Pollock is a cold-loving fish of the cod family that lives in bottom-pelagic layers of water.
Its greatest distribution is recorded in the North Pacific region. Which fish tastes better?
- Cod 49%, 1237 votes
1237 votes 49%1237 votes - 49% of all votes
- Pollock 27%, 685 votes
685 votes 27%
685 votes - 27% of all votes
- Heck 23%, 581 votes
581 votes 23%
581 votes - 23% of all votes
Total votes: 2503
04.12.2019
- Cod 49%, 1237 votes
1237 votes 49%1237 votes - 49% of all votes
- Pollock 27%, 685 votes
685 votes 27%
685 votes - 27% of all votes
- Heck 23%, 581 votes
581 votes 23%
581 votes - 23% of all votes
Total votes: 2503
04.12.2019
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Characteristics of pollock
This fish chooses cold water to live (up to a maximum of 10 degrees) and during the daytime goes to a depth of up to 300 meters. These two points are partly related. At night, the fish prefers to stay in the middle or upper layers of water. Because of this, the pollock fish is characterized as pelagic (that is, it lives in the corresponding pelagic water columns). Since it is not bottom (deep-sea), this determines the ease of catching and what the fish looks like.
Pollock can descend to a depth of five thousand meters or more, traveling to spawning grounds. The life cycle is long and is about 15 years. Spawning forces pollock to move into shallow water, so during this time period large concentrations of spawning fish can be observed directly off the coast (50 meters from the coastline).
Pollock liver: benefits and harms
The liver of this fish is also very popular. It is often used in French cuisine. If you prepare pollock liver correctly, it will not only be a tasty delicacy, but also a healthy product.
The calorie content of the liver is much higher than that of the meat of this fish, but this product contains many useful vitamins. In particular, these are tocopherol and Vitamin D. The liver contains iron, copper, and Omega-3 fatty acids.
These substances are necessary to maintain the normal state of the thyroid gland, skeletal system, and normalize metabolic processes. If you consume liver regularly, you can improve your vision and slow down the aging process.
On a note! The calorie content of caviar is 474 kcal per 100 g.
Appearance
The length of the body reaches 90 cm, and the weight increases throughout life to 5 kg. It has an elongated body shape, which is typical for most fish species. The narrowing is fixed in the direction from head to tail. The body covering consists of silvery scales.
Distinctive features of this type of fish:
- there are 3 fins on the back: the first is closer to the head of medium size, then the most elevated and large;
- specificity of the lower fins: the abdominal ones are located in front of the pectoral ones;
- a small antennae grows under the lower jaw;
- darkened back and spots all over the body, as well as a marsh green tint on the sides;
- disproportionately large head and eyes, which can be seen in numerous photographs;
- the lower jaw protrudes forward in relation to the upper.
Sexual maturation of individuals reaches its peak after 3-4 years of life. During this period, maximum body weight is gained. In the standard, it can reflect different indicators depending on the habitat. More specifically, vary in the following range: 2.5-5 kilograms.
Pollock: description, preparation, composition, benefits and harm
Pollock (lat. Theragra chalcogramma) is a very common fish belonging to the Cod family. The largest populations of pollock are found in the North Pacific Ocean. Pollock, together with blue whiting, was not considered a serious food resource just a few decades ago. However, with the depletion of stocks of other fish species, the volume of catch of these two named species is increasing every year, amounting to about 3,200 thousand tons on a global scale in 2015, and the Russian catch in the same year amounted to 1,652 thousand tons. As you can see, half of the world's pollock production is caught by Russian fishermen. The leading places in pollock production are also occupied by Germany, France and the UK.
Pollock now ranks first in the world in terms of production among all other fish. Pollock is caught mainly by trawls and fixed seines. The size of the catch is highly dependent on the size of the pollock population in the ocean, which can vary quite widely from year to year, as well as from the fishing season. Currently, pollock stocks have begun to decline sharply due to overfishing, which has led to calls from Greenpeace since 2009 to refrain from purchasing and consuming this fish and its products.
A close relative of this fish is the Atlantic pollock (lat. Theragra finnmarchica) discovered in the Barents Sea, which, due to limited stocks, is of no commercial value.
Description of pollock
Pollock is a medium-sized fish. The maximum length reaches 90 cm with a weight of almost 4 kg.
Pollock lives up to 15 years.
