Karelian whitefish fishing
Among the numerous fish that belong to the salmon family that live in the waters of Karelia, whitefish takes pride of place. If you do not have your own home in Karelia, then today you can easily rent a house on the shore of a lake in this region or near another body of water you like. Karelia is an incredibly beautiful Russian corner of Russia, a region rich in natural resources.
Whitefish is a rather cunning fish, so the angler must always be on alert
Whitefish can grow to a considerable weight - up to five kilograms. And at the age of three years they begin to spawn for the first time. Whitefish prefers to stay in the depths and can only occasionally be seen in shallow water. It feeds on a wide variety of insects and crustaceans.
Spring-summer whitefish fishing begins as soon as the snow melts, and then when the water in the reservoir becomes clear and clean. Most often, whitefish are caught on a light fiberglass rod, which can be used to make long casts, perform maneuvers, and also catch large-sized fish. The thickness of the main line is 0.22–0.25 mm, the diameter of the leads is 0.15–0.17 mm. The float is most often the most common: made of polystyrene foam, oblong in shape with an elongated antenna and a short keel, but quite weighted. The tackle is equipped with several sinkers, the heaviest sinker is attached closer to the float, and the lightest one is attached to the hook. The coil needs an inertial one. The most important part of the equipment is a small jig with a cambric attached to the hook.
Since the beginning of summer in Karelia is marked by the massive appearance of mosquitoes, which gather in clouds over the reservoir, and at the same time, often end up in this water, and this is all the whitefish needs.
From mid-July with the onset of summer heat and until September, the time comes that is not acceptable for fishing for whitefish, since nature itself provides the fish with natural food, so any bait and tricks of the fisherman are unlikely to be of interest to the fattened fish.
In mid-autumn, the whitefish goes to spawn, so it begins to actively eat and, as a result, the bite resumes. This is the most successful time for catching whitefish in Karelia. In the fall, whitefish can be caught even from the shore, the only thing is that only small fish can be caught from the shore, and for a large trophy it is best to go to the deeper parts of the reservoir, near the fairway.
Whitefish bites are very sharp. As if taking off, the whitefish swims diagonally towards the bait, lying on its side, and having grabbed the prey, it swims into the depths, while the float dives sharply. But there are exceptions, since whitefish is a rather tricky fish. Having grabbed the bait, he may freeze in place; in this situation, the float will slowly sink, and the fisherman will get the impression that the tackle has caught on an underwater obstacle. Once hooked, the whitefish begins to actively resist. Therefore, it is best to catch it from a boat with a partner to help each other while fishing (it’s also worth catching salmon). Often the whitefish goes under the boat, and when they pull it closer to the shore, it generally turns over on its back and swims into the depths. At this point the hook will often fly out of the fish's mouth.
comments powered by HyperComments
Fishing on Lake Segozero
Almost in the center of Karelia, northwest of Seliger, lies Segozero, whose name is given from the Karelian word meaning “bright lake”. Before the creation of dams on the Segezha River, it occupied 753 km 2 , and after the dam, already in the status of a reservoir, it extended to 815 km 2 . The reservoir is distinguished by its great depths, which average 29 meters, and in some places reach 103. The deepest is the northern part of Segozero with an average water thickness of 40 to 50 meters. In the south and center the water thickness extends to 20-30 meters, and in the southwest it is less than ten.
The level of Segozero lies 119.9 meters above sea level. There are almost 70 islands in its waters. The length of Segozero is slightly less than 50 kilometers with a maximum width of 35.
The lake is fed by rain, snow, waters of Luzhma, Sonna (Voloma), Sanda, Pyulva, Pudashiega and small tributaries, and Segezha carries them to Vygozero, from where they flow along the Vyg River into the White Sea. The reservoir freezes in December and opens in May. During the warmest periods, it does not warm up above 16 degrees.
The rugged coastline of Segozero forms many spits, capes and bays. The pictures of the coast are constantly changing: ledges of rocks are replaced by swampy areas, sandbanks, and a little further from the coast dense coniferous forests dominate. Access to some of the banks is difficult due to their swampiness.
Bottom soils are just as diverse: gray-green and brown silt, ore-bearing sediments, sandy-silty and sandy soils replace each other. The water has a yellowish tint, but it is transparent for more than 4 meters.
Segozero still attracts thousands of fishermen. They used to say about it that the fish here bite on a bare hook. Now it has become a little less, but there is still enough for both commercial and recreational fishing. The water in the lake is well saturated with oxygen and full of biofauna, which serves as food for fish. There is a Sevan trout breeding farm there, and in the 50s it was stocked with caviar from Onega pike perch and Ladoga smelt.
Now Segozero is home to seventeen species of fish: pall, salmon, whitefish, vendace, pike, grayling, ide, roach, bleak, minnow, burbot, bream, nine-spined stickleback, ruffe, perch, sculpin and slingshot goby.
Fishing on the lake is allowed all year round. In the summer, from May to October, they fish from a boat or the shore using a spinning rod, a fishing rod, using girders, mugs and trolling. The rest of the time they use a balancer, a jig or a spinner, and put jigs on burbot and pike. Particularly clear water in summer and early autumn makes this period the most convenient for spearfishing.
Most of the many species of fish prefer to spend time in Panda Bay, Sondal Bay, the Kalichie and Akkonshaari islands, since in these areas the majority of the fish go to spawn in the Voloma, Sona and Seletskaya rivers. Segozer fish spawn mainly in October.
The most common species in the reservoir are: whitefish (seven varieties), roach, vendace and ruff. Their abundance explains the huge population of predators. There are only two species of perch in the lake: coastal, small, and large, large. The small one sticks to areas with thickets of aquatic vegetation closer to the shore, and the large one sticks to open areas of water, which it finds in the warm season in Bolshaya Luda or in the area of Akkonshaari Island.
Pike are found everywhere in Segozero, but most of them are in the area of the Kalich Islands or Sondal Bay. There are individuals up to 90 centimeters long and weighing about four kilograms.
Palia also lives in Segozero, of two types: Yamnaya and Ludnaya. It feeds on ruff or vendace. In summer it prefers open areas or stays under the coastal slopes of Padan Bay and Sondal Bay, and in winter - on the stretch from Akkonshaari Island to Panda Bay, through which it goes into the Seletskaya River in the spring.
Large lake-river burbot, up to 3 kilograms, is caught at the mouth of the Sonya, and smaller lake burbot - near the Kalich Islands or in the Sondal Bay.
