Hello, dear fishermen of the Fishing School! Among our river predatory fish there is one predator that is a coveted trophy for many fishermen, and not just beginners, although not everyone succeeds in catching it. This predator is greedy and gluttonous, but at the same time it is secretive, cautious, leads a twilight lifestyle and is rarely seen. Perhaps it is already clear to you that we are talking about a fanged, spiny-finned predator - pike perch.
Description. Spreading. Lifestyle of zander. Habitats of pike perch.
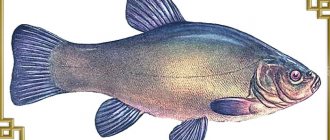
The appearance of pike perch is known to everyone: an elongated torpedo-shaped body, a long pointed snout, a high ridged dorsal fin with sharp spines. And although pike perch belongs to the perch family (the head of this family, so to speak), its body shape is more like a pike than a perch.
Another representative of this family is the bersh, which is like the younger brother of the pike perch, its exact copy, but in a smaller form, perhaps. The eyes of pike perch are large, bulging, covered with a phosphorous reflective layer (glow in the dark!), they are adapted for twilight vision. Another interesting feature of the predator is that its mouth is not lined with a palisade of sharp teeth, like a pike’s, but has fangs for grabbing and holding prey.
The coloring of our spiny-finned predator is protective, dim, grayish-green, with eight to ten “tiger” stripes, allowing the predator to camouflage itself on the bottom and among underwater plants. However, this color depends on the color of the bottom of the reservoir; in reservoirs with a dark bottom and at great depths there are pike perch of a very dark, almost black color, with a golden sheen on the scales.
Small pike-perch have a spindle-shaped body, but as they get older, they become fatter, their sides become larger, and a prominence appears on their back – a hump. The pike perch grows to a meter in length, while gaining weight up to 15 kg (sometimes more! For example, the Austrian record pike perch weighing 18.37 kg). As a rule, giant pike perch are found at the mouths of large rivers flowing into the seas - the Dnieper, Don, Volga.
In general, pike perch - a resident of the rivers of the basin of our southern seas - the Black, Azov and Caspian Seas, is also found in the rivers of the Baltic Sea, in the lakes of Finland, but it is not found in the rivers flowing into the Arctic Ocean.
There are two biological forms of pike perch – residential and semi-anadromous. Residential pike perch constantly lives in rivers and lakes, while semi-anadromous pike perch lives in desalinated areas of the seas, and only in the spring rises to spawn in rivers.
The fanged robber does not settle in any river; it requires running water saturated with oxygen; pike perch cannot tolerate weakly flowing silted rivers with a poor oxygen regime. In recent years, pike perch have been actively populated in many reservoirs, artificial seas, lakes, and even flowing ponds. This is because pike perch is a commercial fish, highly valuable, with tender and tasty dietary meat. So it became an object of fishing and acclimatization.
The spiny-finned “minke whale” is quite picky about its choice of habitats, but at the same time it is quite secretive. It is surprising that many anglers can fish on their river for years and not even realize that pike perch live in it. As already mentioned, pike perch prefers running water, well aerated with oxygen, so on the river it avoids places with stagnant water (oxbow lakes, bays), and settles in places with great depths, on a current and always with a hard or rocky bottom.
Small pike perch swim in schools and can be found in the same place as schools of perch - in the coastal zone, near aquatic plants. Solid pike perch prefer to stay on the riverbed, at depths, in places with sharp changes in the bottom, always with the current. The fanged fish loves snags with a hard sandy or pebble bottom; it is found near bridge supports, under dam spillways, and near sharp coastal ledges.
In lakes and reservoirs it lives on the beds of flooded rivers, near islands and underwater hills - ridges, “tables”. And only in the evening twilight and at dawn does the pike perch come out to feed in the coastal zone, where it causes real massacres.
Pike perch spawns when the water is already relatively warm at the end of April - the first half of May. Spawning occurs in relatively shallow places: in bays with flooded bushes, among reeds, on rocky ridges and sandbanks. This sacrament takes place at dawn and at night. It is interesting that after spawning, pike perch are in no hurry to leave the place where the eggs are laid.
The fanged predator shows enviable care for its offspring, stays for a long time near the spawned eggs and drives away fish that encroach on its offspring. The small pike perch that are born initially feed on zooplankton - daphnia, crustaceans, but already at two to three months of age they begin to prey. Sexual maturity is reached at 4-5 years of age with a body length of about 40-50 cm.
In terms of its biological role in the reservoir, pike perch is a competitor to pike, but their hunting time and methods are different, because pike is a diurnal predator, and pike perch is a crepuscular and nocturnal predator. For night hunting, pike perch are given huge eyes - bulges, which may be why in America pike perch is called “goggle-eyed”.
What can you say about the lifestyle of pike perch? Remember the saying from the movie “Striped Flight”: “The tiger leads a predatory lifestyle all his life.” In the same way, the river tiger - pike perch - leads the same way of life. And it is unlikely that this predator will ever switch to vegetarianism.
Well, as for gluttony, pike perch is not inferior to pike in this regard. As you know, pike is called a “river wolf”; by the same analogy, perhaps, one can call pike perch a “river tiger” because of its tiger-striped coloring and predatory nature.
This analogy is strengthened by the fact that pike perch, like the tiger, is nocturnal - it sits in shelters during the day and goes out hunting at dusk and at night. And then - beware of the young fish, the pike perch will not let anyone escape! However, due to the peculiarities of its narrow throat, pike perch does not hunt wide-bodied fish such as bream and crucian carp; it prefers narrow-bodied ones - gudgeon, dace, bleak.
Our hero’s keen eyes, adapted for hunting in the twilight, allow him to hunt when other river fish are “resting”. Perhaps the catfish can compete with the pike perch at night, but the catfish is clumsy, looking for prey using smell and touch, where can it keep up with the fast-moving “river tiger”!
