Origin of the species and description
Photo: Karas
Crucian carp belongs to the carp family and belongs to the class of ray-finned fish from the order Cypriniformes. Its name comes from old German dialects and the exact meaning of the word is unknown. This genus of fish is very widespread in various freshwater bodies of water. There are several varieties of crucian carp, which we will now describe.
Common (golden) crucian carp has a flat but rounded body shape. The fin located on the back is quite high and has a dark brown tint, like the tail. The remaining fins are smaller and have a reddish color. The sides of the crucian carp are covered with large golden-copper scales, and its back is dark – brownish. The belly of the fish is light in color compared to the ridge and sides. There are very large specimens of this crucian carp, the weight of which reaches 5 kg, and the body length is up to half a meter.
This crucian carp spread throughout Europe, settling in:
- Great Britain;
- Switzerland;
- Norway;
- Sweden;
- Slovakia;
- Macedonia;
- Croatia;
- Italy.
This type of crucian carp also lives in China, Mongolia, and the Asian part of our country, choosing overgrown, swampy, muddy reservoirs.
Silver crucian carp was first an inhabitant of rivers belonging to the Pacific basin, but since the middle of the last century it was artificially resettled on the North American continent, in India, Siberia, China, the Far East, Ukraine, Poland, Latvia, Belarus, Romania, Italy, Germany, Portugal. It is worth noting that in many places of new settlement this crucian carp gradually replaced its golden relative, in comparison with which it is significantly inferior in size.
The mass of silver crucian carp practically does not exceed three kilograms, and its longest length can reach up to 40 cm. The fish has large scales, painted in a silver-grayish or grayish-green tint. It is very rare to find fish that are golden or orange-pink in color. All fins of this type of crucian carp are colored in a grayish-olive shade and are transparent.
The silverfish has a unique ability that allows it to adapt to its environment and change its appearance in accordance with it, thanks to this people have developed a new variety called the “goldfish”.
Goldfish has many subspecies, numbering several hundred. Almost all of them are aquarium fish, the length of which varies from two to forty-five centimeters, and the bright colors are very diverse.
The shape of a goldfish can be:
- spherical;
- elongated (elongated);
- ovoid.
In addition to differences in shapes and colors, this type of crucian carp also differs in the size of its fins. The eyes of these fish can be either small or large, strongly convex.
It is on goldfish that experiments necessary for scientific research are often carried out; they are the first fish to have been in outer space.
Japanese crucian carp lives in Japanese and Taiwanese waters, the wild variety can be seen in the Japanese Lake Biwa, the dimensions of the crucian carp are from 35 to 40 cm.
Crucian carp. Description, habits
I think crucian carp is one of the most famous fish in the whole world. Our domestic fishermen are no exception, because almost everyone had a happy childhood in the village catching crucian carp with a fishing rod, and when you mention crucian carp, thoughts immediately come to mind about the first bites and the first fish caught.
But this article will not talk about the method of catching crucian carp, but about its lifestyle and habits. First of all, you need to start with its description. Crucian carp is a typical representative of cyprinids. It is a well-distributed fish both in European reservoirs and rivers and in the river basins of the Pacific Ocean.
You can also catch this wonderful fish in the rivers of Siberia. There are two types of crucian carp: gold and silver. These two breeds are quite difficult to confuse. Golden crucian carp has a tall, round, laterally flattened body. The color of the scales is brown-golden or reddish-golden with a slight lightening towards the belly. The silver carp has a longer body compared to the gold carp; the back does not make such a steep arc. The scales are quite large and have a silver color, sometimes with a black tint. Sillo is distinguished by its caudal fin: it is noticeably forked. Obvious external differences between gold and silver crucian carp do not prevent them from having the same lifestyle and habits. There is only one difference: silver crucian carp prefers low-flowing water.
Read: A few words about catching spring crucian carp on a feeder
Another very interesting feature of the silver crucian carp is that its population consists exclusively of females. Who fertilizes their eggs? During the spawning of silver crucian carp, its eggs are fertilized by male gold crucian carp or tench, but from these eggs only one female white crucian carp is hatched. Fish spawning occurs late: it begins from the end of April to the end of August and only when the water warms up to 18-20º C. During spawning, the fish gather in schools, occupy the banks overgrown with grass and begin their mating games. Females lay eggs on aquatic vegetation, however, a large number of animals use the same technique. All these actions are accompanied by active movement. In general, the spawning of crucian carp is short and friendly and often lasts longer than 2-3 days. Young individuals feed on plankton (that is, small organisms that drift freely in the water column).
