags Many anglers simply leave places where there are a lot of snags. How can you get out of this situation? Very simple. If we go into a snag, we can remove the bottom tee, and we will only have the front and back hooks. This balancer perfectly catches...
- Winter trout fishing from ice with a wobbler As you know, trout fishing in winter can be done in several ways. The most effective is fishing with lures, where wobblers are used as bait. The choice of a specific company and type of wobbler depends on the fishing location and weather, as well as many other factors.
- Winter fishing for pike with non-hooking spoons (non-hooking) It is very interesting to use non-hooking spoons with wire whiskers and a rigidly fixed hook (Fig. 47-17). Such spoons are, first of all, good for fishing in snags. Thus, with such lures we can catch pike in the most crowbar...
- Winter fishing for bream with a devil Winter fishing for bream is more logical than for bream, since bream are almost inactive at this time and spend almost all the time in their dens. To catch different types of fish, fishermen currently widely use the devil jig. Sometimes, …
- Winter fishing for pike In the midst of winter, pike comes to life during the thaw period and very often becomes an accidental prey for an angler when fishing for perch. At the same time, the pike’s grip can be so unexpected and strong that it can not only knock the rod out of your hands, but even break it off...
- Winter fishing. Catching pike When we go fishing in winter, we want adventure and adrenaline. But, as a rule, we only get hypothermia and a bad catch. However, when hunting for a cunning predator - pike, you will not be bored. So, when going pike fishing in winter, choose...
It also happens: Fishing with a spring rig - There are fish here
Verkhovka habitats
Verkhovka lives in the upper layers of rivers with weak currents, oxbow lakes, lakes, in dug pits and reservoirs, adhering to not very silted places with hard clay-sandy soil. This is a typically schooling fish that feeds all day and in the dark. At night in good weather under the moon you can always see circles on calm water - this is the melting of the tops and bleak. During prolonged bad weather, as well as in spring and autumn, the verkhovka goes deeper. But for the most part, the upper layers of water are its home. This is a very shy fish. Often, from hitting the water with an oar, from knocking and even screaming, flocks of crowned beetles jump out of the water - splashing in all directions. The same picture happens during a driven hunt of perches, which also in a flock drive a flock of perches aground and begin a feast. Then the water boils from the frightened top leaders fleeing. Such boiling “cauldrons” attract seagulls, and they serve as a guide for anglers with spinning rods who come to these places and catch perch with small rotating and oscillating spoons.
How to increase your fish catch?
Over 7 years of active fishing, I have found dozens of ways to improve the bite. Here are the most effective ones:
- Bite activator. This pheromone additive attracts fish most strongly in cold and warm water. Discussion of the bite activator “Hungry Fish”.
- Increased gear sensitivity. Read the appropriate manuals for your specific type of gear.
- Pheromone-based lures.
The baby sisters also differ in their vertical stripe - in the top melt it is more clearly defined than in the bleak. The list of differences continues with the dark humps on the heads of male verkhovkas, which appear during mating games. There is also a difference in age - the perch rarely lives up to four years, and the lifespan of the bleak is at least five. If you look for differences in cleaning fish, you will practically not find them - both have almost no scales.
The fish is found in both large and small reservoirs throughout Europe. In Russia, large schools of whitefish and bleak can be seen in the Northern Dvina, Volga, and rivers of the Caucasus. The basins of the Caspian and Black Seas are also inhabited by Verkhovka.
Unlike many inhabitants of reservoirs, the fish prefers to lead a sedentary lifestyle and not go on long journeys. Rivers in which there is a weak current are a favorite refuge for both the high water and its sister, the bleak. Verkhovka is also found in small ponds and flooded quarries; the fish thrives in reservoirs with a muddy bottom.
The common verkhovka loves warmth and comfort, and in the summer months, especially in June, huge flocks of babies can be seen in open areas. Fishing will be no less fruitful until the very end of July, only just before the beginning of autumn the crumbs will begin to descend to greater depths in search of cozy corners. If you are not too lazy, you can stock up on perennial water for a long time, because it also feels great in an aquarium, which can be built from an ordinary jar.
Despite its tiny size, the fish can be considered a rather aggressive aquatic inhabitant that will not disdain any food:
- crustaceans;
- rotifers;
- insect larvae;
- small bugs;
- fish fry;
- caviar.
When choosing a place for spawning, the fish do not go overboard, the main thing is that the surface to which the eggs will attach is hard. It could be a stone, a board, even a stick, driftwood or your float. You can often find rudd caviar, to which a masonry of verkhovka is modestly attached.
It also happens: Fishing with an elastic band from a boat
At one time, the female can spawn up to five thousand eggs, no larger than a poppy seed. Within a week or a week and a half, the babies appear and immediately go in search of food.
Catching verkhovka usually occurs using nets or homemade spiders.
How does fishing work? There are several tricks that will help you stock up on a considerable amount of small fish:
- The mesh of the net must be very thick, otherwise the nimble kids will easily run away.
- An excellent tackle for catching perched water can be made from gauze; you can build one in a few minutes right at the place where you will be fishing.
- To collect as many crumbs as possible, just stir up the water well - curious fish will certainly rush in to check who dared to do this outrage.