Among the lures for pike, perch and salmon, heavy, up to 60 grams, spinners of natural colors have proven themselves well. Wobblers of the same colors are also selected, the length of which is slightly more than ten centimeters and imitates vendace. For baits intended for playing, it is better to attach the sinker a few meters from it. When fishing from a boat moving at a normal speed of about 4 kilometers per hour, you need to let the line out 50 meters, carrying the bait as far as possible. Fishing with live bait, pickerel, donka and feeder can also give good results.
Fishermen can use the services of numerous recreation centers, owners of private houses, or settle in a tent camp, choosing a non-swampy area of the coast; fortunately, there is enough dead wood and brushwood in the coastal forests. In addition to fishing in summer and autumn, you can quickly pick up mushrooms or berries, or listen to stories about the capricious nature of the reservoir.
SIG in the lakes of Karelia. Whitefish fishing methods
Among the vast family of salmon fish inhabiting the waters of Karelia, whitefish occupies a worthy place. Adult whitefish can reach a considerable weight, up to several kilograms. At the age of three, whitefish spawn for the first time, in the fall or early winter.
Among the vast family of salmon fish inhabiting the waters of Karelia, whitefish occupies a worthy place.
Adult whitefish can reach a considerable weight, up to several kilograms. At the age of three, whitefish spawn for the first time, in the fall or early winter.
Usually it stays at depth and only occasionally appears in shallower places. Its food consists of various crustaceans and insects.
Spring-summer fishing for whitefish begins immediately after the snow melts, and then when the water becomes clean and transparent. Amateur fishermen usually catch whitefish with a lightweight fiberglass rod, which allows them to make long casts, maneuver the tackle, and catch large fish. The diameter of the main line is 0.22-0.25 mm, the leads - 0.15-0.17 mm. The float is usually simple: an elongated foam plastic float with a long antenna and a small keel, but weighted. Several sinkers are used, with the heavy sinker placed closer to the float, and the smallest one near the hook. Reels use inertial ones. An important part of the equipment is a small jig with a cambric attached to the hook.
Since the beginning of summer is marked by a massive flight of mosquitoes, which gather in clouds over the water, while often falling into this water, the whitefish does not sleep at this time.
You, in turn, have an excellent opportunity to catch whitefish. From mid-July with the onset of heat and almost until September, biting is not acceptable due to the fact that nature gives the whitefish a lot of natural food in the form of insects, and your bait is unlikely to interest it.
As mentioned above, whitefish begin to spawn in mid-autumn, so they begin to feed heavily before spawning, and during this period of time the bite resumes. At the same time, you can even catch whitefish from the shore, albeit small ones, but large ones - near the fairway, the deeper part of the river.
The whitefish bite is very sharp. Taking off diagonally towards the floating bait, it lies on its side, and having grabbed the prey, it goes into the depths, while the float, as a rule, dives sharply. But there is an exception, because whitefish, judging by its habits, is a cunning fish. Having taken the bait, he may not move, in this case the float begins to slowly sink, and you get the impression that a hook has occurred. After hooking, the whitefish begins to stubbornly resist. Therefore, from a boat, as in the case of salmon, it is more convenient to fish together, helping each other when fishing. Often this cunning one dives under the boat, and when it is brought to the shore, he lies on his back and goes into the depths. As he does so, the hook flies out of his mouth.
Whitefish (fish of Karelian reservoirs)
Among the vast family of salmon fish inhabiting the waters of Karelia, whitefish occupies a worthy place. The genus of whitefish in Karelian lakes and rivers has over forty varieties and transitional forms. There is no such variety of whitefish in any region of the country.
There are adult whitefish weighing only a few tens of grams, while other species reach a significant weight, 5-6 kg. At the age of three, whitefish spawn for the first time in the fall or early winter.
Whitefish are caught using sporting methods only at certain times. There are times when it is simply impossible for him to choose a suitable bait and he does not pay any attention to the fisherman’s lures.
In March-April, zooplankton is still poorly developed, and whitefish begin to hunt for vendace, smelt, smelt or their own young. At this time, it can be caught from the ice using narrow winter lures. I especially recommend the tried-and-tested whitefish spinner with two soldered hooks. It is made of silver or gold metal, filled with pure tin, and is equipped with a small carabiner. It is useful to tint the hook and head of the spoon with blue enamel paint. The line should be 0.25 mm in diameter, inconspicuous, blue, 25 m long. Considering that the whitefish bite can be found at any depth, for the fastest fishing of the entire water column, it is advisable to use a winter fishing rod with a reel rig, and the diameter of the line winding on the reel should be be at least 60 mm.
To locate the whitefish, the fisherman is forced to examine different parts of the lake, but most often this fish stays at depth. Having found the fishing depth required for a given day, you can move around the reservoir without changing it*. Sometimes whitefish rise to the ice, hunting for a school of vendace.
...The pine trees stood motionless. They stand in a daze among the granite rocks and seem to be listening to something. Perhaps they hear the first steps of spring. Arriving at dawn on the ice of Pertozero, we began to cut holes where, according to our assumptions, the whitefish should have appeared during the day - along the underwater stone ridges. The ice was strong and very thick. After the fifth hole, I sat down to rest and looked at my friend. The air was so still that even the smoke from the cigarette did not dissipate. The cloudless sky, the blue of the ice, not yet covered with white melted spots, were so beautiful that nothing else could be seen or felt.
We lay down on the ice and began to watch through the holes the play of winter spinners, made the day before especially for catching whitefish. The water could be seen to a depth of 3-4 m, and then there was darkness. The spoon, sparkling as it rose, went to the side and fell down, rolling from side to side. There were no fish in sight. A quarter of an hour passed, and suddenly shadows darted from three sides of the spoon. With amazing dexterity and speed, the whitefish flashed around the spoon. They quickly described figure eights, in the center of which there was a spoon. There was still no bite.
I pulled the spoon higher - and at the same moment there was a soft push. The whitefish, with a spoon in its mouth, darted to the side. On the ice, the whitefish turned from a silver beauty into a gray, monochromatic fish, retaining only its slender outline.
Having lowered the spoon into the hole, I again began to observe the underwater world. Flashing like lightning, the whitefish grabbed the spoon again. Then two more fish came in a row. The tension of the long wait for a bite subsided, and the joy of luck filled my heart.
Suddenly, under the hole, I saw something completely unexpected: under the ice, a countless mass of vendace was moving in one direction. It ran like an endless ribbon, the width of which was such that my friend, lying on the ice 20 m from me, saw the same thing under his hole. At times the flock quickly disintegrated, but not randomly, but maintaining an amazingly clear formation and continuous movement. She seemed to be compressed into tight, dense ribbons. The shadows of whitefish flickered in the gaps that formed. Whitefish accompanied the flock, being under it. So, while cruising around the lake in search of a school of vendace, the whitefish periodically appeared near the spoon and quickly disappeared.