Adult crucian carp feed on various small organisms, vegetation, and in general, they have a very wide diet. They get all this by loosening the bottom silt: they bury their nose and dig with their tail out. The usual length of an adult crucian carp is 20-25 cm and weight 500-800g. It is worth noting that the weight of crucian carp completely depends on the habitat and the amount of food consumed, therefore, under favorable conditions, crucian carp can reach from 1.5 to 3 kg. Conversely, in low-food reservoirs the herd consists entirely of dwarf stock.
Read: Catching crucian carp. Search for promising places
The habitats of crucian carp are closed bodies of water - lakes, ponds, various types of quarries and are sometimes found in rivers. They live in thickets near the shore on the shore at a depth of 1.5-2 m. In hot weather, crucian carp rise to the surface of the water and stay near the grass. Home for crucian carp are areas of muddy bottom, where they search for food and to which they are very attached. During winter, crucian carp go into the mud to spend the winter. The harsher the winter, the deeper it burrows (the depth can reach up to 0.5 m). Sometimes, using mud, he makes a rookery for himself. This helps when the lake freezes.
One of the problems for anglers is the capriciousness of crucian carp. There is no way to predict what time is best for a particular bait. Yesterday he took it for bread, today he turns his head. The most common baits are maggots, worms, bloodworms and even bread pellets. For a better bite, you should feed the fish a few days before fishing. For bait, it is better to use pressed cake soaked in anise oil (a few drops are enough). In the end, I would like to say that crucian carp is an excellent target for fishermen and its lifestyle should not raise any big questions for those interested in its description.
Appearance and features
Photo: Crucian fish
Having understood the individual characteristics of each variety of crucian carp, it is worth giving a general description of the appearance of this very common fish. Externally, crucian carp is very similar to carp, this is not surprising, because they are members of the same family. When comparing them, the most important distinguishing feature is the smaller head. The mouth of the crucian carp is also smaller than that of the carp and does not protrude forward as much; it does not have a mustache.
The body shape of the crucian carp is oblong, but high, somewhat reminiscent of a diamond; the body of the fish is flattened on the sides. The large dorsal fin has a smooth outline. The fish is covered with smooth and large scales, the colors of which vary between species, but the most common colors are golden and silver. The fish ridge is quite powerful and thickened.
The small mouth opening contains single row pharyngeal teeth. Basically, the eyes of crucian carp are small. One of its differences is the presence of prickly barbs on the anal and dorsal fins. The standard weight of crucian carp is from 200 to 500 grams; larger and heavier specimens are rarely found.
The life span of different types of crucian carp is different. The Golden Krasya can be considered a long-livers; it can live more than 12 years. Goldfish rarely survive nine years of age, although some manage to overcome this milestone and live for a couple more years, but this happens extremely rarely.
Where does crucian carp live?
Photo: Big crucian fish
It should not be surprising that crucian carp is so widely distributed throughout the globe, because it is very hardy and unpretentious. The widest range of crucian carp was also facilitated by human activity, who settled it in many places artificially. This fish adapts perfectly to all kinds of ponds, lakes, and rivers.
Ichthyologists have found that in swampy areas, underwater holes and when a large amount of silt accumulates, crucian carp feels most at ease and begins to reproduce much more actively. Only water bodies located in mountain ranges avoid crucian carp.
Under unfavorable conditions (excessive frosts, severe drought), crucian carp burrows deeply into the silt (up to seventy centimeters) and successfully survives all natural disasters there.
The crucian carp did not ignore Italy, Poland, Portugal, Germany, Romania, Great Britain, Hungary, Kazakhstan, China, Belarus, Mongolia, Korea, where they live safely. This fish does not disdain the cold Siberian waters, having chosen Kolyma and Primorye. Crucian carp can also be caught in the territories of Pakistan, India, the USA and Thailand.
As you can see, the geography of crucian carp distribution is very wide; it has a permanent residence in other countries not listed here. Here you can catch it almost everywhere; it feels great, both in wild and artificially created conditions. Fishing enthusiasts will undoubtedly confirm this.
