Chekhon (also known as chukhon, sabelnitsa, chesha, cheshka, mower) is a unique fish in appearance, the unusual body shape of which gave it its name. The fish carcass has a curved shape, similar to a saber. Chekhon meat is delicious, with a sweetish taste, low in calories, only 88 kcal per 100 grams of meat. Chekhon is widely used in cooking: delicious soups are made from it, baked, boiled, fried, smoked, salted and dried. In some areas, fishing for saberfish is prohibited due to a significant decline in numbers.
Appearance of saberfish
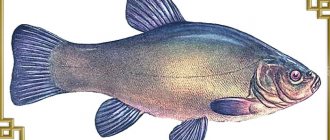
Chekhon in different areas where it is found may have other names - mower, cleaver, saber, chesha, Czech. Here is a photo of saberfish. The body of this fish is long, elongated, slightly curved, similar to a saber, which is reflected in the name of this schooling game fish.
The back of the sabrefish fish is straight, the abdomen is lowered and convex. It is clearly noticeable that the lower jaw is significantly pushed forward, which gives the fish a saber shape.
- Adults that are most often caught in the catch are up to 30 cm in length and weighing up to 0.6 kg.
- At the 10th year of life, individuals can reach up to 2 kg in weight and 40 cm in length.
- The back of the saberfish is painted in gray-brown tones, the belly is silvery-white.
- The caudal and dorsal fins are painted black. The fins on the abdomen are reddish.
- On the relatively small head of the fish there are 2 large eyes, silver in color.
The scales of saberfish are large and have their own peculiarity - they are able to refract light rays. This ability is given to the scales by guanine, a special secretion that covers the scales. When you fish a fish out of water, the scales easily leave the body.
Dangerous Enemies
The main enemy of saberfish is humans, because it is caught in large quantities in nets. They are caught 2 times a year: in the spring, when it goes to spawn, and in the fall. Spring harvest significantly reduces the size of the future population.
The size of saberfish is not that large, so it has plenty of enemies. It often becomes food for predatory fish: pike, pike perch. The caviar of the chukhon is eaten by predatory fish. It often becomes the target of seabirds when it hunts insects near the surface. When a fish emerges from the water, it immediately falls into the clutches of an agile seagull.
Like most river fish, the Czech fish is often affected by parasites.
Where does the saberfish live?
This type of fish is widespread in many parts of the planet. It feels good in both fresh and salt water reservoirs. Where is the saberfish found?
Many numerous shoals of blackfish still live in rivers, lakes and reservoirs with fresh water. In the seas it is predominantly semi-anadromous, but can adapt to any salinity of water.
The mechanisms for regulating the water-salt balance, for the removal of harmful substances, work perfectly in the body of the sabelina - the fish lived and reproduced well in the Aral Sea, where the water is extremely salty.
You can meet saberfish in the pools of the following seas:
- Aralsky;
- Baltic;
- Caspian;
- Azovsky;
- Black.
In some places the fish is numerous, but in others it has a special conservation status and its fishing is prohibited.
You can hunt it in many lakes, rivers and reservoirs in Russia and the former Soviet republics.
The northernmost border of the Czech population's habitat is the Gulf of Finland.
Population and species status
Photo: Chekhon in Russia
As we have already understood, sabrefish lead a school, collective life; the distribution area of the fish is quite extensive, but not uniform in terms of numbers. In some regions it (the number) is large, in others it is insignificant. It has been noticed that in the northern regions of our state (Ilmen, Ladoga, Onega, etc.) saberfish have a high population density.
In the Caspian Sea basin, ichthyologists have discovered a couple of populations of sabrefish – Ural and Volga; the fish differ only in size and age. Researchers note that flocks of Volga saberfish are more numerous and crowded. In addition, the Volga population, when compared with the Ural population, inhabited much larger water areas. There is also evidence that the Azov saberfish is numerous and forms a fairly large population inhabiting the northern regions of Azov, from where schools of fish rush to the Don.
Not everywhere the situation with the population of sabrefish is going well; there are areas where the number of fish has sharply declined, so bans on its fishing are being introduced there. Such regions include Moscow and the Moscow region, where starting from 2021, catching sabrefish in local reservoirs is strictly prohibited. The following objects are included in the list of the same protected places:
- Bryansk region;
- northern Donets;
- upper reaches of the Dnieper;
- Lake Chelkar (Kazakhstan).
In all of the above areas and water bodies, fishing for sabrefish is strictly prohibited, due to its low numbers; in some places this fish has been assigned endangered status, so it requires certain protective measures.
What does it eat?
The diet of saber fish is quite varied. It directly depends on the age and size of the fish, the region of residence, the time of year and meteorological conditions.
The diet of juveniles consists of small crustaceans, zooplankton, worms, zooplankton, larvae and other small animals.