On some lakes, the spring feeding of whitefish continues even after the ice breaks up. At this time, in the rivers, he begins to take on the worm when fishing with summer gear - on the bottom and in the retrieve. Later, during the period when insects emerge, you can catch whitefish by fly fishing, and the bite on live insects is better than on artificial ones. Whitefish catch more often and more accurately if the thrown insect stays on the surface of the water.
Whitefish fishing in Karelia
Whitefish is found in many reservoirs of the Republic of Karelia. This is a valuable and tasty fish that many people want to catch. You can read in detail about its lifestyle and habits in this section, but here we will talk about the Karelian whitefish, which has its own characteristics.
Whitefish in Karelia occurs in different forms (subspecies), which depend on its habitat. Often in one body of water there can be several forms of whitefish, as for example in Lake Onega. There is fundamentally no difference between them from a fishing point of view, and it is often very difficult to distinguish different subspecies from each other. However, the main types of whitefish are:
And these forms can already be classified into many subspecies.
Whitefish fishing in Karelia
Whitefish can be caught using all traditional gear. Most often it is caught with a float rod, but large whitefish in Karelia can be caught with a spinning rod, but you just need to use the smallest spoons.
This fish is caught in summer and early autumn; as is known, it usually spawns in October, but this period can last until winter. In winter, you should look for whitefish in deep holes, where they live in schools. Karelian fishermen, who know the topography of reservoirs well, rarely leave without a good catch.
In spring, you can start catching whitefish in Karelia after the water becomes clear. In South Karelia this is already early to mid-May, and in the northern regions the water can be cloudy until mid-June. This especially applies to rivers.
Where to catch whitefish in Karelia?
This fish is found in almost any more or less large lake. Here is just a small list: Sandalwood, Gimolskoye, Nyuk, Syamozero, Yanisyarvi, Pulozero, Vodlozero, Tiksheozero, Putkozero, Royk-Navolokskoye, Shuezero, Segozero, Muezero, Kuchozero, Yushkozero and many others, descriptions of which you can find on our website. Whitefish can also be found in many rivers of the Republic of Karelia.
Lake Onega is traditionally of the greatest interest; this fish can also be caught well in Ladoga.
Whitefish in Russian lakes. Fishing and methods of catching whitefish
Whitefish is a beautiful commercial fish of medium and large size , weighing from 250-450 g to 6 kg (depending on the species, of which there are more than 60). Belonging to the salmon family, it is a popular prey item. Externally it is distinguished by a small head with a low-set mouth. In males, the body is elongated, mirror-silver in color, with small scales, in females it is bar-shaped, slightly yellowish in color, and the scales are larger.
Whitefish are common in the northern regions of Europe, America, and Asia. In Russia they are found in lakes belonging to the Baltic Sea, in Karelia, the Murmansk region, along the upper reaches of the Volga, in the basins of the White and Barents Seas, in the rivers of Siberia.
Whitefish feels best in clean, running water at low temperatures. Ecological distress in many traditional habitats has damaged the numbers and biological health of the population.
Fishing for whitefish is a fascinating, gambling activity due to the complexity of its habits, good flair, speed and maneuverability of movements. Large individuals prefer deep water, so for fishing it is preferable to use a rod that allows long casting. The fishing line must be very strong (the diameter of the main part is 0.25 mm, the leader part is 0.15). The optimal float design is foam, elongated, with a high load capacity. The smallest sinker should be at a matchbox distance from the hook, the largest should be close to the float, about 25 cm from the light weight weight. It is possible to catch whitefish using a matte black jig, camouflaged with a thread brush.
The behavior of the whitefish during the bite is very interesting: it quickly, diagonally rushes towards the bait, after which, together with the prey, it just as quickly goes into the depths. At this moment the float suddenly dives, and the fisherman’s task is to have time to make a hook. Sig is a freedom-loving and intelligent creature, he always resists strongly and often breaks down at the last moment; it is not easy to cope with him alone.
Fishing for whitefish is excellent in the first 6 weeks of summer, when schools of whitefish rise to the upper layers to feast on mosquitoes that fall into the water in countless quantities. With carefully selected bait in places where mosquitoes accumulate above the water surface, you can count on a good catch.
The worst period for fishing for whitefish is the entire second half of summer, until September, due to the large amount of natural underwater food. The situation improves with the first cold snap, which signals a pre-spawning improvement in appetite and a forced search for additional food. In the autumn months, small-sized individuals bite better near the shore, while larger ones bite better on the river fairway. Whitefish overwinter in large schools in wintering pits, actively displacing other fish from there.
The subtleties of catching whitefish in summer and winter
Whitefish is the most interesting and very valuable fish of the northern reservoirs of our country.
This fish is caught in the European part of Russia, mainly on the Kola Peninsula, the Northern Urals and even in the Leningrad and Vologda regions. In more southern reservoirs, this fish practically does not live or is extremely rare. The value of this fish lies in its very tasty and healthy meat, valued by gourmets. In addition, whitefish meat is considered dietary and very healthy. A large number of different dishes can be prepared from this fish. Today, whitefish have a valuable commercial value, and fishing for whitefish is not allowed everywhere where it lives. In some reservoirs, where there used to be a lot of this fish, its population has decreased significantly and a fishing ban is being introduced in order to restore the number of fish.
Whitefish Lake: Fishing
But the most popular recreation in Shiga remains fishing. The lake provides a stable bite at any time of the year. The reservoir contains bream, pike, ide, bream, and roach. Previously, whitefish could often be found, but due to poaching it is no longer found. Because of the same problem, large specimens of fish disappeared completely, although local fishermen caught a 7-kilogram ide several years ago.
Convenient approaches to the lake are located from the southern and western shores. Near the village of Kurkovo there is the longest area without reeds. You can also fish from the lake island. Winter fishing takes place mainly from the shore. Residents of nearby villages have the opportunity to rent a boat and also stay overnight.
Forum
There are up to 6 breeds of whitefish in Pyaozero. The lake form of whitefish, known among the local population as rantasijka, or coastal whitefish, is of greatest importance both in terms of quantity in catches and in terms of mass distribution.
The habitats of the whitefish vary depending on the seasons of the year, feeding and spawning migrations. But still, this whitefish, to a greater extent than other whitefish of the lake, is associated with the coastal shallow part of the lake. It appears on the shores in the shallows after the lake opens up. Noticeable catches have been observed since the second half of June, when this whitefish begins to intensively fatten in the coastal zone. By mid-summer, when the water in shallow areas warms up strongly, the redfish moves to deeper places, where it remains until the autumn cooling of the water, approximately until the second half of September. In autumn, the habitats of mature and immature whitefish are usually separated. Mature whitefish are concentrated in pools and on rocky placers near islands and in individual bays, while juveniles and immature whitefish are usually found in sandy shallow water, less often on spawning grounds, where they feed on whitefish and vendace eggs.
