Among the wobblers most often used in the upper water horizons, it is worth noting:
- Advantages and disadvantages of bait
- Spinning equipment
- Classification of wobblers
- Models for surface fishing
- Deep-sea wobblers
- Selection Basics
- Basic wiring of wobblers
- Catching different types of fish
- Features of winter fishing
- Tips from experienced fishermen
- At the very end of the “braid” you need to step back a little and tie a small loop. There is no need to tighten it;
- We must pass the remaining tip through the ring;
- We return the tip back again and pass it through the loop we made, but did not tighten;
- We wind the tip around most of the fishing line with three or five turns;
- Again we return the remaining end to the loop and thread it through it again;
- We tighten our knot and cut it off.
A wobbler is a modern artificial fish that resembles the usual food of predatory representatives of the fish “family”. A distinctive feature is its volume, which means the predator will definitely notice the prey and try to get its next prey.
In its movements, it is very similar to the movements of a real fish. Most often, it is made from high-quality plastic, but sometimes models are made from balsa wood. Equipped with double or triple hooks, in quantities from 1 to 3 pieces.
In principle, this is all the introductory information a fisherman needs. This is exactly what our article today is dedicated to. We will try to consider what is somehow connected with wobblers, their choice and use.
Choosing tackle
To make a choice, the fisherman must take into account in advance the following technical data that relates to the reservoir where fishing will be carried out:
- Water color;
- Current speed;
- Depth.
Fishing process
When you arrive at the site, immediately look through the pond. Using the presented bait you can easily catch the following fish: chub, catfish, perch, pike perch, pike, and asp.
The success of fishing will depend on the model, its size, the reservoir itself, fishing technique and compliance with the most important rules for using gear. Most often, to secure the wobbler, fishermen decide to use a knot called “Rapala”. Follow simple rules and your bait will be tied very well:
- At the very end of the “braid” you need to step back a little and tie a small loop. There is no need to tighten it;
- We must pass the remaining tip through the ring;
- We return the tip back again and pass it through the loop we made, but did not tighten;
- We wind the tip around most of the fishing line with three or five turns;
- Again we return the remaining end to the loop and thread it through it again;
- We tighten our knot and cut it off.
After high-quality fastening, you can move on to discussing wiring techniques. It could be as follows:
- Uniform is the simplest and most well-known method. The bait is thrown to the required point and smoothly pulled up. Best of all, it works evenly when the predator enters the active pecking phase;
- Stop & Go or Stop & Go is a wiring method in which winding is carried out with even pauses after every 3-4 revolutions of the spinning rod. Pike loves to catch its prey when it stops and pauses, so fishermen recommend using this method in those reservoirs where there are a lot of pike;
- Twitching is a constant twitching of a wobbler. This method sets the bait in motion and also gives it a sort of randomness. The best bite is perch;
- Walking the Dog - characterized as slowly reeling in the line.
Fishing with wobblers is a promising and interesting activity. The volumetric bait works effectively at a variety of depths. Thanks to the huge assortment, every angler can easily choose the appropriate option for specific fishing conditions. These baits are quite realistic, very similar to wounded live fish, and can be used for more than one season. For successful fishing with wobblers, it is important to know what kind of fish bites on them, what species exist and how to choose depending on the fishing object.
How to choose a wobbler
In addition to wobblers that imitate small fish, you can also find successful versions of animals and insects that live in water bodies. Considering the diversity of artificial baits, it is necessary to understand their main parameters and characteristics.
Form
The quality of the game, the specific application, purpose, as well as possible fishing techniques will depend on the shape of the model. Among the main types of wobblers are:
Topwaters deserve special attention - bladeless models with an elongated body shape, similar to a minnow. Wobblers are suitable for catching predatory fish from the surface of the water in the warm season. This group includes:
There are also composite versions of wobblers. Their shape can be like that of minnows, crankbaits or shads. They have a common name "components". This category also includes swimbaits - bladeless versions consisting of separate segments.
