Characteristic
Fish of the whitefish family are a class of ray-finned fish that belong to the phylum Chordata, order Salmonidae. Today there are about 60 species here, the most famous include salmon, omul, and migratory whitefish.
The fish received its unusual name because of the specific structure of the pupil, which has an angular shape, and in Latin the word “angle” is pronounced “sieg”. Considering how ancient this species is, scientists claim that the first representatives of ray-finned birds appeared on the planet about 440 million years ago. And fish similar to modern whitefish appeared much later, about 160 million years ago, when the Triassic period began. The first scientist who described the characteristics of whitefish was Carl Linnaeus, and this happened approximately in 1758-1759.
For those who do not know what a whitefish looks like, its appearance can be described by the following characteristics and features that are common to all breeds:
- The scales are silver in color while the fins are black.
- The head is clearly defined, large in size but flattened on the sides.
- The body is elongated, oval-shaped, quite wide.
- The mouth opening is small, poorly developed, and there are no teeth on the upper jaw. This specific structure of the teeth and mouth is determined by the diet. Fish do not hunt large prey.
- The muscle tissue of whitefish is white, despite the fact that the fish itself belongs to the salmon class, the meat of which has a red or pink tint. It is for this reason that it is also called white fish.
- Body length – the size of whitefish species can vary in size from 0.2 m to 1 m.
- Weight varies from 1 kg to 6 kg for different representatives of this species. And, although the largest fish that was caught from the whitefish was an individual weighing 12 kg, this rather became an exception to the rule, and a rare one at that.
- The average lifespan is 18 years.
- Sexual dimorphism is expressed by the fact that males are slightly larger than females, and the same rule applies to the size of their scales.
Almost all whitefish species are freshwater. But, there is one exception - the Siberian can live in sea water, albeit with one condition, that it is somewhat desalinated in relation to the normal salinity level. Therefore, it can live in places where sea water mixes with river water - at the mouth.
Yandex pictures
If we talk about the general habitat, it is worth noting that fish are found in lake and river water, preferring freshwater pools. And, despite the fact that the total number of fish living in the same body of water may belong to one breed, here they almost always fall into two forms - few-stamened and multi-stamened. The difference between them is the number of rakers in the structure of the gill slits. This indicator affects the diet - the more stamens, the more likely it is that the fish will feed exclusively on plankton. The fewer of them there are in the gill structures, the more predatory the fish becomes in its behavior - its diet begins to include not only benthos, but also small fish. Therefore, when answering the question of what whitefish eat, it is worth paying attention to its structural features and whether it belongs to a particular species - these parameters will be significant and determine whether we are facing an active predator or a fish that prefers plankton.
If we describe the lifestyle of whitefish, then we can highlight the following characteristic features for different breeds:
- feeds mainly on benthos and small fish, but there are also those whose menu includes exclusively plankton;
- behavior and lifestyle depend in the vast majority of cases on the habitat zone - river, lake and migratory whitefish will have their own characteristics. But despite this, the fish always shows caution in its behavior. If large predatory fish are nearby, they will hide, seeking protection at the bottom, among snags or in dense vegetation. If there are no such predators around, then the whitefish immediately feels its superiority and changes its behavior to a more aggressive one;
- The whitefish loves to hide and spend time when it is not busy searching for fish in pits. By choosing the right one for himself, he is able to displace other representatives of the aquatic world from it;
- but he goes to the surface for prey. But even here it behaves very carefully and cunningly, preferring to hunt from cover. But such tactics are not always typical for this fish. In some periods of the year, it is able to put itself on a more meager diet, switching almost entirely to bottom plankton. And when there is a lot of prey, whitefish can even flock together to increase success;
- adult whitefish are formidable predators, and their eggs, larvae and fry are prey for other aquatic inhabitants.
Describing the life cycles of this fish, it is worth noting that after the whitefish larva hatches from the eggs, most of these individuals are devoured by a variety of representatives of the aquatic world. Those that manage to reach the state of mature fry begin to actively gain body weight and increase their length. This takes approximately one year, after which he becomes young, ready for his usual way of life. Although, sexual maturity in males occurs only at 4 years, and in females even later. Spawning takes place many times; after the first laying of eggs and their fertilization, whitefish do not die.
freepik
Description and photo of whitefish
There are many varieties of whitefish. Some of them are listed in the Red Book. Representatives of the genus can differ quite strongly from each other.
Certain individuals are so different from their counterparts that only an experienced fisherman can understand that it is whitefish. Even if a fisherman knows what the most common whitefish looks like, for example, the common whitefish, he may not recognize the caught muksun, which is from the same genus, as a member of the family.
Characteristic feature: lack of upper teeth.
The following subspecies are distinguished:
- bounty;
- European;
- Siberian;
- Chudsky;
- Volkhovsky;
- multistamen.