“Make pike and pike perch together, and look – their sides are bruised!” - says the proverb. In fact, pike and pike perch, being food competitors, do not want to be friends, but are at enmity and persecute each other. At night, pike perch “clean up” pike runts, and during the day, pike will not fail to grab small pike perch feeding in the grass. “Sudacious cannibalism” is also known, that is, the devouring of its own young by the spiny-finned fish. So in this strange predilection, the pike perch is not inferior to the pike, famous for similar inclinations.
Hydraulic structures
Bridges, locks, pipes - anything that causes a change in the strength of the current is of interest. Promising points are on both sides of the structure in places with recirculating flow and standing water. Driving along the shore from a strong current to a weak one, or vice versa, often leads to a pike perch attack.
Methods of catching pike perch: float, live bait, dead fish, plumb line, track.
Information on the biology of fish is, of course, interesting, but for the fisherman what is more important is how to catch a fanged predator? There is an opinion that catching a “fanged one” is as easy as shelling pears: when it is active, it is caught on everything that moves in the water and even remotely resembles its prey. But finding a predator on the river, especially getting to the place of its active feeding in time, is not so easy! So finding pike perch is already half the success.
Where can you look for a “striped one” on the river?
First of all, we note that our spiny-finned predator is a crepuscular, a night owl. The pike perch’s eyes are adapted to capture insignificant amounts of light, but during the day it seems to “go blind” and is forced to hide from the bright rays of the sun. That is why during the day pike perch hides at depth, in the twilight under flooded trees, boulders and among the unevenness of the bottom.
We also need to take into account that our opponent loves fast-flowing water and a hard bottom. Therefore, it is better to look for it on the riverbed and riverbed edges, under snags. In such places, pike perch often, in order not to waste energy fighting the current, digs out a small funnel for itself in the sandy bottom, where it waits out the daylight hours.
Well, in the places described, the predator waits, hides, this is its “home”, but we are interested in where is its “dining room”, where should it be caught? In summer, especially at dawn, pike perch can be found near sluices and spillways, where it stands behind stones or supports in anticipation of the fry stunned by the waterfall. Loves whirlpools near bridge supports, loves various kinds of reinforced concrete structures that have fallen into the water, the boundaries of direct and reverse currents.
In the evening, at dusk, the “river tiger” becomes active, goes out to the shallows, closer to the coastal vegetation, where the fry splash with a splash. Often this hunt is a school hunt, pike perch, like experienced beaters, surround a school of fry, the splash of predators heated by the hunt is heard from afar. If you find yourself in such a place at the right time, consider yourself lucky! In rare moments of “fight”, pike perch grabs literally everything that moves in the water - be it a spoon or a wobbler.
At different times of the year, of course, pike perch visits different places, so you have to catch it in different ways.
Spring fishing. Around the beginning of May, (the phenological sign is the blossoming of the apple tree), you can expect a very active post-spawning feeding of pike perch. As we remember, at this time the pike perch is in shallow bays, often near flooded bushes and reeds. An important sign of the presence of a predator will be spawning schools of bleak and other white fish. The predator bites greedily at this time, takes any artificial bait - jigs, wobblers, spinners - it’s a pity that this period does not last long.
It is interesting that even during spawning and immediately after it, when pike perch are guarding the spawned eggs, the predator actively takes artificial baits. Obviously, the instinct of defense takes effect: the pike perch grabs everything that comes close to the nest. At the same time, the predator is very indiscriminate, so it’s difficult to call such fishing sport. In addition, just at this time there is a ban on fishing from boats, so such fishing can be equated to poaching. It would be more correct to give the pike perch rest and start catching it after spawning.
Summer fishing. By mid-June, the post-spawning feast begins to wane; pike perch leaves shallow bays and takes its usual places in snags at depth. Getting a “spiny fish” in snags is a great art; it’s probably easier to do this with the help of a float bait fishing rod. The bite occurs mainly at dusk and dawn, but it has been noted that on cloudy days and during periods of prolonged cold weather, pike perch can bite all day long. This is especially true for fishing near dam spillways, in places of direct and reverse currents, where a predator waits in ambush for its victims. The pike perch stays in the “boiler” even during the day, not to mention the morning and evening hours.
Float fishing with live bait is also possible where the float can be released far downstream - from bridges, dams, some water structures, long spits and capes. This method is also convenient for fishing from a boat, because almost all the hidden pike perch places at depth differences, behind rifts, edges and in snags are accessible from a boat.
The live bait is a live, brisk fish of a chased shape - dace, bleak, gudgeon, goby, spined lance. It is important that the live bait moves actively; the pike perch does not take a dead fish. The predator's grip is decisive, one might say vicious, but after the float dives, you should wait a few seconds and only then sharply hook. However, you don’t need to do this in a snag.
Fishing from a moving boat (rafting) also has many minions. Usually they catch it “plumb,” that is, with a loaded bait without a float. The bait can be live bait or a dead fish attached to a small jig head.
With this method of fishing, the liveliness of the bait is ensured by continuous play - a series of small twitches to imitate the play of a moving fry. Each pike-perch fisherman has his own fishing technique, of course, but the basic movements are the same. With a wide and smooth movement, the load with bait rises from the bottom, then with a rather sharp movement it lowers.
The baitfish moves in a wave-like manner all the time, which cannot leave the predator indifferent. They swim over great depths (of course, such a cautious predator like pike perch is unlikely to take it at shallow depths). Particular attention should be paid to snags, sunken trees and accumulations of stones.
For this kind of fishing, you need as calm weather as possible, preferably slightly cloudy; in the wind, it is difficult to control the boat and notice bites. You need a rod that is short but strong, possibly with a hard nod, and a large inertial reel allows you to quickly change the fishing depth depending on the bottom topography; it will also help when fishing for a large specimen. A bite feels like a push, sometimes like a suddenly hanging weight.
Ideally, there are two fishermen in the boat, one sits on the oars, the other fishes, then they change places.
A variation of floating fishing is line fishing, when some kind of artificial bait is pulled behind the boat - a deep wobbler, a spinner, but pike perch responds to the lane less often.