Size
Wobblers range in length from 2.5 to 25 cm, but models from 4 to 9 cm are catchy. To catch trout, perch and chub, the smallest baits are enough, but you can catch bream and carp only with models from 4 cm. When fishing For pike, large lures up to 25 cm in length have proven themselves well.
When choosing wobblers by size, it is worth knowing that the larger it is, the better its stability in the game. Such versions are less susceptible to external factors. It is not worth using small baits in the current; it is very difficult to control their behavior in such conditions.
Fishing with wobblers will be both spectacular and productive only if they are as realistic as possible to natural food. Models with provocative colors, as well as black, silver, and gold, will be attractive to fish.
Lures of natural colors are more suitable for hunting in clear water, where there is sufficient visibility. They work during the cold season. Acid colors are relevant for summer fishing in low light conditions. They are effective for use in cloudy water. Black lures are versatile; a particularly good catch is obtained when fishing in warm weather. Chub and other white predators respond well to them.
Oscillation frequency
This parameter indicates the number of oscillatory movements that the wobbler makes per minute. Their frequency can be different, it all depends on the purpose of the bait, the object of fishing. This characteristic is created by the shoulder blade and the shape of the body. Lures are:
- low frequency;
- mid-frequency;
- high frequency;
- without frequency play.
Catching pike with wobblers will be very effective if you use baits with a wide sweeping amplitude and low-frequency action. High-frequency models are optimal for catching perch and chub.
Degree of buoyancy
The reaction of the predator depends on the degree of buoyancy of the bait, whether it will take it or not. It is indicated on the wobbler in capital Latin letters:
You need to choose a wobbler with varying degrees of buoyancy, taking into account the behavior of the fish and its mood. If hunting is carried out in the cold season, then it is better to give preference to suspenders such as minnows or low-sinking options. A floating wobbler will be appropriate when the fish is active and aggressive retrieve is necessary.
Pike has an impressive mouth with many teeth, so small wobblers are not always used. The size is also affected by seasonality: in cold water, experienced fishermen recommend using smaller models than in the warm season. Individuals up to a kilogram are caught on bait of any size. Sometimes the “toothy” one attacks 2-inch perch silicone.
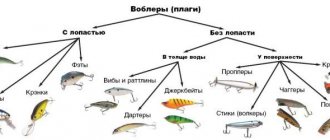
Body shapes of wobblers. Classification of wobblers.
Based on their body shape and structure, wobblers are classified primarily by the presence of a blade. The best idea of the classification of wobblers by shape is given by the following picture.
Wobblers with a blade are deepened due to it. This is an extremely important detail of the bait, which largely determines its behavior in the water. Visually, the blade looks like a transparent plate located on the “chin” or “nose” of the wobbler. When the blade is located at an angle to the axis of the wobbler body, the water pressure on the blade that occurs during movement deepens the wobbler to a certain depth. This is the most common class of wobblers.
Wobblers without a blade move in the water only due to the shape of their body and their own weight. Unlike bladed wobblers, many bladeless wobblers are suspended or sinking. As the retrieve speed increases, these models tend to float up, unlike classic wobblers with a blade. Recently, the number of models of bladeless baits has been rapidly increasing, since they are most similar to the fry of real fish. They are distinguished by the greatest variety of forms, games and applications. Most bladeless models of wobblers are surface or shallow diving, since the excessive weight required for decent depth interferes with stable play. The exceptions are jerktails.
Minnow - translated as “fry” and looks like a live bait roach or bleak. This form is the most common, has a long oblong body shape in the form of a narrow block. They are often similar to one another - this class of baits is very conservative in geometric parameters, but very diverse in colors and sizes. When retrieved, minnow wobblers show varied play and good controllability. Some types of baits form a snake, others seem to roll from side to side, and others seem to “grab” with their sides. There are three types of minnows - floating, sinking and neutral.
