Historically, the territory of the Ivanovo region belongs to the Caspian Sea. The rivers here are thick with many branches. Most of the water flows lie on the plains, their flow is calm, and the slopes are minimal. Next to them are glacial deposits into which the valleys flow. Almost all rivers of the Ivanovo region are high-water.
The diet is predominantly mixed; less common are watercourses that grow due to the melting of snow deposits. Due to the latter process, spring floods are often observed. In summer, natural reservoirs are fed by rain. In autumn, the rivers of the Ivanovo region receive sufficient groundwater. Judging by the observations of hydrologists, the water flows of this area begin to be covered with ice in November, and ice breaks up in April.
Vyazma
The length of Vyazma is only 86 km. It has several tributaries, including such as Peja and Podoxa. The city of Teykovo is located on the banks. The water flow begins in the Shinilovo swamp. It flows in the direction of the southeast, very close to Ukhtokhma.
The width of Vyazma varies from 5 to 15 m. In some areas the banks are covered with forests, and sometimes there are wetlands.
What rivers are there?
Ivanovo is located on the banks of the Uvod River, which is considered a tributary of the Klyazma. The current moves from the north side, dividing Ivanovo. On the territory of the city flow:
- Take it away.
- Talka.
- Kharinka.
These and other small rivers flow into the Uvod, forming branches, oxbow lakes and lakes.
The length of the river in Ivanovo is almost 20 km, the basin stretches over 3,500 square kilometers. It originates in the Andreevsky swamps, not far from Komsomolsk.
The upper section of the stream: this is a tiny lake with riffles and islands. The river acquires a larger volume next to the Uvodsky reservoir, 1.5 km wide and 37 km long. It was formed in 1937 with the goal of providing water to the entire surrounding area.
The Uvod River is low-water, its width is 10 meters. Therefore, it is not able to provide drinking water supplies to a population of over 400,000 people. And besides Ivanovo, on the banks of the Uvodi there is also the small town of Kokhma.
We recommend reading: The Neva River on the map of St. Petersburg
Danilovka
The non-navigable Danilovka, 26 km long, has a completely different name in the upper part - Kichma. The water flows into Ukhtokhma and belongs to the Caspian Sea basin. The source can be called the Ilyinsky district. This place cannot be found on the map, since the reservoir begins at the junction of two regions - Ivanovo and Yaroslavl. The drainage basin has an area of 100 square meters. km.
Irmes
The Irmes River immediately flows in the Ivanovo region and in the Vladimir region. The mouth is the Nerl. The length of the water flow is 72 km. On the left side there is a village. It was opened in 2001. Scientists from the Suzdal detachment found that people lived here in the 9th-10th centuries, as well as in the 12th-13th centuries. The drainage basin area reaches 662 square meters. km.
Interesting nature reserves and reserves in the region
Specially protected sites in the Ivanovo region cover an area of almost 130 thousand hectares. These include nature reserves, habitats of rare animals and bird nesting grounds, as well as parks, gardens and unique natural complexes.
Klyazminsky reserve
- Coordinates: 56.495016, 41.442351.
To see the fabulous landscapes of the northern forests, you don’t have to go to Karelia. It is enough to visit the Klyazminsky reserve, which is part of the Meshchera National Park. This is the only place in the Ivanovo region where you can find century-old pine trees, mossy stones and swampy lakes.
Here you can see one of the same age as crocodiles - the chilim water chestnut, which is on the verge of destruction; wild mallard or teal, which fly to the territory of the reserve to nest and hatch chicks. But the main protected object here is the muskrat - a small animal from the mole family with very valuable fur.
Today its numbers are declining and the animal is listed in the Red Book. Another pride is the white-tailed eagles. Not every reserve can boast of nesting sites for these large birds. Usually, for breeding, they prefer remote places where people cannot reach.
Garden-arboretum of Dr. Saleev
- Coordinates: 1A, Gagarin microdistrict.
There is more than one arboretum in the Ivanovo region, but the best of them, undoubtedly, is the one located in the city of Rodniki. The garden, founded in 1948 around the tuberculosis dispensary by Doctor of Medical Sciences A.A. Saleev still receives visitors today, causing the admiration of city guests.
Here, in a relatively small area, about 1,500 species of plants have been collected: birches, maples, barberries, chestnuts, a huge collection of conifers, which continues to grow to this day.
Roses are fragrant in one of the corners of the garden. Another grows one of the most unusual plants on the globe - ginkgo biloba, preserved from the Paleozoic and called a “living fossil”.
Klyazma
The length of Klyazma is 686 km. The water flow is fed mainly by snow waters. At the end of autumn it freezes, and closer to summer it begins to open. The source is located in the area of one of the hills in this area. Near the village of Cherkizova there is a sharp turn in the waters - the river begins to flow to the east. After the confluence with the reservoir, the width of the Klyazma reaches 12 meters. It flows through a lowland, in some parts the bank on the right side is lower than the left.
The river bottom is mainly covered with sand, sometimes there are areas with clay. It is worth clarifying that 12 meters is not the maximum width of this stream. In some areas this figure increases to 200 m. The depth is no more than 8 m, but the dominant indicators are still 1-2 m.