There are three fins on the back. Characteristic features of the fish are also the presence of a very short barbel on the chin, the location of the pelvic fins in front of the pectoral fins, spotted coloring and large eyes.
Pollock lifestyle
Pollock lives in cold waters (with a temperature of 2-9 o C), preferring to stay at depths of 200-300 m (pelagic fish). It often makes vertical migrations, descending to depths of 500-700 m and even deeper.
Puberty occurs at 3-4 years. By this age, the fish reaches its maximum weight and hardly grows any further.
During the spawning period, it approaches the shores and stays at depths of 50-100 m, forming very dense aggregations. Spawning can take place at different times of the year: in the Bering Sea from March to October, off the coast of the Korean Peninsula from November to March, off the coast of Kamchatka in the spring. The water temperature affects this; females can spawn even at a sea water temperature of -1.8 o C. The eggs are pelagic.
The diet of young pollock includes small crustaceans (plankton), then, as they grow older, pollock switches to feeding on small fish (capelin, smelt) and squid. Cannibalism (eating one's own larvae and fry) is a very common phenomenon among pollock.
Pollock in cooking
If you are not a resident of the Pacific Coast or even just the Far East, you are unlikely to be able to buy fresh pollock in the store. It is usually sold frozen, either whole or as fillets.
Among pollock products in retail chains you can also find salted caviar and pollock liver. The main filler of the so-called “crab sticks” and “crab meat” is pollock (fillet). Surimi is from the same series.
Beer lovers should be well aware of the now widely sold “amber fish with pepper.” This is dried pollock.
Countless dishes can be prepared from pollock. The fish meat is dry and dietary, which should be taken into account when preparing pollock. So, if you decide to bake it, it is best to do it with vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, carrots, onions) and in foil, otherwise it will turn out dry. If you decide to fry fish, then after shallow frying it is advisable to close the pan with a lid and simmer the fish in this way.
Pollock soup will be very healthy and tasty, in which, for variety, you can put several pieces of fattier fish (halibut, salmon, etc.).
Pollock is a very popular fish, the taste of which is known to many citizens since childhood. Back in Soviet times, there were so-called fish days, when workers and employees in canteens were offered pollock on Tuesdays and Thursdays. The size of the pollock population is simply huge, so the fish is widespread throughout the world, including in North America. The famous McDonald's uses fillets of this fish to prepare breaded fish sticks, as well as to prepare a host of other fish dishes.
Diet
In terms of what pollock eats, it can be compared with mackerel, cod, tuna and horse mackerel (“related” fish species). He finds food for himself at several levels of the food chain, not far from each other. Changes in diet are especially evident as individuals grow older.
What to eat at the beginning of life:
- plankton (small crustaceans);
- amphipods;
- krill;
- nematodes.
Then, as they grow, larger prey is added to the diet, which the individuals hunt on their own. Most often these are squid and small fish.
Predator or not
Pelagic fish species are mostly predators. This is confirmed by the above facts about pollock eating other living organisms. Pollock, like all inhabitants of the aquatic world, occupies an important ecological niche in the waters of the world's oceans and individual seas.
It manifests itself when it consumes larvae and fry of its own species (not adults). The fish in question can happily feed on eggs and hatched fry of other fish species. Large fish of other species are not included in the pollock diet.
Are there many bones in pollock?
Naturally, pollock has a large ridge along the body and bones extending from the sides. Small bones are not found in other parts of the carcass. Therefore, the fish is not bony.
The side bones are easily pulled out for later eating of the fish. But provided that the fish is of good quality, that is, it is not small-sized young fish and not frozen during storage.
When purchasing cut fillets rather than whole headless carcasses, during verification they may also contain a small number of individual bones. This aspect depends on the specific manufacturer. That is, on the specifics of the supplies of fish products purchased by him and the method of production of the semi-finished product. According to organoleptic indicators, this is a disadvantage for pollock.
Are there many bones?
Pollock has a large ridge, it runs through the entire body, with large bones extending from the sides. Small bones in meat are almost invisible. Therefore, this fish can be called not bony.
The side bones can be easily removed from the meat. But there is an important condition here - the carcass must be of high quality, large and not frozen several times during transportation and storage. When buying cut fillets, rather than whole carcasses without heads, you can also find a small number of small bones. But here an important role is played by the method of production of semi-finished products and the specifics of the work of specific manufacturers. Due to the fact that this fish is not bony, it is often used to prepare delicious dishes. It is fried, boiled, smoked, steamed, baked in the oven and grilled, and is also used to make fish soup.