General signs:
- the scales are silvery, the body is elongated, the abdomen is light;
- lower mouth;
- fins of a dark shade;
- the adipose fin is small.
Characteristic feature: lack of upper teeth, expressive eyes.
Signs are sometimes subtle and vary in some individuals. The pronunciation of sik is incorrect. This is what the Siberian whitefish looks like: it is quite large, its body can reach 60 cm, and its weight is 2 kg.
In one lake there may be fish that differ in external characteristics.
Individuals are distinguished:
- lake form;
- walk-through form;
- river type.
A trophy specimen can have different colors and sizes, and not every fisherman, having caught it, will be able to recognize the variety.
Representatives of salmon prefer water bodies with a high oxygen content. Some individuals stay closer to the surface of the water. Others sink to the bottom or swim into coastal waters.
On a new body of water, it is not always clear where the desired trophy is found and how to catch it, even if you are absolutely sure that it is possible to catch it in a given place. Whitefish is a cautious fish.
Large salmon, living in medium waters, weigh about 5 kg. These varieties include the pyzhyan, which can weigh 7 kg. In Siberia, where whitefish are found, a fisherman may be lucky enough to catch larger prey. It is not easy to catch such a trophy, and you will have to try hard to achieve it. The Siberian subspecies is a great success for the fisherman.
There are more than 50 varieties. Omul, vendace, peled are all varieties of whitefish. If you compare in the photo what the whitefish of the peled subspecies looks like and the pyzhyan variety, the differences will be visible to the naked eye.
Habitat
Considering the types of reservoirs where it lives, we can highlight the following characteristics to which the fish is sensitive:
- the water should be clean and preferably cool;
- the amount of dissolved oxygen must be high, since this condition is mandatory for the comfortable existence of this fish;
- if one of these conditions does not meet the requirements, the whitefish will definitely leave these places, looking for more comfortable living conditions. If this cannot be done, the fish simply dies.
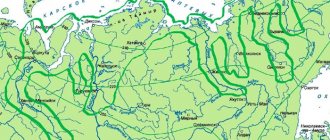
Considering the habitat directly, the distribution falls on rivers and lakes:
- Northern latitudes, where the water temperature does not rise too high.
- In Russia, these are mainly the following zones - in Lakes Peipsi, Ladoga, and Onega. On Baikal. In Siberian rivers such as Pechora and Mezena. It is in these reservoirs that fish not only like to spend their life cycle, but also come here to spawn. It is also found in abundance in all reservoirs of Karelia; individuals are often found in the Gulf of Finland, in the rivers Northern Dvina and Volkhov.
- In Europe and Switzerland it is found in lakes, and in Finland and England it lives mainly in rivers. It is represented in smaller quantities in water bodies of other Northern European countries.
- This is where whitefish are still found - the rivers of North America and northern Asia.
- The fish can also be found in the Arctic Ocean - but here the conditions are suitable only for a certain breed.
freepik
Whitefish in cooking
Whitefish is good fried. Tender, fatty meat, which does not contain many bones, cooks quickly both in a frying pan and on the grill. Whitefish meat contains a small amount of calories, 88 kcal per hundred grams, and fat is easily absorbed by the body, the presence of vitamins A and D makes the meat healthy. Whitefish fillet contains trace elements necessary for the human body: molybdenum, chromium, iron, zinc, iodine. Dried and smoked whitefish are considered a delicacy - the meat fully reveals its taste.
Kinds
There are more than 60 varieties of this fish. The most common:
- Common whitefish.
- Chudsky.
- Baltic.
- Siberian.
It is these species of the whitefish genus that can be found in different zones of Russia.
Yandex pictures
Chudsky
This species is also called sand whitefish. Its habitat is Lake Peipus, Onega and Pskov.
It is distinguished by its small size - this fish can reach a maximum length of 0.6 m, weight is about 4 kg.
Describing the view, it is worth noting:
- the head is small, oblong in shape, with a protruding upper jaw;
- eyes large, slightly protruding;
- The color of the scales is green with a slight brown tint. The color of the fins is gray.
Baltic
The list of whitefish is supplemented by one more individual - the Baltic, which inhabits:
- Bay of the Baltic Sea;
- distributed in water bodies of England, Poland, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Switzerland. In this region they inhabit freshwater lakes and large rivers.
But, despite belonging to the same breed, Baltic whitefish will differ in different conditions. When describing their appearance, they have the following differences:
- Inhabiting the regions of Russia, the Baltic whitefish is more similar in body shape to the herring, although its mouth also has an asymmetrical shape.
- But the European variety has more characteristic and recognizable features.
- The back is darker in color, while the sides and belly are lighter.
- The diet of the Baltic variety includes benthic crustaceans, mollusks and larvae. It feeds on them all year round, preferring to move from the surface to the bottom. But the Baltic whitefish, living in Europe, does not disdain small fish, finding them in different layers of water - both at the very bottom and hunting closer to the surface.