Working with an echo sounder when fishing for pike perch
An echo sounder often shows not only the terrain, but also the fish itself. Of course, it is impossible to say with a high probability that this is exactly a pike perch, but I would like to think so. Most often, the icons of fish, by which we mean or imagine a fanged one, are located at the very bottom, as a rule, in front of (or behind) some kind of anomaly on the bottom. This could be a snag or a tubercle, or an uneven part of the edge. Not just a hypothetical search, but also visual confirmation greatly adds confidence in what you are doing.
Having found a promising point, you begin to fish for it (we’ll talk about how to do this below). If there are bites, or simply if you wish, enter it into the navigator or remember it in some other way, for example, using landmarks on the shore or leaving a buoy on the water. It is not necessary to do this if you are biting: the pike perch may not take it at the time you were fishing, but will become active here later. On one fishing trip there was a completely curious incident that added another chapter to the understanding of the fanged one.
We positioned ourselves on a riverbed slope, casting towards a shallower area. The echo sounder showed 9.5 m and no fish. Nevertheless, the place was promising purely theoretically, and a friend who had sailed here earlier caught 4 pike perch one after another. I fanned out the entire dump and only a few snags responded to the bait, which was not bad. Having decided to have a snack, we turned on the “cinema”, that is, the echo sounder. Soon we noticed fish swimming at the bottom: after one large one there was a school of smaller ones. Silence again, then again a school of fish at the very bottom, sometimes they even merged with the bottom soil - only the number “9” was visible (the depth mark where the fish was). Either jokingly or seriously, I said that these were pike perch swimming and made a cast in the opposite direction from the dump. Closer to the boat, during a pause, there was a good blow from the “zakiloshnik”. However, the pike perch disappeared due to my unpreparedness to bite. With the words “I’ll intercept the flock from the other side,” the partner made a cast - already to the edge... and from under the boat he took out a “one and a half”. The next bite was even more curious: the partner simply lowered the bait to the bottom of the boat, and when the pike perch “started”, he tugged, focused his attention and... took out another, smaller one. You may doubt it, but on that fishing trip we were sure that the echo sounder showed a school of pike perch passing below us, which we were trying to catch. There were no bites when the device screen was empty!
However, I would not completely trust the device: it is worth paying attention to interesting places even when there are no fish icons on the screen, perhaps not as long as the “fishy” areas. If, in addition to promising terrain with changes in depth, and even snags, the echo sounder shows fish at the bottom, stay here longer, experimenting with the nuances of fishing and trying to understand what the pike perch wants.
Catching pike perch with a spinning rod. Tackle and bait.
There is not much honor in catching a pike perch with a live fish, but getting it to bite on an artificial bait is a completely different matter! That is why spinning fishing for our “river tiger” is finding more and more adherents. There is a lot of sportsmanship and excitement in this fishing, because the difficulty is not only in finding the predator, but also in presenting it with the bait correctly in order to arouse interest and grip.
The spinning fishing season begins in March, as soon as the river is free of ice and schools of pike perch begin their movement to the spawning grounds. The spawning routes of pike perch are not constant, they change from year to year, and it is not easy to fish in muddy water, but still there are many who like this type of fishing. As a rule, in the spring jig baits are used - vibrotails, twisters, sometimes worms and slugs, best of all - flavored ones.
We have not yet touched upon the topic of fishing for pike perch in large reservoirs and lakes. Of course, this is fishing from a boat, and fishing at depth, because pike perch even chooses spawning routes closer to the channel edges. In March-April the weather can be very unstable, the waves on the reservoir are quite strong, so you need a good stable boat, preferably a keel boat, or two with a motor. Let’s not forget about such a necessary device as a “fish finder” - an echo sounder.
Searching for schools of pike perch in the vast expanses of an artificial sea is not an easy task, this “fish finder” will help out; with an echo sounder, fishing turns into “sighted”. It is better to use an echo sounder with a “real” fish indication mode, rather than a “symbolic” one. And not only the “fish icons” themselves interest us, it is also important for us to be able to read the picture of the bottom of the reservoir. Most often, a school of zander hunts on some pronounced bottom anomalies - on underwater elevations, hills, ridges. And the riverbed edges also cannot be ignored.
The main way to catch schooling pike perch is fishing with jig baits. Most often, small vibrating tails are used, 7-8 cm in size. The color of the vibrating tail is not very important, but its shape, game, as well as the weight of the jig head used are very important!
There have been cases when replacing a vibrating tail with an active game (for example, MANNS Predator) with a bait with an inactive game (like BASS ASSASSIN) brought success. And sometimes excellent results are brought by “passive rubber”, that is, worms and slugs that do not have their own game, and are flavored and made from “edible” rubber.
The weight of the jig head must be selected depending on the depth and speed of the current in the fishing area. The choice is considered correct if, when throwing the bait, the speed at which it falls to the bottom is 1-2 seconds. Sometimes small weights of baits bring benefits, when the bait literally “floats” above the bottom.
However, it happens when pike perch refuses light baits and takes heavy ones with a jig head weighing 20-30 g. The wiring, as a rule, is ordinary, stepped. Hinged mountings have proven themselves to be quite good, when a twister or vibrating tail is movably attached to a Cheburashka weight.
In the place where one specimen was caught or at least there were bites, it is worth dropping anchor. Pike perch is a schooling fish, and there is a high probability of hooking a couple more fish.
If the found school is at a depth accessible to wobblers (no more than 5-6 meters), you can use deep-water wobblers. Pike-perch wobblers are deep-water wobblers with a minnow geometry and a length of 7-12 cm, both sinking and floating.
It is also good when the immersion depth of the wobbler is slightly greater than the depth of the reservoir in a given place and from time to time the wobbler pokes into the bottom, leaving a cloud of turbidity, thereby imitating a fish swarming at the bottom. Wobblers used: RAPALA Tail Dancer, RAPALA Husky Jerk DR, BOMBER Long A,
Now about another way of catching pike perch, perhaps the most romantic and exciting. We are talking about night fishing for “fanged” on shallows and rifts. As is known, the fanged predator in the summer at dusk comes out to the rifts and river shallows, where the “pike fight” begins - a flock of driven hunt for fry. This hunt does not stop even after complete darkness sets in, so you can fish almost all night long.