Mature fish switch to a different diet:
- Caviar and fry of other fish species;
- Large flying insects (in the summer you can often see fishes jumping out of the water and grabbing a flying insect.);
- Bell mosquitoes, smooth mosquitoes;
- Small crustaceans.
Diet
Feeding for sabrefish lasts all year, excluding the spawning period. It feeds on plankton of animal and plant origin, various worms, insect larvae, as well as the insects themselves.
Its menu also includes medium-sized mollusks and crustaceans.
Starting from the age of three, saber fish begin to hunt small fish.Lifestyle and habits
Sablenica is a schooling species of fish; it can safely be classified as a sedentary species; it does not often migrate from its inhabited area. Most individuals spend their entire lives in one area. Chekhon, which constantly lives in the sea, travels many kilometers to spawn in fresh water. Lack of food can force the saber grass to migrate to another place.
This fish loves space. For its habitat, it chooses wide areas of rivers or lakes, with great depth, an abundance of plants and complex bottom topography. The fish prefers to rest in the depressions at night, hibernate and wait out bad weather. The saber fish does not often emerge to the surface of the water, and practically does not enter shallow water.
Sabelina loves rapid areas of reservoirs with active currents.
Chekhon is an active, fast, dexterous fish; during the hunt it behaves sharply and confidently.
Description and biological characteristics
Chekhon is the only species of the genus of the same name from the carp family. At the same time, although its appearance is similar to its relatives in its silver color, it is very different in body structure.
The sabrefish has a long, straight back and an outwardly curved belly, which gives it a similarity to a saber. The body itself is flattened laterally, almost flat.
The body color of the saberfish is silver over a larger area, only along the back there is a darkening with a gray or greenish tint. At the same time, on the abdomen there is a so-called keel - an area not covered with scales.
Attention! The lateral line of sabrefish is located lower than that of other representatives of carp fish. It runs close to the belly and has a zigzag appearance.
The scales easily come off with a light touch; in this respect, they are similar to bleak, with which they are often located in the same layers of the water column.
The eyes of the saberfish are very large compared to the size of the head, and even quite convex.
The usual size of sabrefish in catches is 30–40 centimeters in length and weighs from three hundred grams to half a kilogram. At the same time, it is worth noting that individual specimens are capable of reaching trophy levels - weighing up to two kilograms.
There is reliable information on the Internet that the largest saber fish weighed three and a half kilograms and exceeded 60 centimeters in length. This record was caught in the nets of a fishing crew more than a hundred years ago in one of the southern provinces of Tsarist Russia.
Reproduction of saberfish
Females and males of saberfish, living in different climatic zones, reach sexual maturity at different ages. In more southern regions, the squash becomes ready for reproduction at 2-3 years, in northern latitudes - at 4-5.
- Depending on weather conditions, sabrefish begin to spawn in April (in northern reservoirs - in May), when the water temperature warms up to +12 degrees Celsius, and ends in June.
- Spawning lasts 4 days. The size of the eggs is about 2 mm; when they enter an aquatic environment, the mechanism of water absorption is activated, due to which the diameter of the eggs increases significantly. As they become heavier, the eggs sink to the bottom.
It takes about 5 days for the eggs to mature and the fry to begin to hatch.
The babies immediately form flocks and move with the flow. In the first year of life, juvenile Czech fish grow very quickly. At one year of age, the fish are already 9-10 cm long.
Spawning
Spawning maturation of the female begins at 2-3 years of age, and the male a little earlier, upon reaching 1-2 years of age. The female is capable of laying up to 70 thousand pieces at a time. caviar.
Before breeding, sabrefish, which previously gather in flocks, make rather long journeys against the current, while simultaneously entering the floodplains. The reproduction process itself begins when the water temperature warms up to 15-20 degrees. It spawns both in the river bed and in shallow riffles near the coastal floodplain, which is affected by the increase in water level from flood waters.
Breeding sites are covered with sparse shrubs and dense thickets of meadow aquatic vegetation, and the depth at which spawning occurs does not exceed 1 m.
The caviar itself does not have an adhesive shell, but swells greatly, which gives it buoyancy and easily goes with the flow during spawning. The embryos, floating with the flow, simultaneously develop, they are carried into the river bed, after which they turn into fry and develop independently. After spawning, the saber fish returns to rest in the reservoir.
Up
Features of catching sabrefish
The peculiarities of catching sabrefish are related to its lifestyle and hunting habits. First of all, it should be taken into account that before spawning the Czech fish eats poorly, and immediately after it begins to fatten up. Therefore, hunting for saberfish before and during the spawning period should be postponed. Active absorption of food in the scalefish begins in June.
What to use to catch saberfish? In order for the bite and catch to be frequent and successful, you need to choose the right bait:
- Dung or earthworm;
- Gadfly, fly or dragonfly;
- Maggots, grasshoppers, bloodworms.