Yandex.Pictures
Where does it live in Russia?
Trademarks produce their products in different regions of the country: Kamchatka, Murmansk region, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, Moscow and Moscow region, Ryazan, Kaluga regions, etc. But this does not mean that pollock is found everywhere. Supplies are made from a limited number of locations. Domestic pollock or pollock caught in China ends up on store shelves (we remind you that this country borders Russia, which is why supplies from here are financially profitable). But Chinese manufacturers can artificially increase the water composition of the carcass, thus increasing the mass of the frozen product. Therefore, domestic catch remains prerogative.
Pollock where it lives and lives near the Russian Federation:
- Barencevo sea;
- Bering Sea;
- Japanese Sea.
Aquaculture (when fish is sold through artificial cultivation) is not relevant for pollock. This activity is more justified for salmon and more expensive varieties of fish. Pollock (unlike even salmon, and even more so eel, sturgeon, etc.) is a cheaper fish that is easier to catch on a large scale in the natural environment.
River or sea
Important information for determining whether a fish is bony or not is the place in which it lives. That is, whether the fish is sea or freshwater river. Pollock is not characterized as a river variety and belongs to the first type. This means it has fewer bones (especially small ones in the pulp itself). But to be extremely precise, the habitat of pollock is most likely in oceanic waters. Therefore, pollock is categorized as either Pacific or Atlantic. Since the seas flow into the oceans, schools of pollock eventually spread by geolocation and constantly live in the sea area. The main parameters of the waters in which this fish lives are salinity and temperature. Pollock is found where it does not exceed 10 degrees, and the habitat is not freshwater.
Why is it sold without a head?
An important aspect for answering the question posed here is the frequent detection of helminths in the head area of fish. And also the overall usefulness of the product is questioned when selling a full carcass along with the head.
Pollock can indeed have worm-like parasites in its body. The favorite place for parasites is the space behind the gills, but many species of other fish suffer from this problem, not just pollock.
The main point is still the overall value of the whole fish carcass. Previously, in the Soviet Union, pollock fish was not considered valuable or edible. It was mined on a large scale, but for the production of animal feed. That is, it went towards the development of agriculture and ensured the production of food for pets (to a lesser extent). Because of this, its population began to decline sharply, and pollock was transferred to the category of valuable species. At the same time, it entered the diet of residents of the fraternal Soviet countries. Its production has decreased. But it can be said affirmatively that it makes up the majority of the world's fisheries. Its production is very simple (since pollock fish lives in the upper layers of water) and inexpensive. Therefore, the value of the carcass completely disappears. Usually, buyers' heads and entrails go to waste anyway. And for the production of feed, all this is still valuable. Therefore, they are used for production purposes, and carcasses without heads and without tripe enter the consumer market.
The assumption that the fish has an unsightly head and this may aesthetically discourage the buyer from purchasing it is not entirely tenable. You can verify this by looking at a photo of pollock.
Composition and benefits
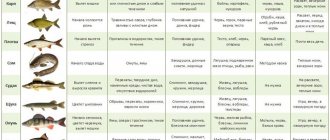
Since we are talking about which is healthier, pollock or cod, we should consider the chemical composition of both representatives of the cod genus. Each of them contains vitamin A, thiamine and other B vitamins in sufficient quantities, including cobalamin and pyridoxine, ascorbic acid, vitamins E, H and PP. The mineral composition is also rich, and all cod varieties contain large amounts of iodine for the thyroid gland, calcium for joints and bones, and phosphorus to improve brain function. Many people today are thinking about extra pounds, so the question of which is better, cod or pollock, for them comes down to which has more calories. Nutritionists assure that both fish have the same calorie content, so they can be safely included in the diet.
Is it possible to eat the head
Parasitic worms are found inside various representatives of the animal world and humans (ascaris and pinworms are common in the human population). Therefore, their presence in fish is not something shocking. The life cycle of such worms involves the transition from one host to another in the form of eggs, larvae or adults. They can enter the body when they are present in unprocessed food. Therefore, consuming raw fish is dangerous to health. After all, worms can settle not only inside the head.
During heat treatment, the danger to humans is reduced to zero. But this is an additional point for refusing to sell carcasses together with the head. Fundamentally, this by-product has no nutritional value for consumers themselves, because the fish is cheap.