Night hunting for pike perch is incomparable in terms of emotions. The riffle rings and gurgles, the lunar path splits across the water, “whiskers” spread out from a wobbler moving across the water surface, and suddenly the water explodes - grab!
Which wobblers are best to use for night fishing? Any wobblers with a purlined geometry are suitable; they float better, because fishing occurs at shallow depths. The color of the wobbler is not important, it is only important that the wobbler is visible to the fisherman himself, so light colors are better, fluorescent ones are good.
Nowadays they even sell light-accumulating wobblers that glow in the dark. The speed of the wobbler is slow, with small stops when the wobbler oscillates in the current. For those who are interested in specific models, you can specify RAPALA Original, RAPALA Team Esco, YO-ZURI Crystal minnow, DAIWA TD Minnow. In a word, during the evening and morning dawn exits of pike perch in shallow water, shallow-water floating models with fractional play are suitable.
In the fall, when most predatory fish have an appetite, fishing for pike perch using artificial baits in a vertical line becomes very productive. The fact is that with the first frosts, schools of “striped fish” go to depth, chasing schools of forage fish. How to take pike perch from the depths?
The predator's preference for baits moving vertically in the water column helps. This is a very unusual phenomenon in the hunting instincts of the “river tiger”; this is not observed in either perch or pike. They fish from a boat, fishing for traditional “pike-perch spots”: sharp drops in depth, the boundaries of pools and holes, heaps of stones and snags. Actually, vertical fishing with artificial baits is almost no different from the already described method of vertical fishing for fry.
They take narrow-bodied small pike perch spoons with one hook soldered into the lower part, but any other bait that plays on the rise and fall is also suitable: jigs, balancers, “helicopters” (large jigs with a tassel on the hook). For unknown reasons, the pike perch frantically grabs the outgoing up the bait.
The playing technique consists of a slow rise of the spoon, free fall of the bait and a pause. The rod is smoothly raised up, then sharply lowered down, allowing the bait to glide freely, deviating from the horizontal, and pause.
The bait is played 30-40 cm from the bottom, raised no more than 50-60 cm. Quite often, a fry, a fish head, sometimes even a pickled sprat are placed on the single hook of the spinner. The smell of the bait increases catchability; it can play a decisive role when, coming closer to the bait, the pike perch decides to grab it.
Sometimes this technique of holding a spinner works: the spinner is thrown 5-10 m, given the opportunity to glide to the bottom, then pulled towards you with short, smooth movements, without lifting it from the bottom. The pike perch falls on the spoon from above; this is its main technique when catching bottom fish.
Where to look for pike perch? At the right time in the right place
As will be seen later, the influence of the world above the water is reflected in the world below the surface of the water, and, accordingly, on the behavior of the pike perch. However, individual factors overlap or depend on each other, as a result of which they can manifest themselves multiple times.
Seasons
Until recently, there was an opinion that it was possible to lure pike perch with bait only from May until late autumn. In reality, they are ready to hook you almost all year round, only the spawning period constitutes a certain moral restriction.
But still, the best periods for fishing are spring, after spawning and somewhere in October. In the first case, they need to gain strength as quickly as possible; both periods are characterized by moderate water temperatures, at which predators are especially active.
Their behavior is much more inert at the height of summer and winter. But even at this time it is quite possible to catch them. You just need to be patient and the bait must be particularly enticing, such as extremely active and yet slowly driven spinning lures.
Time of day and weather
“Pike perch only bite in cloudy weather or in the dark.” Those who trust this meaninglessly repeated saying miss the best chances of catching and limit their fishing to dusk and night. Because, in fact, pike perch bite all day long. Besides, pike perch, apparently, doesn’t care whether it’s a full moon or something in between. It’s just that pike perch don’t seem to tolerate thunderstorms very well, but it happens that even in bad weather you can catch something. Snow and rain apparently don't bother them either.
In principle, a fisherman should only know the characteristics of a given species and look for prey in the right places depending on the weather and time of day. In addition, the time of pike perch bite depends a lot on the uniqueness of the reservoir. For example, a well-known expert on pike perch and catfish, Oliver Portrat, claims that in Spain pike perch go for bait even under the scorching sun and in shallow water.
Speaking about pike perch, it should be remembered that these predators are still afraid of clear water. So, if the sun shines through to the bottom, it is unlikely that walleye will be found in this area. However, the situation can quickly change if the weather is cloudy or raining. Then even shallow water over a sandbar or close to the shore gives the walleye the desired cover. It also appears at great depths, where pike perch can swallow bait even on a clear, sunny day.
Showers don't seem to suit the pike perch, while warm and steady rain whets the appetite.
In addition, increasing atmospheric pressure has a positive effect on the predator’s appetite. Perhaps the reason is that peaceful fish, in conditions of high oxygen content, show more activity, thereby provoking pike perch to hunt. Also, constant pressure is favorable for fishing, while falling pressure negatively affects the appetite of the fish due to the simultaneously falling oxygen content in the water. In this case, as a rule, only very active and colorful artificial baits can provide a catch.
Water
Like other fish, pike perch only becomes alert when the water temperature is around 8 °C. In early spring, pike perch appear in shallow water. Real hunger develops in him at a temperature between 12 and 18 ° C. In the summer, on the contrary, in the desire to fill its stomach, the pike perch slows down the speed by a couple of revolutions, and in the fall it starts hunting again. In general, the comfort zone for pike perch is apparently between 14 and 22 ° C, with large fish preferring cooler temperatures and small fish preferring higher temperatures. If the temperature drops below 8 °C, there is a lull. Therefore, it is advisable to use a thermometer to measure the water temperature at different depths.
Just in order to find a pike perch of the desired size within its comfortable area, the fisherman needs to be aware of the different temperature layers in the reservoir, especially in lakes.
In winter, the “warmest” and heaviest water, with a temperature of 4 ° C, lies above the bottom surface.
A thermometer is indispensable for detecting the standing depth of pike perch.