Rantasiya spawns on shallows with hard soils (sand mixed with pebbles and individual stones). The depth of the spawning grounds does not exceed 3-4 m. Spawning time is the second half of October, water temperature is 4-5.5°. Spawning is quite extended and sometimes lasts until November 10-15; Mass spawning occurs at the end of October. The largest spawning concentrations of this whitefish are observed off the western and northern shores of the island. Maloshuari, at Fr. Kurgonshuari, in the bays of Paiguba and Chulkolahti, at the southern end of the island. Lupchang and Fr. Talvishuari. The fertility of whitefish weighing 1 kg is approximately 20 thousand eggs. Sexual maturity occurs at 4-5 years, at 175-200 g of weight. The coastal whitefish is a relatively slow-growing form. Whitefish are caught during the entire navigation period. Until September it is caught with a seine, but later mainly with nets.
The second form of Pyaozer lake whitefish is represented by deep-sea whitefish, locally called Lattaneni. It has been recorded in commercial quantities at Cape Kalliniemi, between the islands of Vartisuari and Lupchanga, off the southern coast of Maloshuari and in Umbikanda Bay at depths of 20-40 m. It is a small deep-sea whitefish: its weight ranges from 100 to 400 g. Previously, Lattaneni were hunted from the second half July until freeze-up, for which they used fixed nets with a mesh of 26-30 mm.
The third form of whitefish on Pyaozer is represented by the migratory whitefish kutcheri. It rises to the river in October to spawn. Sofyangu and its tributaries - Ponchu, Varba, into the rivers Kitti, Tawang, Olanga. Of all the large and medium-sized rivers of Pyaozer, the whitefish kutcheri does not rise only into the Pundoma River, which carries heavily swampy waters into the lake. The kutcheri whitefish spawns in rivers, mostly under rapids, at a depth of 1-3 m, choosing mainly sandy and pebble places. Its fertility is low and ranges from 7-15 thousand eggs. Sexual maturity occurs at the age of 4-6 years.
In commercial catches, kutcheri whitefish are found between the ages of four and fifteen years; the bulk of the catch falls on whitefish aged six to nine years. This whitefish grows more slowly than the Rantasian whitefish.
Small quantities of kutchery are caught in autumn on the spawning grounds of the lake whitefish Rantasija. But this is a whitefish with underdeveloped reproductive products. It does not participate in spawning.
In the total catches of whitefish in Pyaozero, whitefish kutcheri occupies the main place, especially during the period of mass entry into rivers for breeding, when it is mainly caught.
The remaining three forms of anadromous whitefish: suurisiga, lehtisiga and kukkaneni are associated with the Sofyanga River and its tributaries Poncha and Varba.
general description
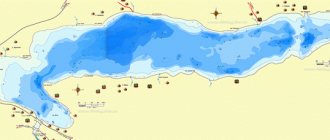
The area of Lake Segozero is 815 square kilometers. The length of the coastline is 410 kilometers. Length – 48.7 kilometers, width up to 35 kilometers. The drainage basin area is more than 7,400 square kilometers. The volume of water is 23.5 cubic kilometers.
Segozero is a deep reservoir, the average depth is 29 meters, the maximum is 103 meters. There are no depth maps in electronic form, but on the Internet you can find scans of Soviet maps that will give a general idea of the depths of the lake. Generally speaking, the approximate depth map of Segozer looks like this:
- In the southwestern part there is shallow water, the depths here rarely exceed 10 meters;
- The northern part is the deepest - this is where the deepest section is located, and the largest area is occupied by depths of over 40 meters;
- The southern and central parts of Segozero are generally homogeneous; at a distance from the shores, the depths here range from 20-30 meters.
The shores are mostly high and rocky, covered with coniferous forest. The coastline is very indented (especially in the northern part, where there are a lot of bays, bays and peninsulas). The southern coast is more flat.
There are 80 islands on Lake Segozero, most of them are concentrated in the northeastern part; there are no islands in the southern half of the lake (except for a few small ones that are located near the shore). There are no islands in the central part.
Many streams and rivers flow into Segozero, the largest of which are Sanda, Luzhma, Pyulva, Voloma. The Segezha River flows out. The reservoir is quite cold; in summer the water temperature on the surface rarely exceeds 16-17 degrees. The lake usually freezes in early December and is cleared of ice in May. The water has a yellowish tint, its transparency in some places reaches 4.5 meters, the average is about 3 meters.
There are not too many settlements on the banks of Segozero, but they are concentrated on the southern and western coasts. The largest are Padany and Karelian Maselga. There are only a few settlements on the northern and eastern shores.
Recreation center=»on»>
It is worth noting that on the shore of the lake there are recreation centers that willingly provide rental services. Thus, lovers of extreme recreation can rent a snowmobile, ATV or boat, depending on the time of year. Here you can visit a real Russian bathhouse, as well as book a hiking trip to nearby attractions - Lake Pisan and Mount Vottovaara.
Many travelers give their preference to the Segozero recreation center, which is located on the outskirts of the village of Padany. This is not only the place where the Luzhma River flows into the lake, but also one of the most convenient approaches to the reservoir. Four-bed cottages are available for accommodation, fully equipped with basic necessities. The tourist base operates all year round, and therefore offers its guests both winter and summer types of entertainment. Those who want to spend time comfortably on the shore and sunbathe will certainly be pleased with the wide sandy beach, the cleanliness of which is carefully monitored by the staff. Some of the most interesting recreational activities are fishing and hunting: they can be carried out either independently or with the participation of an instructor. Moreover, the base administration organizes river rafting trips, the duration of which varies from 1 to 4 days. Travelers note that the most pleasant thing after such a holiday is to relax in the local bathhouse.
Another equally popular recreation center “Perekat” is located a kilometer from the village of Popov Porog on the banks of the Segezha River, which originates in Segozero. The base has three guest houses with a capacity of 3 to 6 people. Travelers are invited to participate in winter and summer fishing, and picnic trips are also organized. Guest houses have areas for installing barbecues, and some of them have their own Russian bathhouse. Moreover, guests can rent a boat and go with tents to one of the islands of the lake.