Chemical composition and KBZHU
Pollock contains:
- valuable acids: polyunsaturated (arachidonic, omega-3, linoleic), saturated (stearic, myristic, palmitic), monounsaturated (oleic, palmitoleic);
- vitamins: A, C, Retinol, PP, B1 and B2, as well as B6 and B9;
- microelements: calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, etc.;
- trace elements: zinc, iron, iodine, fluorine, etc.
Pollock is a leader in the level of beneficial selenium, iodine, and protein. It also has low histamine levels, which is a positive feature.
Nutritional value per 100 g:
- fats - 0.9 grams;
- proteins - 15.9 grams;
- cholesterol - 50 milligrams;
This fish has no calories. There are approximately 70 kcal per 100 grams of product. Thanks to this, pollock can be considered dietary. But when frying, the calorie content increases due to the oil used.
Pollock: benefits and harm
Marina Kopytko
Ph.D., nutritionist, head of the department of dietetics at the Revital Park clinic
Pollock belongs to the category of low-fat fish of the cod family, therefore it is quite actively used in dietary nutrition. The fat content in its meat is only 1 gram per 100 grams of product, but there is a lot of protein - 16 grams. The calorie content of pollock fillet is very low - only 70 kcal. The meat is not bony, with a neutral, pleasant taste. And what is especially valuable is that this white fish is suitable for both adults and children. The most valuable part of pollock is the liver. Vitamin A, which is one and a half times more in pollock liver than in cod liver, is necessary for maintaining good vision, immunity and cell renewal. The calorie content of pollock liver is very high (more than 500 kcal per 100 grams of product) due to the fat it contains as much as 50 grams! Therefore, its recommended intake is no more than 20 grams, which is only one tablespoon per day.
See the results of a study of pollock fillets conducted by Roskachestvo
HERE
It should be separately noted that pollock liver contains most vitamins and minerals in quantities significant for health, I would especially like to highlight vitamin D, vitamins B2, B9, E and such important minerals as copper and iron. In addition, pollock liver contains polyunsaturated fatty acids of the omega-3 class, the role of which in maintaining brain function and immunity cannot be overestimated.
Pollock caviar is a high-protein, low-fat product. It is a source of vitamins B6 and B2, copper, phosphorus and sulfur. However, it is important to remember that in terms of chlorine and especially sodium content, just 50 g of caviar will almost double the daily salt intake of a person.
Vitamins and minerals
Pollock meat contains B vitamins, including folic acid (B9), which is vital for the human body. It should be noted that there is a fairly high concentration of vitamin PP (4.6 mg per 100 grams of fish), which reduces cholesterol levels, promotes fat metabolism and helps synthesize hemoglobin and red blood cells. It also contains vitamins A and C, which are necessary for redox processes.
Of the minerals, pollock contains the most fluorine, potassium, calcium and phosphorus. Thanks to this composition, pollock is considered a very healthy fish.
Another undeniable advantage of pollock is its high iodine content. In this regard, pollock can be used as a tasty and effective remedy for the prevention of thyroid diseases. In addition, its meat contains iron, sulfur, magnesium, zinc, which are necessary for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and immunity.
Minuses
The fact that pollock is a low-fat fish is both a plus and a minus at the same time. The fact is that precisely because the product is lean, many people cook it in breading and batter. But in this form, fish cannot be classified as dietary.
In addition, pollock caviar, which uses salt in its preparation, is not recommended for people suffering from hypertension, as well as those with stomach or intestinal problems. You should not include pollock caviar in the diet at the time of exacerbation and remission of peptic ulcer, gastroduodenitis and bile duct dyskinesia.
Those who are allergic to fish and seafood should also limit their consumption of pollock.
For those for whom fish is not contraindicated, we offer a recipe.
Pollock in mustard sauce
For 4 servings: 4 pollock fillets (200 grams each), 500 ml vegetable broth, 1 bay leaf, small bunch of parsley, 6-10 white peppercorns, sea salt. For the sauce: 4 tbsp. spoons of olive oil, 3 tbsp. spoons of flour with bran, 1-2 tbsp. spoons of any mustard (according to your taste), 1 tbsp. a spoonful of lemon juice, sea salt, freshly ground white pepper.
Preparation
- Place the fish in a wide saucepan, placing a few sprigs of parsley under each fillet. Pour in cold vegetable broth, add bay leaf and peppercorns. Bring to a boil over low heat and cook for 5 minutes. Remove from heat, cover and let stand for another 5 minutes.
