One of the most valuable fish of the salmon family is omul. Its meat is very healthy and is considered dietary. Due to the decrease in the number of these fish, a fishing ban has been introduced since 2021. In Lake Baikal you can’t even catch it with a fishing rod. But still there is very little omul and it is quite expensive.
| Class | Ray-finned fish |
| Squad | Salmonidae |
| Family | Salmonidae |
| Genus | Sigi |
| View | Omul |
| Security status | Not endangered, but fishing is prohibited in some places |
| Size | Up to 64 cm, up to 3 kg |
| Lifespan | 15-20 years |
| What does it eat? | Crustaceans, invertebrates, small fish, zooplankton |
| Optimal feeding time | All year round, good night fishing in summer |
| Enemies | Unknown |
| What do they bite on? | Crustaceans, fry, flies |
What does it look like
Many people know what omul looks like, since it can often be found on sale fresh frozen or smoked. This is a small fish, its size does not exceed half a meter. Usually there are individuals 30-40 cm, Baikal varieties are even smaller. Despite the fact that some individuals can grow up to 3 kg, fish weighing more than one and a half kilograms are rarely found.
The body of the omul is narrow, elongated, tapering towards the tail, and covered with small scales. At the same time, its back is darker, its sides can have an emerald tint, and its belly is almost white. If we look at the photo and description of the omul fish, we can note the following features of its appearance:
- A lateral line runs along the body, as in all salmonids, but sometimes it is almost invisible;
- the back can be brown or green;
- there is a small adipose fin on the back near the tail;
- all fins are light;
- the head is small, the mouth is straight, located below;
- Silver eyes are large and round.
The description of the Baikal omul is practically no different from this. Only its size is smaller, it rarely grows to 35 cm. Due to the fact that it lives in fresh water and the living conditions are not so harsh, it is not very fat.
Description of the species
In a larger biological taxonomy, omul belongs to the salmon family (lat. Salmonidae), but at the same time it has delicate, light-colored meat without the slightest bitterness. In addition, like any whitefish (ludoga, vendace, pyzhyan, tugun, peled), it has a small symmetrical head and medium-sized silvery scales without scattered dark spots.
Other features of the appearance of omul include:
- elongated body of regular spindle-shaped shape;
- strongly compressed sides;
- presence of an adipose fin on the tail;
- small mouth with jaws of equal length;
- light thickened abdomen;
- the central axis of the body passing through the pupil;
- brown, brown or greenish color of the back.
The color of individual populations can vary depending on the diet of the habitat and taxonomic group.
Many fishermen are interested in the question of how whitefish differs from omul. There is no definite answer here due to the extreme polymorphism of the species (different external forms). Unlike the omul, in some reservoirs the whitefish has a characteristic expansion in the first third of the body, a hump, a cartilaginous elongated snout, and a large size (up to 12 kg).
Arctic omul
The base subspecies (lat. Coregonus autumnalis), which gave the name to the fish population. It is characterized by maximum size for the species and an anadromous lifestyle. Regularly goes out to feed in the coastal zones of the Arctic Ocean. It easily tolerates water salinity of 20-22% with an average of 35% in the World Ocean.
To learn more:
Salmon is a red fish from the salmon family.
Sexual maturity of individuals occurs at the age of 7-8 years, when the body length reaches 32-35 cm. With an average life expectancy of 10-11 years, the fish has time to spawn only 2-3 times.
Baikal omul
A smaller semi-anadromous subspecies (lat. Coregonus migratorius), which swims in fresh water all the time. The ability to spawn develops in the 5-6th year of life with a length of 27-28 cm. Due to its valuable nutritional characteristics, it was uncontrollably caught in the hungry post-war years at the level of fishing cooperatives, which caused irreparable damage to the population.
This species of omul fish is characterized by two plausible versions of its appearance: penetration from the polar seas and origin from an ancestral unique form. Modern Russian ichthyologists are more inclined to the latter.
Where does it live?
Omul is a migratory fish. This means that it lives in the sea, but descends into rivers to spawn, often traveling very far. Its habitat is the Arctic Ocean. This helps to understand where omul is found. It descends into the rivers of Siberia, Canada and Alaska. In Russia it is found in all Siberian rivers except the Ob. This is the Arctic or Yakut omul. There is also a variety that lives in the Far East, it is also called Amur, but there is little of it there.
The most famous is the Baikal omul. Its meat is most prized and considered a delicacy. But now catching it is prohibited, as its number has sharply decreased. In the lake itself, this fish is unevenly distributed. It is not found on the northwest coast. Most likely, because his favorite food, crustaceans, is not there. Omul is found where rivers carry silt rich in these crustaceans into the lake.
Most of it is in the south and in the area called the Small Sea. It is the Malomorsky omul that is considered the most delicious. According to their habitat, the following varieties are also distinguished:
- ambassadorial;
- Selenga;
- North Baikal;
- Chivyrkuisky;
- Barguzinsky
In addition, depending on the place where the fish most often feed, coastal, deep-sea and pelagic varieties are distinguished. The latter stays in the water column and grows the most.