As temperatures rise, shallow water zones warm up first, and until summer, three layers with different properties form in the water (see graphs).
The warm layer at the surface, the epilimnion, can be only half a meter thick or extend to a depth of five to six meters. Anyone who has ever floundered in water knows the feeling of your torso resting in almost home-bath temperature while your feet are stirring in the comfortably cool water. The epilimnion then reaches a depth of a maximum of a meter. Only small fish swim in this oxygen-poor area.
Next begins a layer called the thermocline, or metalimnion. Most fish like it because it combines pleasant temperatures and high oxygen levels. This is where it is best to fish in the warm season, and not just for pike perch. The water in this zone gradually cools down to the next layer above the bottom. In the deep zone, the hypolimnion, the water is coldest. In addition, there is the lowest oxygen content, and, accordingly, the fisherman should not expect fish to appear there. In autumn, when the temperature drops, the boundaries of the layers expand.
Factors affecting oxygen content:
- Photosynthesis of aquatic plants.
- Movement of water.
- Water temperature.
- Atmosphere pressure.
First, the sun's rays contribute to the beginning of photosynthesis in aquatic plants, i.e., the beginning of oxygen production. At night and under ice covered with snow, this process stops.
Wind, waves and currents carry oxygen from the air into the water.
Therefore, it seems pointless to fish while standing on the shore with the wind blowing at your back; Of course, the wind is a great help when casting, but in this case it is useless. Because fish will rather look for food where there is enough oxygen. Therefore, it will be more profitable to fish where the wind blows from the water. The flow of the inflowing reservoir also brings additional oxygen.
You should also not neglect measuring the water temperature. Because the higher it is, the less gases, and therefore oxygen, the water can be saturated with. This is clearly noticeable when water is heated, when tiny gas bubbles appear on the walls of the vessel as the temperature increases.
And when atmospheric pressure drops, oxygen escapes from the water - similar to what happens when you open a bottle of soda.
Pike perch avoids clear water without a cloudy color. For example, in the highly transparent Wicker Bay, on the Rügen River, it is practically not found, while in the distant Saaler Bay, which is only forty kilometers away, but also muddy, there is plenty of it. Just the opposite situation is observed with the number of pike individuals, since this predator prefers clean water. However, in German-speaking territory, truly clean bodies of water, at least on the plains, are considered a rarity. And a little turbidity is enough for pike perch, thanks to which it is able to take root in most rivers, canals and lakes.
These needle knights like the current. A relatively strong inflow or outflow in a lake is enough to attract walleye. In rivers, they willingly look for the edge of the current or the current itself, even if there are very calm backwaters at their disposal.
Only enough fish to feed can lure walleye away from the current and into calm waters. In addition, the mouths of inflowing rivers with the corresponding movement of water are, as a rule, places of pilgrimage for pike perch.
When a tide or wind brings fresh salt water into a bay, estuary or adjacent area and the salt content of the water increases accordingly, walleye begin to bite more often. In addition to the direction of the wind, an angler can recognize this by the whitish foam near the shore, or simply by tasting the water.
Standing places
Like other types of fish, pike perch have their own preferences regarding where to stay in a body of water. And it is necessary to find these places in various types of reservoirs. It is important, firstly, to find places that are interesting specifically for pike perch, and therefore, places with a hard bottom and, if possible, with twigs and branches in the water.
In addition, fish for food play an important role, which should be sufficient within reach. And they can be found where they have the best possible living conditions at their disposal - this, first of all, is a sufficient amount of food. In early spring, this may be shallow water, where the water warms up first and, accordingly, the fry grow faster. When the water warms up a little in summer, the fry move to deeper water, where pike perch follow them. In winter, pike perch and the fish they feed on look for deep water, especially since the bottom has the highest temperature. Since water at a temperature of 4 °C is the heaviest, it sinks to the bottom.
Those who, while fishing in the bay using an echo sounder, have discovered a promising place, can be advised to immediately mark it with a marking buoy. An example of one tested model can be seen here, under the bench.
Just in case, you can try to hunt pike perch in places previously fed by peaceful fishermen. Where an amateur fished during the day, it wouldn’t hurt to cast a fishing rod in the evening.
Pike perch rarely comes alone
Since pike perch, with the exception of large specimens, often live and feed in large flocks, then after catching one such needle knight, further fishing in this place
It can justify itself with a subsequent bite. Often, after contact with an angler, fish remain in place for more than one hour before swimming further.
Finding the location of pike perch in the river
"Red or green?" - asks Carmen. “Green,” I say, “after all, it’s the end of September, and the pike perch should already be somewhere deeper.” And Carmen takes the boat straight to the left bank of the Rhine. A huge field of small dams stretches in front of us, the breakwaters that form them stretch almost to the fairway. Upon arrival there, we move on at a snail's pace. Using the echo sounder, Carmen searches the area between the breakwaters, trying to feel the irregularities of the bottom, while I try to make out signs on the surface. Blurred holes, a broken edge of the bank or a trench lying next to a stone embankment - all these places in the fall and spring are simply impenetrable, since they provide protection and cover for pike perch throughout the day.
Eat! The search paid off: a couple of small whirlpools at the edge of the stones reveal a deep hole, a fishing rod’s distance from the opposite stone. Here, it seems that the cargo ship, during its maneuvers, got too close to the shore and drilled this large hole in the stone wall with its propeller. Without hesitation, we search this place with an echo sounder, assessing the direction of the current and water pressure. The water depth here is about five meters, almost twice as deep as in other places along the entire coast. We choose 20 gram lead weights and Ki . The bait reaches the bottom without drifting and immediately begins to bite.
Scene change: three months earlier, mid-July, high summer. It's a completely different picture: the school holidays are in full swing and the shallow sandy coves along the river attract countless visitors. However, pike perch and company love warm water just as much as anyone else. Although during the day they are more happy to stand further away, in the refreshing current, allowing their gills to be saturated with oxygen. In the early morning and late evening, predators are still drawn to eat in shallow water. At the same time, knee-deep water often becomes a gathering place for the fattest robbers. Now the swimming competition for life begins for countless young and fry. But the chaos ends quickly.