- With a little skill, you can catch several dozen individuals, so it is better to keep a container near you into which you can immediately send the caught prey.
Live bait from perch is indispensable when hunting large representatives of perches. Don’t despair that you won’t be able to get hold of crumbs in winter, because you can use a winter fishing rod to catch them. The ideal option is light tackle made by yourself. If you have experience in building a filly, then there will be no difficulties here - the tackle for the top is only slightly smaller in size.
You can also catch baby fish with a nodding rod, but this requires considerable skill. What are the top leaders going for? Preference should be given to light-colored baits:
- small burdock;
- larvae;
- small bloodworm.
How to make bait for carp with your own hands - here.
Read about attractants here.
The redfish is a rather interesting fish, and you should not think that catching it will not be difficult. Often you will have to use a lot of skills to get your hands on nimble babies that will serve as excellent live bait. Taking into account the characteristics and habits of the fish, choosing the right tackle and showing a little patience, you can stock up on appetizing bait for large representatives of reservoirs for a long time.
Verkhovna spawning
Verkhovkas become capable of reproduction quite early - by the age of two years of their short life, when they reach a size of four centimeters. Spawning occurs in several stages, starting from May-June and often in July. The optimal water temperature for spawning verkhovka is 15-25 degrees. The eggs are deposited at a depth of about one and a half meters. Females stick it to the bottom of aquatic plants: water lilies, pondweed, arrowhead, even to objects floating in the water. The eggs mature for about a week and the larvae hatch ready for independent life, that is, capable of moving in the water and feeding.
Fishing on the verkhovka
In mid-July, many nocturnal predators, including pike perch, almost completely stop feeding during daylight hours, and in early August, the fastidious pike joins them. In addition, in the middle of summer, a fattened predator becomes very picky and capricious in its choice of live bait. Water bloom and its stratification lead to the fact that live bait remains viable only at a shallow depth, usually no more than 1.5-2 meters. Predatory fish also begin to experience oxygen discomfort, and their feeding activity sharply decreases. In July and August, during the day it becomes useless to fish with large live bait, since it practically does not hold depth, and using imported crucian carp, for example, when fishing for pike perch, is just a waste of time. And yet, the fisherman always has a chance to be left with a good catch: it is during this period of time that almost all predatory fish, having temporarily abandoned their daily food, switch to feeding on small fish, in particular the redfish, which in this case is out of competition (with the beginning of water bloom verkhovka is the main food of the predator). Naturally, using such a small fish as live bait requires appropriate delicate equipment, but this, as they say, is a matter of technique.
Equipment
When fishing on the top, lightweight perch circles are used, the weight of which does not exceed 30-50 g, and the force at which the inversion occurs is 10-12 g. Since fishing usually takes place with the pins raised to the maximum, even a slight increase in wind is a serious obstacle, since a large number of false inversions occur. It is almost useless to put a top on ordinary mugs. The capricious predator, having felt significant resistance from the circle during its grip, immediately throws the top when turning over. The capricious predator is also alarmed by the rough equipment. The exception is individual perch bites, which occur very violently and dynamically. “Striped”, feeling the resistance of the circle, not only does not throw the top, but begins to pull the tackle with redoubled force, as if not understanding what’s going on. When fishing on the top, a leash with a length of at least 600-800 mm is installed. On a long leash, the leash looks more attractive, and is even capable of weakly moving a pinless circle along the surface. When fishing with a “square”, the fishing line is always inserted into the corner slot, which significantly reduces the friction of the circle on the water and prolongs the life of the small fish. If the angler is conservative or is too lazy to replace the circle with a lighter one, then when fishing with small live bait, his equipment includes additional elements such as a float-buoy, which will be discussed in the next chapter. The weight of the sliding load - the “olive” - should be no more than 3-5 g. A load of greater weight hinders the movement of the fish and slows down the speed of its movement. The hook is always single No. 7-8 (according to domestic numbering). Hooks with an elongated shank and additional notches at the bend or a double with hooks of different sizes have proven themselves well (see photo 7, fig. 9-a). Such hooks are usually used for tying homemade flies. Naturally, the hook should be branded and as powerful as possible, since, despite the minimal dimensions of the live bait, it can be taken by predators of different weights, including seasoned pike perch and pike.
What does the verkhovka eat?
At first, the fry greedily feed on zooplankton, which includes rotifers and cladocerans. Next, the verkhovka begins to feed on various larvae, eats beetles, insects, and will not refuse fish eggs, being a very harmful fish in cultural reservoirs. During the daytime it feeds on mayflies, flies and other flying insects, and by night it goes to the depths, where it continues to feed, only now on zooplankton. Despite its small size, it is a very voracious fish.
Spreading
The verkhovka lives in most reservoirs of Russia, Europe, southern and northern latitudes, without affecting the northern rivers and reservoirs of the Middle and Far East. Although the verkhovka is distributed in many countries and regions, and in large quantities, this fish, due to its insignificant size, is not in demand as a food product, although its meat is fatty and tender. They say that canned food, sprats, and cutlets are made from verkhovka. True, cleaning and gutting such a fish is hard labor.
How to cook verkhovka