The Chinese were the first to begin artificial breeding of crucian carp; this happened back in the seventh century AD.
Lifestyle
Crucian carp is an unpretentious fish that can live almost anywhere, although it prefers reservoirs with stagnant water and a lot of mud. It is usually found in the bottom layer, where it searches for suitable food in the vegetation.
With the onset of cold weather, crucian carp burrow into the silt and survive even in the harshest winters, when the water freezes to the very bottom. There are known cases when this fish was dug out from a depth of 0.7 meters, while the reservoir was completely dry. Thanks to this feature of their body, crucian carp survive well in wetlands, which freeze entirely during the cold season. The golden members of the family are especially tenacious.
After leaving wintering grounds, crucian carp are always hungry and willingly eat any food. For this reason, it is very easy to catch in early spring.
Crucian carp is not afraid of cold water, so it is found in reservoirs of the Urals, Siberia, and also at great depths with running water.
In small ponds or lakes, crucian carp often appear by chance, usually after the spring flood. It has long been proven that fish eggs can be carried over long distances by wild waterfowl on feathers. Thanks to this, crucian carp inhabit reservoirs located at a considerable distance from civilization. If the habitat conditions are suitable, then within four to five years there will be a large population of this fish.
Crucian carp is a clumsy and clumsy fish, so it does not resist even a weak current. Predators take advantage of this feature and very quickly exterminate the entire population in a reservoir if the crucian carp has nowhere to hide. Young fish and eggs suffer the most.
The crucian carp spend the entire winter and early spring buried in the silt, and only when the ice has completely melted do they dig out of their shelters. The fish shows its main activity shortly before spawning, when the water warms up well, becomes cloudy, and aquatic vegetation rises from the bottom.
Spawning for crucian carp begins in mid-to-late May, sometimes in early June, and lasts about a month. In the first days of this period, the fish are still actively feeding, but soon the bite completely disappears. The eggs and fry of crucian carp are destroyed in large quantities by frogs, newts and diving beetles - large water beetles. They all take advantage of the lethargy and slowness of the crucian carp, which does not have time to escape from them.
What does crucian carp eat?
Photo: River fish crucian carp
Crucian carp can be called an omnivorous aquatic inhabitant. Its menu is quite varied. Let's trace the taste preferences of fish, starting from the moment of birth. The fry that are born have a yolk sac with them, which remains with them after embryonic development; they use the contents of this sac for nutrition, which maintains their strength and energy.
Slightly mature crucian carp begin to feed on daphnia and blue-green algae. Closer to the month, bloodworms and larvae of various insects living in the water appear in the babies’ diet.
Mature fish have a richer and more varied menu. Their diet includes annelids and small crustaceans, all kinds of insect larvae. The roots and stems of plants in the coastal zone also serve as food for crucian carp. He loves to eat duckweed and various algae.
Fishermen have long understood that crucian carp are not averse to eating all sorts of cereals:
- buckwheat;
- wheat;
- pearl barley
The buttery dough and crumb of bread for fish are real delicacies. Crucian carp's sense of smell is simply excellent, so it senses a particular type of bait from afar. It has been noticed that crucian carp like harsh and strong odors (for example, garlic), which fishermen use for their baits.
The lateral line of crucian carp can be called an organ of its finest sensitivity, with the help of which the fish scans the water column, receiving data about the location of prey, its dimensions, and the distance to it. It also determines the presence of predatory ill-wishers.
From the fact that crucian carp did not like hornwort, it contains a lot of tannin, which repels insects and larvae, which crucian carp like to eat.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Karas
The unpretentiousness and endurance of crucian carp are one of its most important features, thanks to which it has spread widely across all kinds of reservoirs. The level of oxygen in the water column is not as important for it as for pike, so it can easily survive the harshest winters in small lakes.
Crucian carp gives its preference to standing water; it does not like even a weak current, but where it is present, it also takes root. It should be noted that silver crucian carp is more often found in running water than its golden relative. But the latter has greater endurance.
Silt, mud, dense coastal growth, duckweed - these are the attributes of a happy and carefree life for crucian carp, who adore reservoirs with all these attractions. The crucian carp finds food in the mud; it can skillfully burrow into the mud to wait out any danger or unfavorable climatic conditions, and the depth of its immersion in the muddy bottom can exceed half a meter. In general, crucian carp feels at ease where other fish have a hard time surviving.