The fish also bite well on artificial baits of bright, clearly visible colors. She will be satisfied with various options for attachments, the main thing is that they are brightly colored:
- Wobbler,
- Edible silicone,
- Colored threads,
- Styrofoam balls,
- Various flies,
- Spoons of various modifications.
Summer fishing
The increased appetite of fish is usually called zhor. Fishing for saberfish will be especially successful during the period of increased fish famine. You can catch starving fish with any bait, using any gear.
It is good to use a worm or maggot as complementary food. Clay is taken, worms are chopped, everything is mixed and a ball is formed, which is lowered in the place of intended fishing. Such a mouth-watering, aromatic delicacy is sure to attract a flock of scales.
- During the day, the fish stay closer to the surface, where the water is warmer. As the sun sets it goes deeper.
- You can fish both from the shore and from a boat. Where the gear is thrown, the depth should not be less than 2 meters.
- Since the fish is a cautious fish, it is especially convenient to use a 6-meter match rod equipped with a reel for catching it. The tackle is supplemented with: thin fishing line, float, sinker.
To avoid breaking the fishing line, sharp cuts should not be made when using light gear.
Winter fishing
Catching sabrefish in winter will be successful if you choose a place where the flock has decided to spend the winter. Most likely, this will not be the place where the school of saberweed lived in the summer. In the winter season, this fish prefers to live at greater depths, in pits.
To leave fishing with a good catch, it is better to prefer equipment called a garland over jigs or perch spoons.
To assemble the “garland” you will need:
- The fishing rod is a fishing rod with a foam handle or a “balalaika.” You can attach a reel.
- It is better to choose a bright one for the bite alarm at the end of the whip.
- 15-30 meters of good nylon fishing line, 0.14 - 0.16 mm thick.
- Sinker. Its weight depends on the depth of the reservoir and the intensity of the current.
- The fishing line leash is mounted at a distance of about 30 cm from the hook. Line diameter 0.12-0.14 mm. the same ones are tied every 20-30 cm.
- Each leash is equipped with a jig or a small sharp hook.
The baits you can use are those described above. If you don't have them, you can use a piece of lard or bread crumb.
Habitat
Where is the saberfish found? This representative of cyprinids lives in reservoirs near the Baltic, Black and Azov seas. It prefers clean, deep, fast-flowing rivers.
Moreover, during the day the flock stands either at the surface of the water or in the middle layers, and goes to the bottom to spend the night.In the warm season, the fish constantly moves around the water area near its favorite area. Schools can be found at depth and at the boundaries of currents, in places of whirlpools, near sunken snags and trees inclined towards the water.
By winter, the Czech fish occupies deep holes with little current and stays at a distance of 1 m from the bottom.
Photo of sabrefish
How and what to catch
As for bait, the fish is unpretentious. But the bait must be of animal origin:
- dung worms;
- maggot;
- grasshoppers;
- flies;
- bloodworm.
For spinning, it is best to use a wobbler, twister or vibrotail. The latter is the most effective. You can also take a closer look at flies and baits made of edible rubber.
Recipes for cooking dishes from chekhon
Chekhon is widely used in cooking, as its meat has a pleasant taste. It is slightly sweet and leaves an amazing aftertaste after eating. Among the disadvantages in the properties of sabrefish, the strong bony nature of the fish should be noted.
Fish meat contains a sufficient amount of vitamins, micro- and macroelements. These are molybdenum, zinc, nickel, fluorine, chromium, etc., which makes dishes not only tasty, but also very healthy. Especially for those who do not suffer from allergies to fish products or other precautions.
The calorie content of sabrefish is quite low and is only 88 kcal in 100 g of its meat.
Due to its bonyness, low calorie content and low fat content, this fish is not used in the preparation of fish soup. But in other dishes it can take its rightful place. The most popular among connoisseurs is dried, salted and dried sabre. It is also pickled, smoked, fried, baked, canned, and stewed.
Fried with potatoes
To prepare the dish you need to stock up on fish,
The fish is cleaned, gutted, washed well, the tails are cut off, and private shallow transverse cuts are made along the entire length of the body on both sides.
Prepare a frying mixture from flour, salt, and ground pepper.
Pour oil into a frying pan set on medium heat. Place the fish on it, having first rolled it in the frying mixture.
Fry for 5...7 minutes, then turn the carcasses over to the other side and fry the fish again for 5...7 minutes.
Potatoes are fried in oil that is left over from the fish, adding fresh oil so that its layer becomes 7...10 mm thick. You can cut potatoes any way you like, just like anyone who likes to eat them fried.
First, the potatoes, just placed in the frying pan, are fried for 2...3 minutes; then mix and repeat this periodically, bringing each slice to a golden color. Then add onion, pepper and salt. Stir and after 5...7 minutes. remove - the potatoes are ready.
Serve everything together.