Recreation and entertainment on Segozero=»on»>
The rugged coastline, picturesque green bays and a large number of islands turn Segozero into one of the most picturesque places in Karelia, which is ideal for those who want to have a good time in nature. Surrounded on almost all sides by dense coniferous forest, the pond is protected from strong winds, and is therefore ideal for those who want to have a picnic or pitch a tent. When choosing a location, you should know that only the southwestern side of the lake is considered shallow: the maximum depth in this part is 10 m.
Many travelers note that wild berries grow abundantly in the vicinity and on the banks of Segozero, the collection of which can perfectly complement your vacation. Depending on the month, you can taste strawberries, blueberries, cloudberries, lingonberries and even cranberries. But it’s not just berries that can please vacationers—local forests are also rich in mushrooms. The most attractive time for this is from the second half of July to the end of September. Most tourists easily find boletuses, milk mushrooms, saffron milk caps and chanterelles.
In addition to the above leisure options, hunting wild animals and birds is especially popular in Karelia. As a rule, in this area you can get moose, bear, hare and wood grouse as prey. Duck hunting is also in demand. However, if you decide to choose this pastime option, you should familiarize yourself with the rules of the hunting season, which are annually established by the Karelian regional public organization of hunters and fishermen.
Fishing in Karelia
Karelia is a protected region, where the skating rink of civilization has not yet passed. The natural beauty of this untouched area is simply mesmerizing. Finding yourself among the picturesque landscapes and breathing in the clean, dizzying air, you want to stay here forever. But this is not what attracts fishermen from all over Russia to the republic. They are looking for what they find everywhere – unforgettable fishing in Karelia. And she is truly memorable here. How can you forget catching a large whitefish or salmon if you are a resident of the Moscow region? Of course not.
There are more than 26 thousand deep rivers in Karelia, and almost three times as many lakes. There are so many fish there that even ordinary ecotourists become seasoned fishermen in a matter of days.
Features of the region
When going to Karelia for a multi-day fishing trip, it is worth considering some important nuances. For example, you immediately need to decide on the type of active recreation. What will it be like: comfortable, at a camp site with all the amenities, or wild, in your own tent far from populated areas? If the choice is made in favor of the second option, then you need to think through every little detail and take everything you need with you. You will definitely need means of protection against the ubiquitous insects, because near bodies of water there are always a lot of ticks, mosquitoes and midges. There are also creeping reptiles - poisonous snakes. Although they never attack first, high boots will not be superfluous.
Relaxation on Whitefish Lake
Many tourists have repeatedly come to Whitefish Lake. Holidays in these places are simply magnificent. First of all, the weather contributes to this. The climate of the region is favorable and temperate. Average summer temperatures reach +17… +20 °C. There is practically no scorching heat due to the close location to water bodies. Summer lasts 100 days. As a rule, the highest temperatures are observed in July.
Despite the lake's remoteness from civilization, you can have a wonderful time and relax here. In addition to the picturesque nature and mild climate, tourists go on excursions to get acquainted with historical sights.
Sanatoriums and recreation centers have been built on the lake for the services of vacationers. There is a lot of entertainment here for both passive and active recreation. Well-maintained sandy beaches, sports grounds, swimming pools on hotel premises, even a mini-zoo and a helipad - all this can be found on the Shiga coast. There is an opportunity to walk along walking paths in the pine forest. The only thing to be wary of is the swamps on the eastern shore.
What kind of fish is caught in Karelia?
In addition to toothy pike, in almost all Karelian reservoirs you can catch perch, roach, silver bream, rudd, and ruffe, but the listed species are also found at home; no one will go fishing for them tens of kilometers away. The northern region is attractive to fishermen due to such lake and river inhabitants as salmon, grayling, trout, vendace, whitefish, and palia. These species are considered migratory because they spend more time in the White Sea, and visit rivers and lakes only for the sake of procreation. The exceptions are large lakes - Ladoga, Onega, Sredne Kuyto and a number of others. In them, the chances of catching the same salmon or palia are quite high.
Heat-loving crucian carp, tench and catfish are rare in these places, although if you wish, you can find a reservoir where they feel great and are caught well. Separately, it is worth mentioning bream. Standard Karelian bream is a fish weighing up to 3 kg, which is caught not with maggots or corn kernels, like ours, but with a good bunch of dung worms. You should look for these on calm lakes or quiet sections of rivers.
Many spinning anglers come here for the pike perch. The fanged predator is usually hunted from a boat, fishing for exits from pits and places with a rocky bottom. With a successful combination of circumstances (favorable weather, high activity of the target, and so on), you can return from fishing with such a catch that everyone will be jealous.
This is not all that is caught in the reservoirs of the Republic of Karelia. Anglers often find bleak, minnow, spined lance, and sculpin on their hooks. True, no one needs this little thing, except for use as live bait. Moreover, sometimes it greatly interferes with the serious fishing process.
Bite forecast
White amur
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for grass carp. Grass carp are found in deep places.
Loach
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
0
There is no loach biting The loach is found in deep places
Chub
13
There are no chub bites. The chub is found in deep places.
9
There are no chub bites. The chub is found in deep places.
10
There are no chub bites. The chub is found in deep places.
10
There are no chub bites. The chub is found in deep places.
8
There are no chub bites. The chub is found in deep places.
25
There are almost no chub bites. The chub is found in deep places
38
Sluggish chub bite The chub is found in deep places
38
Sluggish chub bite The chub is found in deep places
22
There is almost no chub bite. The chub is located at shallow depths
47
The chub bite is worse than average. The chub is found in deep places.
58
Average chub bite Chub is found in deep places
58
Average chub bite Chub is found in deep places
35
Sluggish chub bite The chub is located at shallow depths
53
Average chub bite Chub is found in deep places
59
Average chub bite Chub is found in deep places
59
Average chub bite Chub is found in deep places
Minnow
19
No minnow biting Minnow is found in deep places
11
No minnow biting Minnow is found in deep places
13
No minnow biting Minnow is found in deep places
11
No minnow biting Minnow is found in deep places
13
No minnow biting Minnow is found in deep places
30
There is almost no minnow bite. The minnow is found in deep places.
51
Average minnow bite The minnow is found in deep places
46
The minnow bite is worse than average. The minnow is located at shallow depths.
32
Sluggish minnow bite The minnow is found in deep places
74
Good minnow bite The minnow is located at shallow depths
77
Good minnow bite Minnow is found in deep places
65
Good bite for minnows Minnows are found in deep places
46
The minnow bite is worse than average. The minnow is found in deep places.