Important!
The Baikal and Arctic varieties may differ in appearance and nutritional properties, but they are the same fish. It is believed that it came to Baikal during the Ice Age, so over the millennia it began to differ from its Arctic ancestor. But sometimes a separate species stands out - the Baikal omul.
Nutrition and behavioral characteristics
The omul fish prefers cold, oxygenated water. It usually lives in slightly salted and fresh waters near the confluence of rivers with the Arctic Ocean and in their upper reaches. On Baikal it lives in the lake itself and surrounding rivers. It prefers depth, often descending to 300 m. In the warm season, before spawning, it actively feeds in shallow water close to the shore.
Thanks to its narrow, elongated body, reminiscent of a torpedo, and tightly fitting scales, the omul swims very quickly. This fish most often feeds at a depth of up to 5 meters. It prefers a flat bottom, where the water warms up well, there is more food for it.
The omul feeds on zooplankton, so it is considered an omnivorous fish. Its favorite food is amphipods or epishura crustaceans. But when basic nutrition is not enough, it happily eats invertebrates, small fish, and insect larvae. Can feed on mollusks and detritus.
Omul habitats
Whitefish prefer clean, cold and deep water with a high oxygen content. These conditions are fully met by the reservoirs of the tundra zone, the rivers of the Arctic Ocean basin and the sea shelf.
The Arctic subspecies of omul lives in most northern reservoirs, which are located in a huge area between the Mezen River (Komi Republic) and the Chaunskaya Bay in Chukotka. Numerous populations are found in the rivers Yenisei, Khatanga, Kolyma, Lena, Indigirka, Pechora and their tributaries:
- Lower and Podkamennaya Tunguska;
- Aldana and Vilyue;
- Big and Small Anyue;
- Prodigal and Popigae;
- Berelekha, Allahikha and Uyandina;
- Tsilma and Pizhma.
The fish spends a lot of time in salt water (Laptev Sea, Kara Sea, East Siberian Sea, Barents Sea), where it feeds intensively and gains weight.
The Baikal omul lives in a limited range, which includes reservoirs in the southern part of Eastern Siberia. The main habitat of the subspecies is Lake Baikal. The length of the reservoir, the diversity of relief, conditions and ichthyofauna led to the formation of several populations-races, differing in color and minor physiological characteristics, for example, the time of puberty and the number of gill rakers.
To learn more:
Smelt: description of a fish from the smelt family
It is customary to distinguish four populations that are constantly tied to certain places on Lake Baikal:
- Severobaikalskaya (north coast);
- Posolskaya (Small Sea);
- Selenga (delta of the Selenga River);
- Chivyrkuiskaya (eastern coast).
In addition, Baikal omul populations are classified according to the depth of residence and feeding: coastal, pelagic (middle layers) and bottom-deep-sea (up to 300-350 meters).
Spawning
Spawning for this fish lasts from late September to late October. But she goes out into the river already in August, since it takes at least a month for her to go to the spawning site. All fish participate in reproduction from 7-8 years of age, some Baikal species earlier. Each fish spawns only a few times, since sexual maturity ends at 11-13 years of age.
The omul travels quite far to spawn, sometimes 1500 kilometers from its habitat. At the same time, it avoids coastal areas and shallow waters. Does not feed during spawning. At first, the fish move in large schools, gradually breaking up into small schools.
Attention!
Unlike the Arctic, the Baikal omul begins to spawn at 5-6 years of age. He doesn't go that far into the river, swimming close.
Spawning begins at a water temperature of 40. The female can lay 60-70 thousand eggs. But now the fertility of these fish has decreased. Young females lay 7-8 thousand, and in large individuals the number of eggs does not exceed 20 thousand. After spawning, the fish return back to their habitats. At the same time, she begins to have an active “zhor.”
Caviar develops only in clean water at a temperature of 1-30. An influx of oxygen is required, so omul spawns on a sandy or pebble bottom, where the current is shallow and good. The caviar is not sticky and breaks up into individual eggs. The fry appear after 200 days, when the water warms up to 10-120. Usually, out of 10 thousand eggs, no more than 10 fry survive. At first they stay in flocks in the same place, then swim with the flow to their permanent habitat.
Attention!
From the end of August to the end of October there is a ban on fishing for omul in all water bodies. But despite the heavy fines, the omul population is still decreasing.
Diet and spawning of omul
Favorite food is planktonic crustaceans, amphipods, larvae, eggs of other fish, whitefish and perciformes, especially gobies. In sea conditions, the omul eats a lot of gammarus, mysids, large crustaceans, small cod and sculpin species: smelt, capelin, navaga, cod, and Arctic sea slingshot.
The feeding of omul stops in August-September. Sexually mature fish gather in large schools and come from the sea to the deltas of Siberian rivers to spawn. Finding a suitable spawning site can take more than a month. During this time, the fish manages to rise upstream by 1.0-1.5 thousand kilometers, while remaining cautious and preferring to stay at the maximum distance from the shore. The Baikal subspecies does not have such problems and mainly moves short distances deep into the Selenga, Angara, Kichera, and Barguzina.