If you're lucky, you yourself will be able to watch such a performance and catch a couple of hunters. A wobbler running in shallow depths, a piece of rubber on a light sinker or an unloaded spinning rod in low water will provide at least eight kilograms of impressions.
As examples show, knowledge of the reservoir at different times of the year and the associated decision on choosing a place are decisive for the outcome of fishing.
Someone who does not have sufficient knowledge can catch a lot of fish in the fall, while nothing happens in the summer.
In summer, pike perch hunt in shallow waters, where the water temperature allows standing without a suit or boots.
And the whole point is that they fish all year round on the same side of the river - on the one where there are many short, deep breakwaters, as well as washed out external turns along the fairway. Long, partially submerged breakwaters and low gravel mounds, on the other hand, are often simply ignored. While in the warmer months these are the most promising places.
Using an echo sounder, I was able to establish that when the surface temperature is above 17 ° C, the pike perch stands in the current and does not want to know anything about shady places. At temperatures below this, it prefers to be in the shade with the current. And the colder it gets, the deeper the holes and gutters should be. Also, during heavy floods, pike perch have to look for deep, protected places. After the hunt, predators digest their food, for example, behind a breakwater, where the water is much deeper and calmer. And if they get a little hungry, they make short, energy-saving forays into the food-rich whirlpool of the current.
Shallow stretches of still water can be easily recognized by elongated sand and gravel banks that can be waded across without fear. The sand-filled inside corners reveal themselves as small waves on the usually stationary surface. Deep places can be found with an echo sounder, or you need to study the river bed, preferably in low water, starting from the shore. Armed with paper, pencil and camera, I try to figure out the exact course of the river with all the bends, inlets and other way markers. Then I mark those places that are deeper and, even at a low water level, can contain enough depth. Thus, I want to detect deep, washed out areas that, at normal water levels, are still about five or even eight meters deep.
This is an important property for winter fishing. These holes appeared either over the years due to constant floods, or artificially - thanks to ship propellers, excavators or anchors. By the way, such bays can appear after each new natural disaster associated with spring floods. In that case, I'll have to update my water maps. Those who do not want to spend effort on drawing up their own map can navigate by the boards, tanks and buoys intended for the movement of ships. They can indicate areas of shallow water, fairways or even obstacles.
In addition to the fact that the direction and speed of the wind, as well as the associated atmospheric pressure, definitely influence the desire of fish to eat, the direction of the wind can also affect the structure of the river.
For example, I know sections on small rivers where, thanks to the westerly wind, over time a natural, nutrient-rich part with eroded banks has formed. In the same way, wind and waves can change your river so that one side of the bank produces and receives more fish than the other.
River
Although pike perch live in lakes, they still love currents. Therefore, they often willingly stand at least at the edge of the current in the river, where slow and fast water meet. However, if in shallow water, for example, in the shadow of the current behind the breakwaters, there are enough food fish swimming, then casting in this place can bring much greater results. The same applies to rip currents or slopes where unwashed deposits of sand or gravel form shallow areas. During the day, during the hot season, pike perch settles in deep gutters washed with cool water or in ship fairways. Between these extremes, in “medium temperatures,” sections with large rocks, ship docks, and other visible structures promise success.
In winter, predators again stand in deep gutters or in areas of warm water runoff from power plants.
Channel
The monotony of the channel does not seem to disturb the pike perch in any way, as can be seen, as a rule, from the often large number of individuals. For this reason, they also feel good above the flat bottom of natural reservoirs. Thus, it is precisely in such conditions that pike perch form a welcome addition to the fish stock with which pike no longer finds a common language. Only catfish equally willingly live in channels poor in internal structures. Here predators are attracted primarily to fish for food.
Proper fishing in the canal
For walleye fishing in a canal, the best options are dead fish bait or artificial soft plastic bait, as well as a vertical float with a ball inside. Bait is used when the fish is in a limited area and you don’t have to search for it for a long time. Even if there were no ships for many days, but there was at least a slight operation of the locks and there was a weak current, it is recommended to use bait in the form of fish in clear water. It is attached to the head on one hook, and the length is adjusted so that the bait is at a palm's distance from the bottom.
If the water is moving and shipping is in full swing, then you will first have to find fish in choppy, muddy water. Here, compared to a float, it is much faster and more efficient; rubber fish, “Blatt-pilker”, or a sinking vertical float, besides, natural bait with strong suction does not allow accurate behavior. As when fishing from a boat (see the chapter “Artificial bait”), it is necessary to move the bait along the sheet piling wall in small jerks. The walls amplify the sound and shock waves created primarily by clanking floats, which often leads to fierce, aggressive fish bites.
When fishing in a canal, it is easy to be deceived by the changing currents. You need to choose one direction of the current and consistently fish in that direction. The most important thing is to endure to the end. Then success is guaranteed.
Thus, both species in early spring prefer places near rough stone embankments, near the shores and in warm water near mooring bollards and other noticeable areas. The sunny side of the canal also belongs to them, because there is more greenery on the walls. Thus, small fish find more food here, and therefore predators are nearby. Additionally, concrete and sheet piling walls are good locations. Inconspicuous intersections and bays (ship turning places) also add variety to the game and give hope for a good pike perch.
In addition, by casting a fishing rod in the edge of the current on the edge of the port pool and locks in warm weather, you can lure other pike perch onto the hook. In real heat, you need to try closer to the fairway, where fast water brings more oxygen.
Winter brings the best catches in deep water and near power plant drains. A little advice : before you go to the power plant, it is better to find out when the cooling water will start. Because only then does this place acquire advantages in relation to other areas. In general, pike perch are more at ease in the place where something is wrong compared to the rest of the channel.
Lake
The simplest and at the same time the most complex version of a lake is an artificial reservoir with the same bottom depth. There, pike perch can stand and hunt with equal success almost anywhere in the lake. This is where only a proven search for the fish that pike perch feed on will help, or, in extreme cases, stupid fishing with wiring to demolish the entire lake, or an echo sounder from a boat.