84
Very good minnow bite The minnow is located at shallow depths
79
Good minnow bite Minnow is found in deep places
66
Good bite for minnows Minnows are found in deep places
Gorchak
0
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
7
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
6
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
7
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
0
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
20
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
23
There is almost no bitterling bite. Gorchak is found in deep places
25
There is almost no bitterling bite. Gorchak is found in deep places
0
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
37
Sluggish bite of bitterling Gorchak is found in deep places
34
Sluggish bite of bitterling Gorchak is found in deep places
38
Sluggish bite of bitterling Gorchak is found in deep places
0
There is no bite for the bitterling. The bitterling is found in deep places.
43
The bite of bitterling is worse than average. Gorchak is found in deep places
35
Sluggish bite of bitterling Gorchak is found in deep places
39
Sluggish bite of bitterling Gorchak is found in deep places
Dace
30
There is almost no dace bite. Dace is found in deep places
12
There is no bite for dace. Dace is found in deep places.
12
There is no bite for dace. Dace is found in deep places.
12
There is no bite for dace. Dace is found in deep places.
20
There is no bite for dace. Dace is found in deep places.
33
Sluggish dace bite Dace is found in deep places
50
The dace bite is worse than average. The dace is located at shallow depths.
50
The dace bite is worse than average. The dace is located at shallow depths.
53
Average bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
68
Good bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
75
Good bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
81
Very good bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
83
Very good bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
77
Good bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
83
Very good bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
77
Good bite for dace Dace is located at shallow depths
crucian carp
14
There is no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is in deep places.
7
There is no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is in deep places.
8
There is no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is in deep places.
8
There is no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is in deep places.
10
There is no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is in deep places.
20
There is no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is in deep places.
28
There is almost no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is found in deep places.
34
Sluggish bite of crucian carp Crucian carp is located at shallow depths
21
There is almost no bite for crucian carp. Crucian carp is found in deep places.
35
Sluggish bite of crucian carp Crucian carp is found in deep places
43
The bite of crucian carp is worse than average. Crucian carp is found in deep places.
43
The bite of crucian carp is worse than average. Crucian carp is found in deep places.
31
Sluggish bite of crucian carp Crucian carp is found in deep places
39
Sluggish bite of crucian carp Crucian carp is found in deep places
44
The bite of crucian carp is worse than average. Crucian carp is found in deep places.
44
The bite of crucian carp is worse than average. Crucian carp is found in deep places.
Carp
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
12
No carp biting Carp is located at shallow depths
11
No carp biting Carp is located at shallow depths
17
No carp biting Carp is located at shallow depths
22
There is almost no carp bite. The carp is located at shallow depths
19
No carp biting Carp is located at shallow depths
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
36
Sluggish bite of carp Carp is located at shallow depths
25
There is almost no carp bite. The carp is located at shallow depths
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
0
No carp biting Carp are in deep places
Rudd
15
There is no bite for rudd. Rudd is found in deep places.
11
There is no bite for rudd. Rudd is found in deep places.
12
There is no bite for rudd. Rudd is found in deep places.
12
There is no bite for rudd. Rudd is found in deep places.
10
There is no bite for rudd. Rudd is found in deep places.
30
There is almost no rudd bite. The rudd is found in deep places
43
The rudd bite is worse than average. The rudd is found in deep places.
43
The rudd bite is worse than average. The rudd is found in deep places.
29
There is almost no rudd bite. The rudd is located at shallow depths
59
Average rudd bite The rudd is located at shallow depths
65
Good bite for rudd The rudd is found in deep places
65
Good bite for rudd The rudd is found in deep places
45
The rudd bite is worse than average. The rudd is located at shallow depths.
67
Good bite for rudd The rudd is located at shallow depths
66
Good bite for rudd The rudd is found in deep places
66
Good bite for rudd The rudd is found in deep places
Bream
24
There is almost no bream bite Bream is found in deep places
11
No bream biting Bream is found in deep places
11
No bream biting Bream is found in deep places
12
No bream biting Bream is found in deep places
16
No bream biting Bream is found in deep places
30
There is almost no bream bite Bream is found in deep places
42
Bream bite is worse than average Bream is found in deep places
47
Bream bite is worse than average Bream is found in deep places
40
Sluggish bream bite Bream is found in deep places
58
Average bream bite Bream is found in deep places
64
Good bite for bream Bream is found in deep places
71
Good bream bite Bream is found in deep places
58
Average bream bite Bream is found in deep places
65
Good bite for bream Bream is found in deep places
65
Good bite for bream Bream is found in deep places
73
Good bream bite Bream is found in deep places
Tench
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
0
No tench are biting Tench is found in deep places
lake trout
41
Lake trout bite is worse than average Lake trout are found in deep areas
17
No lake trout biting Lake trout are found in deep places
17
No lake trout biting Lake trout are found in deep places
17
No lake trout biting Lake trout are found in deep places
27
There is almost no lake trout bite Lake trout are found in deep places
45
Lake trout bite is worse than average Lake trout are found in deep areas
68
Good bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
68
Good bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
72
Good bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
93
Excellent bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
100
The best bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
100
The best bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
100
The best bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
100
The best bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
100
The best bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
100
The best bite for lake trout Lake trout are located at shallow depths
Perch
0
No perch biting Perch is in deep places
15
No perch biting Perch is in deep places
13
No perch biting Perch is in deep places
12
No perch biting Perch is in deep places
0
No perch biting Perch is in deep places
23
There is almost no perch bite. The perch is in deep places
39
Sluggish perch bite Perch is in deep places
36
Sluggish perch bite Perch is in deep places
0
No perch biting Perch is in deep places
48
The perch bite is worse than average. The perch is in deep places.
60
Average perch bite Perch is found in deep places
54
Average perch bite Perch is found in deep places
0
No perch biting Perch is in deep places
61
Good perch bite Perch is found in deep places
61
Good perch bite Perch is found in deep places
56
Average perch bite Perch is found in deep places
Roach
21
There is almost no roach biting Roach is found in deep places
12
No roaches biting Roaches are found in deep places
12
No roaches biting Roaches are found in deep places
12
No roaches biting Roaches are found in deep places
14
No roaches biting Roaches are found in deep places
33
Sluggish biting of roaches Roaches are found in deep places
46
Roach bite is worse than average Roach is found in deep places
46
Roach bite is worse than average Roach is found in deep places
36
Sluggish roach bite Roach is located at shallow depths
63
Good roach bite Roach is found in deep places
70
Good roach bite Roach is found in deep places
70
Good roach bite Roach is found in deep places
54
Average roach bite Roach is located at shallow depths
72
Good roach bite Roach is found in deep places
72
Good roach bite Roach is found in deep places
72
Good roach bite Roach is found in deep places
Podust
17
There is no bite for the underdust. The underdust is found in deep places.
14
There is no bite for the underdust. The underdust is found in deep places.