As already mentioned, the current is the enemy of crucian carp, it exhausts it, adding clumsiness. And in this state, it’s not difficult to become some predator’s lunch. Where the bottom is sandy or rocky, you won’t find this fish either, because in such places it is difficult for it to find food and there is almost nowhere to hide. In swampy, impassable, overgrown places, crucian carp breeds well and develops quickly, often being the only fish in such reservoirs. Sometimes crucian carp appears where it has not lived before, this is explained by the fact that its eggs are carried on their feathers by birds that live on the water.
Although the crucian carp is a little clumsy and clumsy, its sense of smell is simply amazing, it is able to detect the slightest odors at a very long distance. The highly sensitive lateral line of crucian carp is also its important attribute, helping to detect various objects in the water from afar, which often saves the crucian's life. Crucian carp are most active in the early morning or in the evening; in some places, crucian carp can be active at dusk. In general, crucian carp is a peaceful and calm fish, preferring not to enter into conflicts, but to lie low.
Behavior of crucian carp in spring, and how to make crucian carp fishing successful
As a rule, fishing for crucian carp in the spring becomes effective after a significant warming of the water. The golden-bellied bite directly depends on weather conditions, so any sudden cold snap negatively affects the fishing result. There are situations when crucian carp takes well in early spring, even in March. In this case, it is necessary that the water temperature rises to at least 10-12 degrees. It has been noticed that the warmer the water, the more active this fish is.
At a temperature of 8 degrees, the crucian carp only begins to wake up and become active; after 10, it takes the bait weakly; at 12-15, the active biting phase begins..
As the water warms up, the crucian carp begins to feed intensively. Often in the spring it walks in flocks in quiet shallow areas, eating the first stems of young vegetation and larvae of aquatic insects hiding among the leaves. Moreover, the following pattern of biting is observed: the smaller crucian carp takes the smaller ones first, and only later begins to take the larger ones.
In spring, the golden-bellied fish actively moves throughout the reservoir, so when the bite stops, you should not sit in one place for a long time. Since it is very careful in clear water, you need to move along the shore carefully, camouflaging behind bushes and coastal vegetation. You need to approach the fishing point while bending down and very carefully throw the tackle.
By the way, for successful fishing, it is better to bait three nearby theoretically promising places at the beginning of fishing. This will make it possible not to stop fishing if the bite has stopped in one of the places, or the fish has moved to depth. If fishing for crucian carp in the spring is based on such mobile tactics, then crucian carp fishing will be more effective.
If fishing takes place on a river, then the main place where you can find this fish is as follows - depth from 0.4 to 1.5 meters, clay, muddy bottom, mandatory presence of aquatic greenery. These can be water lilies, thickets of aquatic grass or reeds; in general, everything that creates a rich food supply should be present. And besides this, it serves as a fairly reliable shelter from predators. In places with a sandy or rocky bottom, crucian carp is extremely rare.
Crucian baits and baits
It is definitely necessary to feed crucian carp in the spring.
The recipe for bait for crucian carp is to take one kilogram of millet and cook it in three liters of water until completely boiled. Afterwards, let it cool a little, and mix with flour and finely chopped worms. Instead of millet, you can use a cell. Having arrived at the place, we form small balls of bait and carefully scatter them in the place of intended fishing. After about half an hour, the fish will smell it.
Preparing mastyrka from peas and semolina A classic fishing bait for carp is pea mastyrka with semolina. One of the most catchy baits for bream, crucian carp and crucian carp.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Small crucian carp
As for the social structure of crucian carp, these fish can be called schooling, although it happens that specimens that are quite large in size prefer to live completely alone. Crucian carp are sedentary and very cautious fish, but during the spawning period they can go to the nearest river tributaries.
Crucian carp become sexually mature when they are closer to four or even five years old. Usually, their spawning period occurs in May-June, it all depends on how warm the water is; its temperature should be about 18 degrees plus. Spawning can take place several times a year. At this time, the crucian carp is not interested in food at all, so catching this fish is useless.
To spawn, females move closer to the shore, where there is more vegetation. The spawning of crucian carp is multi-stage, taking place with ten-day breaks. One female can lay up to three hundred thousand eggs. They all have excellent stickiness and cling to aquatic plants.