An excellent situation opens up if there is a flow or inflow. Pike perch loves currents that create crowded places. This principle remains virtually unchanged in structure-rich lakes. But despite this, there are many other interesting places on offer. In spring and early summer there are shallow waters where there are plenty of small fish to feed on. Later, as the temperature rises, pike perch hunts closer to the depths and only after dark returns to search for food in shallow water.
During the daytime, the depth at which fishing will be successful depends on the transparency of the water, since pike perch is wary of clear water.
Thus, it makes practically no sense to fish in deep water with almost one and a half meters of transparency. In this case, the bait should be at a depth of 2.5 meters. The greater the visibility, the greater the length you need to choose. Moreover, you can quite count on ten or more meters.
This artificial reservoir is already several years old, which is noticeable from the bank overgrown with reeds and greenery.
Artificial lakes have proven to be very good in terms of pike perch catches, because a hard bottom is a significant prerequisite for the development of needle knights.
In addition, there are usually notable structures, such as a steep bank or sharp changes in bottom depth. If there are already tree plantations on the shore of the old lake, then the pike perch will have fallen twigs and branches at their disposal for spawning.
Brackish water
In bays and calmly flowing river mouths, as well as in adjacent areas, standing sites are most comparable to a lake. In addition, fairways are added to them, which provide special structures with their ruts and deep standing areas that are suitable for fishing. The easiest way to detect such places is with an echo sounder. The greatest variety is offered by adjacent areas, such as those near the Swedish coast. Between numerous islands, at different depths and under the influence of salt water, pike perch find a generously laid table, at which, as in the bay, pike feast.
Outstanding signs
While other predators, say, pike and perch, often and noticeably hunt on the surface, pike perch, on the contrary, prefers to feed near the bottom.
Thus, fishermen have to navigate by other signs, and small fish will be a good help here. Thus, when a loon dives, it reveals the location of small fish, which means that predators are not far away. The same can be said about cormorants, although they can hunt for larger prey.
Winter fishing for pike perch
Oddly enough, such a finicky fish as pike perch remains active in winter and therefore can be caught from under the ice. “Fanged” may well become a trophy in that icy season, when the warlord frost reigns on reservoirs covered with ice.
Winter fishing for pike perch is a topic for another discussion. There are devoted adherents of this fishing who go to snow-covered reservoirs in whole teams, as if on a hunt. In the vast expanses of reservoirs, fishing for winter pike perch is always popular; you have to explore a lot of snow-covered expanses before you discover a wandering flock of pike perch. It’s a good idea to have an echo sounder or some other “underwater vision” devices (nowadays even video cameras are used!)
Flocks of fanged predators constantly move around the reservoir in winter, but if a flock is discovered, then you have to use all your skill to tempt the “fanged” one to bite. Fishing can be done using balance beams or vertical pike-perch spoons. These are classic ways to catch pike perch in winter.
Balancers made a real revolution in winter fishing for spiny predators, and they still remain very effective. The RAPALA and NILS MASTER balancers are good; the main attraction of the balancer's game is its deviation from the vertical and its slow turn.
However, many anglers note that the balancer is a bait for active fish; their use gives excellent results in the first ice and at the end of freeze-up. But when the pike perch is passive, and this state persists for most of the winter season, vertical spinners give the best results.
Pike-perch spoons are medium-sized 6-7 cm narrow spoons of silver or golden color, sometimes with colored holographic stickers. Oddly enough, an excellent winter lure for pike perch is a small castmaster (ACME Kastmaster).
The game of a vertical spinner consists of a slow rise and long pauses (up to 30 seconds) with one or two weak twitches. A spinner playing while falling creates the illusion of a potential victim. By placing a whole fry or just the head of a fry on the hook of a vertical spoon, you can increase the number of bites. How can this be explained?
The pike perch approaches, attracted from afar by the game and the shine of the spoon, but when it finds itself next to the bait and smells the living smell, this fact turns out to be decisive. At the same time, the predator often takes a pause when the spoon makes small vibrations, like trembling, calming down after rising. This is why a long pause between the rise and fall phases is necessary. To provoke the predator, additional movement of the bait during a pause helps - a slight tremor of the rod tip.
After swinging the spoon with the fry for 10-20 seconds, pause for 20 seconds to 1 minute. This is followed by a rise of 30 cm higher, another swing and a pause. You can’t say anything, of course, fishing is boring, not everyone will like such monotony, but it is precisely such a leisurely game that brings success in the wilderness. More active play with a spinner can simply scare away winter pike perch, but lazy play appeals to the sluggish predator.
In winter, you can catch pike perch on winter baits using live bait, letting it go about 0.5 m from the bottom. Pike perch prefers live bait, does not take dead fish, and besides, the hole must be covered with snow, which is a suspicious pike perch I didn't suspect anything. It should be taken into account that pike perch biting on a zherlitsa does not always result in capture; often the pike perch, feeling the resistance of the fishing line, leaves the victim without swallowing it. Therefore, catching pike perch with passive gear is less common than winter trolling.
text and photo by Yuri Zheltyshev
"Artificial" driftwood
Often, when examining the edges, fishermen do not find natural snags on them. Such “bald” mounds or spots are especially common in natural bodies of water, in particular lakes. The pike perch comes to them, but not regularly, and there are periods when it does not appear there for several weeks: it drives the little things away from this place and leaves for a long time. Naturally, over time, spinning anglers stop paying attention to such “bald spots”, preferring to fish in places that are more stable in terms of bite. In order to keep fish here, some experienced fishermen flood one or several snags on a “bald” edge, write down or remember the corresponding alignments, and then for a long time, sometimes several years, until the snag is washed away or carried away by the tip, they successfully fish in This place has good fish. A fisherman who drowns a snag becomes, as it were, a private owner of this place and jealously ensures that he does not accidentally “expose” it; he will never stand there if anyone is nearby.