15
There is no bite for the underdust. The underdust is found in deep places.
14
There is no bite for the underdust. The underdust is found in deep places.
11
There is no bite for the underdust. The underdust is found in deep places.
37
Sluggish bite of Podust Podust is found in deep places
63
Podust has a good bite. Podust is found in deep places.
57
Average bite of podust Podust is found in deep places
35
Sluggish bite of the underdust The underdust is located at shallow depths
90
Very good bite of the underdust The underdust is located at a shallow depth
95
Excellent bite for Podust Podust is found in deep places
87
Very good bite of the underdust. The underdust is found in deep places.
55
Average bite of the Podust The Podust is located at a shallow depth
100
The best bite for underdust The underdust is located at shallow depths
98
Excellent bite for Podust Podust is found in deep places
89
Very good bite of the underdust. The underdust is found in deep places.
Rotan
21
There is almost no bite for rotan. Rotan is found in deep places.
11
There is no bite for rotan. Rotan is found in deep places.
10
There is no bite for rotan. Rotan is found in deep places.
10
There is no bite for rotan. Rotan is found in deep places.
14
There is no bite for rotan. Rotan is found in deep places.
16
There is no bite for rotan. Rotan is found in deep places.
32
Sluggish bite of rotan rotan is found in deep places
32
Sluggish bite of rotan rotan is found in deep places
34
Sluggish bite of rotan rotan is found in deep places
39
Sluggish bite of rotan rotan is found in deep places
48
Rotan bite is worse than average Rotan is found in deep places
48
Rotan bite is worse than average Rotan is found in deep places
49
Rotan bite is worse than average Rotan is found in deep places
49
Rotan bite is worse than average Rotan is found in deep places
49
Rotan bite is worse than average Rotan is found in deep places
49
Rotan bite is worse than average Rotan is found in deep places
Zander
26
There is almost no pike perch bite. Pike perch is found in deep places
13
No pike perch biting Pike perch is in deep places
12
No pike perch biting Pike perch is in deep places
12
No pike perch biting Pike perch is in deep places
17
No pike perch biting Pike perch is in deep places
20
No pike perch biting Pike perch is in deep places
31
Sluggish pike perch bite Pike perch is in deep places
31
Sluggish pike perch bite Pike perch is in deep places
36
Sluggish pike perch bite Pike perch is located at shallow depths
41
The pike perch bite is worse than average. Pike perch is located at shallow depths
48
The pike perch bite is worse than average. Pike perch is found in deep places
48
The pike perch bite is worse than average. Pike perch is found in deep places
56
Average pike perch bite Pike perch is located at shallow depths
52
Average pike perch bite Pike perch is located at shallow depths
49
The pike perch bite is worse than average. Pike perch is found in deep places
49
The pike perch bite is worse than average. Pike perch is found in deep places
Bleak
0
No bleak bite Bleak is found in deep places
0
No bleak bite Bleak is found in deep places
0
No bleak bite Bleak is found in deep places
0
No bleak bite Bleak is found in deep places
0
No bleak bite Bleak is found in deep places
0
No bleak bite Bleak is found in deep places
20
No bleak bite The bleak is located at a shallow depth
20
No bleak bite The bleak is located at a shallow depth
21
There is almost no bleak bite. The bleak is located at a shallow depth
27
There is almost no bleak bite. The bleak is located at a shallow depth
30
There is almost no bleak bite. The bleak is located at a shallow depth
42
The bleak bite is worse than average The bleak is located at a shallow depth
43
The bleak bite is worse than average The bleak is located at a shallow depth
30
There is almost no bleak bite. The bleak is located at a shallow depth
43
The bleak bite is worse than average The bleak is located at a shallow depth
30
There is almost no bleak bite. The bleak is located at a shallow depth
Grayling
11
No grayling bite Grayling is in deep places
14
No grayling bite Grayling is in deep places
14
No grayling bite Grayling is in deep places
14
No grayling bite Grayling is in deep places
7
No grayling bite Grayling is in deep places
38
Sluggish bite of grayling Grayling is found in deep places
56
Average grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
56
Average grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
18
No grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
77
Good grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
85
Very good grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
88
Very good grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
27
There is almost no grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
87
Very good grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
91
Excellent bite of grayling Grayling is located at shallow depths
87
Very good grayling bite Grayling is located at shallow depths
Pike
0
No pike biting Pike are in deep places
18
No pike biting Pike are in deep places
12
No pike biting Pike are in deep places
12
No pike biting Pike are in deep places
0
No pike biting Pike are in deep places
27
There is almost no pike biting Pike are in deep places
46
Pike bite is worse than average Pike is located at shallow depths
46
Pike bite is worse than average Pike is located at shallow depths
0
No pike biting Pike are in deep places
58
Average pike bite Pike are found in deep places
70
Good pike bite Pike is located at shallow depths
73
Good pike bite Pike is located at shallow depths
0
No pike biting Pike are in deep places
73
Good pike bite Pike are in deep places
74
Good pike bite Pike is located at shallow depths
71
Good pike bite Pike is located at shallow depths
Ide
20
There are no bites for ide. The ide is found in deep places.
12
There is no bite for ide. The ide is located at shallow depths.
12
There is no bite for ide. The ide is located at shallow depths.
12
There is no bite for ide. The ide is located at shallow depths.
14
There is no bite for ide. The ide is located at shallow depths.
34
Sluggish bite of ide Ide is located at shallow depths
51
Average bite of ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
51
Average bite of ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
38
Sluggish bite of ide Ide is located at shallow depths
69
Good bite for ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
77
Good bite for ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
83
Very good bite of ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
60
Average bite of ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
79
Good bite for ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
85
Very good bite of ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
79
Good bite for ide. Ide is located at shallow depths.
Ruff
30
There are almost no ruff bites. The ruff is found in deep places
15
There is no bite for the ruff The ruff is found in deep places
13
There is no bite for the ruff The ruff is found in deep places
13
There is no bite for the ruff The ruff is found in deep places
20
There is no bite for the ruff The ruff is found in deep places
23
There are almost no ruff bites. The ruff is found in deep places
40
Sluggish bite of the ruff Ruff is found in deep places
40
Sluggish bite of the ruff Ruff is found in deep places
44
The ruff bite is worse than average. The ruff is located at a shallow depth
50
The ruff bite is worse than average. The ruff is located at a shallow depth
61
Good bite for ruff Ruff is found in deep places
61
Good bite for ruff Ruff is found in deep places
67
Good bite for ruff The ruff is located at a shallow depth
64
Good bite for ruff The ruff is located at a shallow depth
62
Good bite for ruff Ruff is found in deep places
62
Good bite for ruff Ruff is found in deep places
Add:
Recommended gear
What tool can you go with? It all depends on personal preference. Fans of sports fishing with a fishing rod, in addition to the rod itself, should take a set of floats for different fishing conditions, a supply of fishing line, hooks and weights. Of course, you should have a reel in your arsenal that allows you to fish at longer distances.