Teza
The Teza River is a tributary of a larger watercourse - the Klyazma. The length of the reservoir is about 192 km. On its banks there are several villages and one city. Over time, it was noticed that the Teza River in the Ivanovo region is constantly increasing its flow level, and the banks are rising. The channel has a winding type. The width of the water flow is constantly changing: it varies from 6 to 30 meters (depending on the current).
Tunoshonka
Tunoshka (or Tunoshonka) is a river that flows in two regions at once. It captures the areas of the Ivanovo and Yaroslavl administrative centers. Most of the reservoir is located on the territory of the latter. The source covers the Komsomolsky district. We are talking about a tract called Podozerye. It’s nice to think of a reservoir as an estuary. The river has several large tributaries, all of them are on the left side. There are more than 10 settlements near the reservoir. In one area, Tunoshonka crosses a railway, in another – a road.
Water resources, presence of rivers, lakes
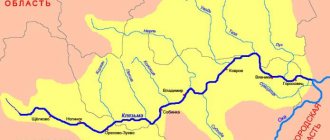
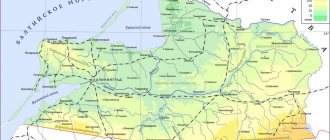
There are about 2,000 rivers in the region, including 50 with a length of 25 km or more, 120 with a length of 10-25 km and over 1,500 with a length of less than 10 km. The largest river is the Volga, flowing through the region for a distance of 173 km with a water flow of 1590 m3/sec; the second largest is r. Klyazma. All rivers belong to the Volga basin, which crosses the northeastern part of the region. The Gorky Reservoir extends into the region. The left tributaries of the Volga (Unzha, Nemda, Mera) are richer in water, the right ones are low-water and short. The left tributaries of the Klyazma (Nerl, Uvod, Teza, Lukh) flow from the southern slope of the Volga-Klyazma watershed. Rivers are used mainly for water supply. The Volga-Uvod canal was built, improving the water supply of cities and industrial centers of the region. The rivers are of the flat type with a low slope and calm flow. They are characterized by the predominance of snow supply - which accounts for more than 50% of the annual runoff. The rest comes from rainfall (mainly in summer) and groundwater (mainly in autumn). The Volga and Teza rivers are suitable for navigation. The Volga is navigable along its entire length within the region, the Teza - for 90 km from the city of Shuya to the mouth, the required depths here are maintained by five locks. There are over 200 lakes of glacial, floodplain and karst origin in the region. The largest number of glacial lakes is concentrated in the western part of the region. The most significant, heavily overgrown, glacial lakes are Sakhtysh and Rubskoye. Lake Sakhtysh is located in the lowest part of the Teykovsky peat bog. Its area is 549 hectares, the average depth is 1 m. The greatest depths of the lake are from 2 to 3 m. The sapropel layer reaches 6 m. The south-eastern part of the region is an area of karst development. The largest karst lake is Bogoyavlenskoye; its diameter is 1.5 km, its area is more than 100 hectares. North of Bogoyavlenskoye is the deepest lake, Kleshchinskoye Lake. Its depth reaches 35 m, the diameter of the funnel is 250 m. About 4% of the territory is occupied by swamps with a predominance of low-lying peat bogs fed by groundwater. Swamps are distributed unevenly throughout the region, although they are present in all regions. The most significant swamps and wetlands are in the southeast and west. There are 45 reservoirs in the region with a total capacity of 93.9 million m3 (excluding the volume of the Gorky Reservoir). The groundwater. Operating groundwater reserves are 1.6 million m3/day. There are more than 2,300 bore wells at industrial and agricultural enterprises, including a large water intake in the village. Strokino for the city of Ivanovo.
Raskolina
This river is known by three names. Her official name is Raskolina. Among local residents it is better known as Raskolikha. And on some maps the water flow is signed by Sabelka. The length of the reservoir is 10 km. The mouth of the river is Inveshka, it is a left tributary. The source is located near the village of Zavrazhnevo (village). The river flows towards the west.
Several years ago, the state created a small reservoir here. Its area is 31 hectares, and it is located near Peshcheny (this is a village). The water flow is not navigable, as it is very shallow or swampy (depending on the area of a particular site).
Attractions
First of all, the city and the entire region are famous for the abundance of architectural and historical monuments. The beginning of the 20th century was marked by periods of dawn, the formation of revolutionary and proletarian culture. During these years, the main historical monuments appeared here, the number of which is slightly less than in Moscow.
Among the architectural monuments of avant-garde and constructivism, almost 50 buildings are noted. Among them: “Horseshoe House”, “Ship”, Railway Station and the building of the Ivanovo Rural Bank.
Unfortunately, most of the monuments dating from 1920-30 are very worn out and need immediate major repairs. Several buildings can no longer be restored and a decision is made to demolish them.
The most ancient buildings are considered to be the Shchudrovskaya Tent and the wooden Assumption Church (almost completely destroyed by fire five years ago).
The center of Ivanovo was a place of cultural life; merchant estates were built there, dating back to the end of the 19th century. Of industrial architecture, pre-war textile factories are noteworthy.
We recommend reading: River in Chelyabinsk on the map, on which river the city is located
Religious monuments (ancient temples) were destroyed under Soviet rule. Of the remaining ones, the oldest (built in 1787) Kazan Church is noted.
But the “Crystal Slipper of the Bride” is popular among tourists in the “city of brides.” It is a framed flower arrangement located on campus.