- Carefully, so that the fish does not fall apart, drain the broth and strain into a clean saucepan. Place over medium heat and evaporate a little - you will need about 400 ml. Keep fish warm.
- For the sauce, heat the oil in a frying pan and mix it with the flour. Fry, stirring, 3 minutes. Then, stirring constantly, pour in the broth. Continuing to stir, bring the sauce to a boil. Cook until thickened, about 5 minutes. Add mustard, lemon juice, salt, pepper and stir. Place fish on prepared plates and pour sauce over.
Find recipes for delicious and simple pollock dishes HERE
Be the first to know about new materials from Roskachestvo by subscribing to our newsletter .
Selection and storage
Pollock is often supplied to stores frozen. When choosing it, you need to pay attention to certain parameters. First, what the fish looks like. The surface of the carcass should have a light and uniform shade. The presence of stripes and extra inclusions of yellow or green color (not spots of natural origin in the color of the fish) indicates that the carcass was thawed and frozen again. The presence of snow and ice indicates improper storage with a possible loss of the taste of the fish during its preparation. According to GOST, frozen specimens must be stored at a temperature not lower than -18 degrees. This is the only way the fish retains its taste and beneficial properties.
When choosing by manufacturers, keep in mind that the Far Eastern ones are more often than others characterized by the high quality of their product. Russian manufacturers sell a cheaper product, so it is popular as an export.
“After purchasing fish and for its further preparation, you need to defrost it correctly. It is better to do this in a gentle mode, that is, move the carcasses from the freezer to the main cooling chamber. Otherwise, the fish dish becomes tasteless.”
How to choose and how to store
You need to be able to choose the right product. Pollock is almost always sold frozen. Pay attention to the skin color of the pollock. It should be a light shade without blemishes.
If there are dried areas of the skin, this indicates that the product is not fresh. You should also avoid products with a thick layer of icing. In addition to the fact that you will have to pay for ice, this is probably a sign of repeated freezing.
Pollock is stored in the freezer at a temperature of about 18 degrees. Temperature changes should not be allowed. If stored improperly, the surface of the fish changes and a specific smell appears. Shelf life is indicated on the product packaging.
It is best to defrost fish in the refrigerator. To do this, simply move the fish from the freezer to the refrigerator. The taste of meat deteriorates significantly when defrosting in a microwave oven or hot water.
The best way to bake fish is in the oven.
Properties
General useful qualities:
- strengthening the immune system thanks to the beneficial substances and vitamins contained here;
- maintaining the functioning of all vital systems of the body (increased zinc and iodine content ensures the normal functioning of the reproductive system and other properties);
- strengthening teeth and bones;
- reducing blood cholesterol and reducing the risk of developing atherosclerosis (when switching to proper nutrition including pollock);
- also increasing the elasticity of vascular walls;
- improving skin quality;
- etc.
Fish contains many useful substances, which is why its consumption is recommended for children and adults.
Negative properties are extremely difficult to identify. For example, an allergy to seafood is acceptable. But pollock in this regard can be called a non-allergenic product.
Composition and calorie content
Due to its low fat content, pollock remains one of the most useful marine inhabitants. 100 grams of product contains 16 grams of protein and only 1 gram of fat. The same amount of pollock contains only 70 kilocalories.
On a note! Fried pollock already contains 127 kcal, fried in batter – 145 kcal, baked – 77 kcal, stewed – 76 kcal. Calorie content also depends very much on the ingredients you add to the dish.
Pollock has a neutral taste and smell. Fish meat contains very few bones, which means it can be cooked even for children. The liver is considered the most valuable part. It contains a lot of vitamin A, which is necessary for good vision.
The fish also contains vitamin B9 and folic acid, which expectant mothers need for the proper development of the fetus.
As for minerals, the product also contains:
- potassium,
- phosphorus,
- iodine,
- calcium,
- zinc,
- iron,
- fluorine,
- magnesium,
- sulfur.
On a note! Pollock is digested in the human body in about three hours.
Pollock fillet
Fishing
If we take cod species into account, pollock occupies a leading place among them in terms of catch volume. To a greater extent, this volume also depends on the place of production, the fertility of the pollock generation and seasonality.
It should be noted that in the 90s. its production was estimated at about five million tons per year. Since this caused the threat of extinction of the species, many countries reduced its production several times.
For Russia, the production of this species in volume is almost half of the total fishing volume.