You will also have to take bait with you, since finding a worm among the Karelian stones is very problematic. You can also take maggots; in the local reservoirs this mobile larva has no competition. True, it has one significant drawback - its shelf life is too short. For this reason, it is advisable to use maggots in the first days, and then you can switch to caddis flies, pearl barley, semolina and even regular bread crumbs.
There are many predators in the region's waters, so spinning fishing is quite a popular activity here. There is no point in giving any advice on choosing tackle; it all depends on what kind of prey the spinner is targeting. For example, you can catch perch with an ultralight set, but a superlight rod is unlikely to withstand salmon. The supply of equipment must be impressive, because the bottom of Karelian lakes and rivers is mostly rocky, and unfortunate losses are not uncommon here. Including in shallow water. It would seem that here it is, a hooked spinner, very close. You just need to go waist-deep into the water and get it out. But no one wants to go into this very water, because it is very cold (even in summer).
The more different baits the fisherman has, the higher the chances of success. And there are more opportunities. Therefore, we take with us silicone, spinners, spinners, wobblers and other baits of all existing sizes and colors. The predators here are unpredictable. On the same body of water, a pike or perch can change their preferences several times a day: in the morning they take large oscillating spoons, at lunchtime they are actively interested in edible rubber, and in the evening they switch again to “hardware”.
Peaceful fish can be successfully caught using feeder gear. Depth maps in Karelia are scarce, it is almost impossible to find them, and without knowledge of the bottom surface topography you can’t hope for good fishing. Therefore, a fan of English donkey needs an echo sounder like air. This useful device will help you quickly find a fishing spot.
Where is the best place to go as a savage?
Let's look at the most popular bodies of water in Karelia, where you should go wild fishing:
Lake Ladoga is the largest body of water with inexhaustible reserves of fish. Thanks to fisheries surveillance, local and visiting poachers cannot expand their black fishery to its full potential. Underwater inhabitants multiply and reach decent sizes. You can catch trophy pike and pike perch, burbot are caught at night, bream and whitefish are biting well. Salmon and trout are less likely to be hooked, but such catch brings so much joy. In total, there are more than fifty peaceful and predatory species in the lake. It is better to fish in quiet bays and small bays, as well as near numerous islands. Since the shores of Lake Ladoga are not very convenient for fishing, it is advisable to come here with a boat. Those who are eager to hunt salmon should try their luck on the northern side of the lake. It is there that the Vidlitsa, Svir and Burnaya rivers flow into which Ladoga salmon and trout spawn. A sterlet or sturgeon may also be on the hook, but, unfortunately, this happens less and less every year.
Lake Onega is smaller than Ladoga, but is in no way inferior to it in popularity. At the height of the season, a whole army of fishermen gathers on its shores. Basically, these are groups of several people united by a common hobby. There are also many who combine fishing with family outdoor recreation. If the choice fell on Lake Onega, then you need to take care of a special license for salmon fishing in advance; without it, catching this fish is prohibited. Roach and bream, pike perch and pike are also well caught in the reservoir.
Pyaozero is a large freshwater reservoir in the Louhi region, located in the north of the republic. The average depth is 15 meters, there are also 50-meter holes. Compared to other lakes, there are few species living in this lake (16 in total), but you can imagine what kind of fish can live at such a depth. Trout, for example, can be caught weighing up to 10 kg! The grayling here are also decent, which has long been appreciated by fans of spinning fishing. Instances weighing 1 kilogram are considered standard. The same can be said about pike perch.
If we talk about rivers, the most attractive in terms of fishing are Keret (Loukhsky district), Voinitsa (Kalevalsky district), Kolezma (Belomorsky district) and Kem (Kemsky district). No one has ever left here without a catch.
Seasonal fishing in Karelia
The main flow of amateur fishermen is observed in the summer, during the holiday season, but in the heat the fish bite somewhat worse than during the spring feast (before and after spawning). In June the bite noticeably subsides. The second surge occurs with the arrival of autumn. The first temperature drops in September force underwater inhabitants to begin preparing for winter, that is, to actively feed and accumulate fat. Already in November, in the northern part of the region, on whose reservoirs the ice becomes earlier, the ice fishing season starts.
Features of fishing on Segozero
Fishing on Segozero can be an exciting, memorable activity both in summer and winter. The lake has a large number of perch (200-300 g), and grayling and trout are well caught. For fishing, you can use all different types of gear, both for shore fishing and from boats and boats. The size of the trophies may surprise the most discerning fishermen. When preparing for fishing, it is worth considering that the reservoir is very large and has a complex topography. Don't forget about changing weather conditions. In summer there can be strong storms on the lake. This is especially true for watercraft and water safety.
The shores of the lake are sparsely populated; in general, the reservoir is considered inaccessible. The coastline is heavily indented. The shores themselves are very diverse. There are both high cliffs and low-lying wetlands here. The coast is covered with coniferous forests. The topography of the lake bottom is also diverse; as already mentioned, the deep-water part occupies a significant part of the reservoir. The main part of the bottom is covered with silt deposits. A rocky-sandy bottom is typical for depths less than 10 m. There are a large number of islands on the lake, especially in the northern part, more than 70 in total. The main hydrological characteristics of the water are similar to other reservoirs in the region. Nutrition and regime depend primarily on snow nutrition. The color of the water has a yellowish tint and weak mineralization. The water level is currently regulated by the dam's flow and can reach 2.5 m. Ice sets in December and melts in May. The lake belongs to the White Sea basin and the main tributaries are the following rivers: Voloma, Luzhma, Sanda and Pyulva. In the northeastern part the Segezha River flows out and flows into Vygozero.
Despite regulation and partial human use, the lake is considered sparsely populated. There are several small villages along the banks of the reservoir; there is passenger and cargo shipping, as well as timber rafting. Dulmek Island is considered a geological natural monument due to the ancient dolomite outcrops present here. For fishing enthusiasts, a positive factor is that due to rising water levels, the shallow water zone has increased. The coastal area of the lake, due to its inaccessibility, can delight lovers of recreation in the wild with the presence of a small amount of “fruits of human activity.” At the same time, there are several tourist centers and camping sites on Segozero. The developed tourism infrastructure in the region allows you to find recreation options for both fishing lovers and relaxing time in the lap of nature, including “family vacations.”