But there is nothing secret that would not become obvious. Over time, such a place nevertheless becomes, as they say, public. And the “owner” of the snag can only console himself with the fact that fishermen most often call it by his name. So, at the Istra Reservoir near Moscow, the question is still answered: “Where did you get this pike perch? “You can hear the answer: “I removed the driftwood from Zenka.” The fishermen who knew the spinning player Zenkin himself may no longer be found, but his snag continues to work.
Flooded driftwood
Spinning for zander
Spinning fishing is carried out both on the shore and from a boat. The length of the rod should be selected taking into account the location and fishing characteristics. For long casts, the spinning rod must have a rigid base. The spinning test varies depending on the weight of the baits used.
The optimal size of the rod is 270 centimeters, and for fishing from a boat a spinning rod with a size of 210 centimeters or more is suitable. Reel requirements: sensitive clutch, Shimano size 2500-3000. A strong cord with a weaving thickness of 0.12 to 0.2 mm will serve as a working line.
Recommended spinning rod for fishing is Major Craft Rizer 832MH. The rod has the necessary sensitivity and rigidity for hooking. The material from which the rod is made is carbon fiber. The length of the spinning rod is 2.52 meters, the test weight is from 8 to 35 grams. Read also: Rating of spinning rods for jigging
Is it possible to catch pike perch and if so, how?
In most regions it is prohibited to catch pike perch. In 2021, it was possible to fish only in the Veselovsky and Proletarsky reservoirs on the Manych River, and only during the period when there is no spawning. The norm applies to the entire territory of the Don Forbidden Space - 2 fish per day and in total they should weigh no more than 5 kg. Next we will talk about catching pike perch while observing the above laws.
Pike perch is a keen and secretive predator, especially if it is a large fish. You can’t catch such fish with a big bright spoon. It is better to catch it with live bait or with a tackle with small white fish.
Pike perch, although one of the early fish, can be caught during the day. At night and at dawn, he approaches the shore to hunt in the shallows. Here the pike perch swallows all kinds of small fish. During the day, the predator goes into the pits, from where it can make short-term forays for prey.
You need to catch pike perch at a certain time:
- At dawn - when the sun has not yet risen. As soon as the sun rises, fishing can be stopped.
- After sunset. Fishing is possible until 12 midnight.
During the bite, the pike perch comes close to the shore and can even jump out of the water.
Pike perch, unlike pike, does not sit in ambush all the time; it moves a lot. They catch him from the bottom. The predator comes to the surface only to hunt for small things. The optimal time for fishing is at the end of winter and after the cessation of spawning. But now you can’t catch pike perch everywhere; there is an official ban on catching pike perch in most regions.
Equipment
To catch pike perch, natural and artificial live baits, wobblers, spinners, and jig heads are used.
To deceive a predator, fishermen often tie several hooks (3-5 pieces) above the spoon, on leashes 30 cm long. Small white twisters are attached to them, you can also attach tassels made of feathers or threads. The pike perch, having decided that the spoon is chasing the hooks, gets ahead of the “competitor” by attacking the hooks.
Fishing by season
Pike perch feeds all year round, so there is a chance to catch it in any season. The main thing is to approach fishing correctly, taking into account the biting characteristics characteristic of each time of year. The method of catching pike perch depending on the time of year is in Table 1.
Table 1
| Season | Fishing method |
| Winter | It bites well on a baitfish with live bait. You can also catch pike perch from the ice - for this you use a balancer made in the shape of a small fish. If you manage the tackle correctly, it realistically imitates the movement of the fry. Pike perch respond best to yellow gold and red baits. In winter, the predator is inactive; it bites well on large jigs with sprat attached. The pike perch is not afraid of noise - you can safely drill holes in the ice. |
| Spring (before spawning) | At this time, it is best to catch pike perch on a spinning rod with equipment in the form of a spinner spoon. You can also use polyurethane fish. Consistently effective for fishing and shore jig. In spring, the predator actively hunts for fry, emerging from its deep holes. When the feeding starts, it’s easy to catch pike perch, the main thing is to find it. |
| Summer (after spawning) | Fish must be looked for in all layers of the reservoir. Wobblers are most suitable for this purpose. The optimal length is 3-6 cm. It is necessary to take wobblers that are characterized by buoyancy and depth. In summer, the predator looks for places with differences in depth. Often pike perch stand near breakwaters or bridge supports, under dams and rapids. In summer it is best to catch it at dawn. |
| Autumn | At this time, pike perch chooses the quietest and deepest areas. The bottom is rocky-pebble or sandy. It avoids silt in the fall. In the fall, pike perch go best on bottom fishing rods and dead fish. The optimal biting time is September to mid-October. |
At any time of the year, as long as the reservoir is not frozen, you can catch pike perch on a donka - this tackle consists of a short rod (up to 3 m), a spinning reel and a sinker up to 60 g. They take a fishing line with a thickness of 0.25 mm - up to 100 m. In addition to live bait , you can attach fat leeches, a bunch of worms, a piece of fish or a frog.
Fishing
The pike perch's grip is not particularly sharp, but is similar to that of a pike. To catch a predator, you need to hook it well - sharply and energetically. Most often, the notching occurs behind the jaw or into the mouth, but swallowing occurs rarely.
The pike perch does not resist for long. Immediately after hooking, a violent reaction occurs - the fish spins in place, jerks strongly and shakes its head, trying to free itself. When you try to move the pike perch, it rests on the bottom. When brought to the shore, the fish begins to fight - but not for long. It is enough to pull out the body halfway for the caught predator to calm down.
When removing pike perch from the hook, you need to be careful - you can easily get hurt on the sharp gill covers and fin rays.
The pike perch brought ashore practically does not break. If you leave him on the shore, he falls asleep in a matter of minutes.
How is bersh different from pike perch?
Bersch is very similar to the common pike perch. Coloring, transverse stripes, structure - everything is almost the same. You can distinguish bersh from pike perch by the following characteristics:
- In bersh, the transverse stripes are darker and have more regular outlines.
- He has no fangs, all his teeth are straight.
- The head is wider and shorter.
- The scales are larger.
Catching bersh is punishable by law, since this type of fish is listed in the Red Book of Russia.