Whitefish. Yandex pictures
Ordinary
An ordinary variety joins the general list. It is this subspecies that has a wide distribution area - it can be found in many parts of Russia. Its habitat is not only freshwater bodies of water, but also pools with brackish sea water.
This is not the largest species - it can measure up to approximately 0.6 m, but it strongly resists when fished with a rod. For this, fishermen value it, since such sik (as this fish is also called) increases fishing excitement.
Ordinary siq is characterized by:
- the body is not too high - its dimensions in relation to the total length are no more than 1/3;
- the back is visually darker than the underbelly and sides;
- tail and fins - not too pronounced; their sizes are averaged in relation to the sizes of these body parts in other varieties.
In terms of lifestyle, the common subspecies leads an anadromous and semi-anadromous lifestyle. An ordinary breed of fish leaves its home in the period from April to November. The most active movement is observed in the first 2 autumn months.
Siberian
The Siberian fish is large in size - the fish lives in harsh conditions in terms of temperatures and has a wide “range” in terms of food choice.
Its habitats are the basins of the Arctic Ocean, the Barents and White Seas, as well as the northern rivers flowing into this basin of the World Ocean.
In terms of lifestyle, it is worth highlighting the fact that the fish prefers to be in the lower part of cold rivers, periodically entering salty water areas, mainly into bays. The diet of the Siberian variety includes small crustaceans, mollusks, plankton, caviar, and larvae. But these whitefish do not often feast on small fish.
Siberian whitefish is often called pyzhyan - its meat has high nutritional value and excellent taste. These fish grow slowly, gaining large mass and size only by the age of 9. Among the external features:
- small number of gill rakers;
- the caudal peduncle is large and located high.
Yandex pictures
Whitefish nutrition
The common whitefish feeds on benthos and plankton, starting from the first days of independent life. Depending on the variety of whitefish, after 2-3 years it begins to feed on fish and caviar, switching to a predatory lifestyle. Whitefish often feed on rifts, near holes, lying in wait for prey there. Whitefish fry stay in the coastal zone, where they feel safe. Depending on living conditions, whitefish easily combine food with fish and benthos, switching from one to another food if necessary. Medium-sized fish feed from the surface of the reservoir, attacking insects or their larvae. Large representatives of whitefish feed mainly on fish, this is evident from the activity of whitefish near schools of whitefish.
Fishing Features
Anyone who dreams of fishing for whitefish needs to know all the intricacies of fishing for representatives of this genus:
- When choosing a bait, you should pay attention that the best dimensions for it are a length of 6 cm and a diameter of no more than 2 cm.
- You can use crab meat, freshwater shrimp, large worms for bait. But worms most often attract young individuals, so you should not count on a large one when using such bait.
- When choosing a jig, choose those that look like “devils”.
- You can go fishing for whitefish at almost any time of the year. But, nevertheless, experienced fishermen talk about the predominant fishing season - from mid-October. These are the best dates for Russia, since at this time the fish begin to spawn, which increases the chances of catching a large fish.
- It is advisable to continue fishing from March to April, then it will be much more difficult to catch whitefish. And its taste characteristics then deteriorate significantly.
- Since fish love calm places where they feel protected, it is worth choosing places on reservoirs that differ in depth and width. This is where you have a high chance of catching a big whitefish. Near the shore, the bite of this species is almost never observed, so they either go out to the river or lake in boats, or drill holes in the ice in the middle of the reservoir when freeze-up has already occurred.
Yandex pictures
Spawning period of the common whitefish
Depending on the species, as well as the habitat, most whitefish spawn in the fall and winter. The exception is the Bauntovsky whitefish, which spawns in the second half of spring. The amount of eggs also depends on the species, ranging from 4,000 to 80,000 eggs (the average number is 20,000 pieces). The color of caviar is lighter than that of its noble relatives, and its content of microelements is not inferior to them. The incubation period is long, reaching 200 days, after which the larva develops for another 30 days. The formed fry slide downstream to feed in shallow lakes and flooded areas.
Population and species status
From the point of view of conservation status, this fish at the international level is classified as “threatened”, that is, its numbers are declining, but the emerging trend is not irreversible or dangerous. Therefore, many states are taking a number of measures to preserve the population.
Such a deplorable decrease in numbers occurs due to the fact that the meat of fish of this genus has excellent taste characteristics and has high nutritional value. But, thanks to a number of measures - such as artificial stocking, raising fry with their further release into the natural habitat, the global community for the protection of biological resources has hope that it will be possible to stop the large decline in the whitefish population.
Yandex pictures
Differences from omul
The omul also belongs to the whitefish genus. But this fish has its own characteristic features that distinguish it from the large, chudsky, northern or ordinary sika:
- smaller body dimensions;
- his body is more flattened on the sides and has a more pronounced spindle-shaped shape;
- This type of fish does not have the thickening characteristic of whitefishes in the first third of the body.
Yandex pictures