Autumn spawning of omul is associated with a long incubation period of larvae (190-220 days). The main time for laying eggs (up to 65 thousand) falls at the end of September-October, when the water temperature drops to +3-4C. For this process, flowing places with a depth of two meters and sand and pebble soil are selected. The masonry is not attached to the bottom substrate, which allows the current to freely carry it to secluded places, where it slowly develops at a water temperature of +0.5-1.5C.
After the omul has completed spawning, its appetite returns, and it begins to gradually migrate from the spawning grounds to its usual feeding areas. At the same time, nothing threatens the health of the fish, and unlike many migratory salmon (sockeye salmon, chum salmon, pink salmon), it does not die after spawning.
To learn more:
Halibut: types of fish, differences and lifestyle features
Fishing Features
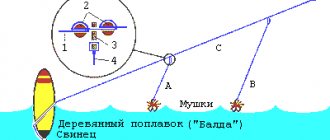
Omul is a very popular fish for fishing. Catching it is interesting, it is a kind of sport. This is a rather cunning fish, so many people catch it for fun. Amateur fishing is allowed everywhere except Lake Baikal. Fishing is prohibited only during spawning season. Summer and winter fishing are interesting, although they have their own characteristics.
In summer it is better to catch omul from the shore, but you can also fish from a boat. It is best to use a float rod or spinning rod. This fish bites on moving bait. You need to take a lot of different baits with you, since this fish is capricious, it is not known what it will like. Small baits of different colors are better. Most of all she loves red, pink, orange.
The following attachments are used:
- worms;
- flies;
- live bait;
- pieces of meat;
- red foam.
Important!
The omul has very thin lips, so it is recommended to use a landing net when fishing. And it is better to use hooks without a barb.
Night fishing is popular and can be even more productive. An interesting method is when they illuminate the water with a spotlight from a boat. The crustaceans flock to the beam of light, and the fish themselves come after them. They also fish at night using a donk; it is good to use different flies as bait. They are made from any bright shiny material, most often from beads.
In winter, you definitely need bait from crustaceans, since the omul moves little. Winter fishing through the hole “sneak peek” is popular. By looking into the water, you can evaluate the behavior of the fish, adjust the fishing method and choose the bait that it would like.
The advantage of winter fishing is that at this time of year the omul stays in schools. When the whole school approaches the hole, you can catch a lot of large fish.
Fishing for omul is an exciting activity. And when choosing the right bait, it is also useful. Photos from the most successful fishermen amaze with the richness of the catch.
Eating
Now only the Arctic variety is of commercial importance. The price per kg of omul fish is 500-600 rubles; in Siberia it costs less. It has tender, tasty meat with a high fat content. Therefore, there is absolutely no need to add oil when cooking.
But despite the large amount of fatty acids, this fish is considered low-calorie - it contains only 88 kcal. This is a dietary food that is useful even for obesity and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition to unsaturated fatty acids, omul meat is rich in other useful substances:
- amino acids;
- proteins;
- B vitamins;
- vitamins PP, E, A, D;
- minerals.
It is recommended to use it for diseases of the heart, kidneys, nervous system, blood thickening, infertility, and frequent colds. It is useful for children and women with hormonal imbalances. Contraindicated only in case of individual intolerance.
Attention!
Almost all of the Baikal omul is infected with parasites. Therefore, it can be eaten only after heat treatment or salting.
Omul is used to prepare many dishes. It has few bones, the meat is considered a delicacy. It is delicious in any form: fried, boiled, baked. Fishermen make rich fish soup from this fish. It is also used for preparing sauces, casseroles, aspic, and pie fillings.
There is a specific dish that is prepared only from Baikal omul. It's called gaghutai. It is a fillet without bones and skin, filled with a special brine. It includes salt, vinegar, vegetable oil and spices. After this preparation, local residents eat fillet within a few hours.
Pickling omul is popular. Many people prefer the dry method, when the fish is not gutted, only the gills are removed. It is preferred by fishermen. The fish is rubbed with salt and topped with nettles. During normal salting, it is gutted and salted on all sides. But some people don’t like the specific aroma of lightly salted omul. Therefore, it is often smoked and boiled. You can fry and bake without oil.
You can find a wide variety of omul products on sale. In addition to fresh frozen fish, salted or smoked fish is also sold. It costs from 800 rubles per kg. Straws or pieces of fillet are popular; they cost more – from 1,500 rubles. Various canned foods are sold in their own juice or tomato. The price for a standard jar is from 200 rubles. These canned foods are considered dietary food.
Salmon fish are considered the most delicious. One of them is omul. Due to its high nutritional value, the number has greatly decreased. Therefore, only recreational fishing is now allowed. There is a serious fine for poaching or catching during spawning. You can easily buy omul in any form in the store. This diet food is beneficial for everyone.