Crucian carp caviar is light yellow in color, and the diameter of the eggs is only one millimeter. After about a week, embryos emerge from it, about four millimeters long. Closer to the autumn period, babies can grow up to 5 cm in length. Typically, their survival rate is 10, and this is under favorable circumstances. Scientists have noticed that goldfish give birth to much more females than males (approximately five times).
The size of crucian carp and their development depend on the amount of food. If it is in abundance, then already at the age of two years the fish has a mass of about 300 grams; with meager food, crucian carp can survive, but will weigh only a few tens of grams at the same age.
A process such as gynogenesis is characteristic of crucian carp. It occurs when male crucian carp are not observed in the reservoir. The female has to spawn with other fish (carp, bream, roach). As a result of this, exclusively female crucian carp are born from eggs.
Natural enemies of crucian carp
Photo: Crucian fish
It is not surprising that larger predatory fish are enemies of crucian carp. The first among them is the pike, which simply loves to snack on crucian carp. Just remember the well-known saying: “That’s what the pike is for, so that the crucian carp doesn’t sleep.” Clumsy crucian carp can also be caught for lunch by fish such as pike perch and asp.
Of course, adult and large crucian carp have many times fewer enemies than young animals, fry and eggs of this fish, which often end up in the mouths of newts and frogs. They destroy eggs and newborn fish in huge quantities. Surprisingly, various aquatic insects (garglers, bugs, swimmers) attack crucian fry with great aggressiveness, and the gluttony of their larvae is simply amazing.
In addition to troubles from the water column, the crucian carp is also subject to lightning-fast air attacks from birds. Kingfishers and seagulls like to eat crucian carp this way. Birds can also carry dangerous fish diseases. Waterfowl ducks are also not averse to feasting on small crucian carp, and long-legged gray herons eat dozens of them.
Animal predators are also not averse to grabbing crucian carp, which can become a tasty snack for otters, muskrats, muskrats, and ferrets. Even the common red fox manages to catch crucian carp in shallow water if she is lucky.
As you can see, crucian carp have a lot of bad friends, especially young ones. But most of all crucian carp are destroyed by people who are keen on fishing. Usually crucian carp bites well on a regular float rod, although there are many other devices for catching it (spinning and feeder fishing, elastic, donka). Fishermen have long studied crucian carp habits and taste preferences, so they know how to attract this fish. As a fishery, crucian carp are highly valued. Their white and tasty meat is considered dietary and very healthy.
Behavior of crucian carp before spawning
The spawning of crucian carp begins at a water temperature of 14 to 18 degrees. Depending on the weather, water temperature and the characteristics of the conditions in a given reservoir, spawning can continue in portions for a month or more with interruptions.
Small individuals begin to spawn, then medium and large ones. In small, well-warmed, overgrown reservoirs, the spawning of different groups of crucian carp can almost coincide in time, but the spawning sites will differ.
The preparation of crucian carp for spawning is now almost complete. That is, the crucian carp takes the places of its usual summer camps, gains weight and waits for the creation of weather conditions suitable for this. The fact that this fish in the reservoirs near Moscow has taken up its summer camp sites is evidenced by fishing practice in recent days.
Firstly, schools of crucian carp have finally separated from roach, bream and bleak. Large crucian carp prefer to stick to deep places and go out into shallow water with warm water either at night or in good weather, but provided that they are not in danger from anglers. During the day, crucian carp rolls away to deep places, and in shallow reservoirs it gets stuck in vegetation.
In a week or two, schools of medium and large crucian carp will begin to rise at dawn and on warm, windless days to the very surface. At this time, crucian carp will be caught better in the late afternoon and at night.
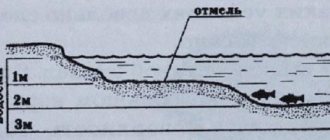
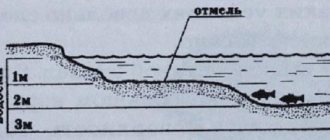
Small crucian carp occupy places near coastal vegetation, usually on its edge, where the fall into depth begins. In quarries that are practically devoid of underwater vegetation, small crucian carp are distributed at a certain depth level, usually from one and a half to three meters, and come closer to the shore only at dawn.
With the development of underwater vegetation, crucian carp do not move far from it during daylight hours. The exception is underwater hills at a decent distance from the shore, but it is quite difficult to catch cautious fish here.