Shad is a thick and short wobbler, vaguely reminiscent of a herring in shape. Shads (or “sheds”) often have a large shovel and are therefore designed for great depths. Some models also sink. Shed are successfully caught in the current. The shad is structurally designed for both continuous wiring and twitching. They are rarely used for trolling. Shad wobblers have built-in weights with a shifted center of gravity. They have a very steep dive trajectory (almost vertical). Wobblers of the “Shad” type are recommended for use in deep-water areas of the reservoir. The game of these baits is of medium intensity.
Crank is a wobbler with a wide, laterally flattened shape, similar to a bream or silver bream. Due to its shape, it creates its own aggressive play of varying intensity during wiring: wide amplitude, rather significant vibration frequency. The cranks withstand strong currents well and play well on a uniform retrieve even at very slow reeling speeds. Some cranks twitch very well, but some tumble ridiculously, get lost in space and even get caught in the fishing line. Like other classifications of wobblers, cranks have floating, neutral (suspender) and sinking options. There are models with a large blade with sharp and rapid penetration of up to 6 m.
Fat (Fat) - thick-bellied drop-shaped wobblers. The ratio between length and width (more precisely, height) is up to a maximum of 3:1, and the ratio between width and thickness (i.e., two transverse dimensions) is up to 1.5:1. Most fat wobblers are floating, shallow-water, small in size (perch), and quite short. Fats are designed for aggressive, high-speed wiring without pauses. Since the attachment points of the tees are minimally spaced, the tees of thick and short wobblers tend to cling to each other. Fetas are liked by perches, pikes and ides.
Rattlin is a bladeless flat wobbler model with rattling balls inside. When guiding, it stands at an angle, with its nose down, and creates frequent play of small amplitude with noise and vibration effects. It also differs in the form of a ring for attaching fishing line located on the back of the bait. Rattlins are basically a sinking bait.
Darter - a wobbler with an unpredictable game, as a rule, sinking, a jerking technique is used when retrieving, allocation to a separate classification group is doubtful, there are few references to these wobblers, some anglers consider them a kind of jerkbets, others find in them something between minnow and shad. Darter wobblers are often larger than other wobblers. They are distinguished by intense, sweeping play. The wiring is jerky. Wobblers are noisy. One of the most famous darters is the Chubbi Darter from Salmo.
Jerkbait (jerkbait, “jerk”) is a bladeless, laterally flattened heavy wobbler for pike, usually of large size, which does not have its own game. The operating principle is based on simulating the behavior of a sick, wounded, thrashing fish. It requires special wiring, only thanks to it the bait begins to move in its characteristic style, making sweeping, wagging movements when moving from side to side. This is where the name comes from: from two English words, “djerk” - jerk, “bait” - bait. The large size of the Jerk Bait attracts the attention of pike of different sizes, even weighing up to a kilogram. Jerkbaits are used when fishing with a spinning rod, the test of which exceeds the weight of the wobbler by 10-20 grams. Jerkbait wobblers can also be used for trolling type fishing. This type of wobbler is further divided into sinking “divers” with a diving depth of more than 1.5 meters, and floating “gliders” up to 1.5 meters. Swimbait is a compound jerkbait.
Popper. According to the classification of wobblers, popper belongs to the group of surface, floating wobblers. The name translates as “gurgling.” The popper is shaped like a fish with its mouth open. This blunt nose creates the characteristic gurgling, smacking sounds and splashing waves when pulling poppers. The “target audience” of the popper is mainly pike and perch. Fishing is carried out in shallow water, preferably in “calm” water. A popper can often be used to fish in dense thickets of grass where the use of other wobblers is difficult.
Walker The body shape is spindle-shaped or “banana-shaped”. Bladeless wobbler, floating, surface. When correctly guided by jerking and twitching, the walkers make zigzag movements along the surface. This “snake” attracts not only pike, but also trout, chub, ide and perch. Sometimes walkers are also called Stickbaits.
Chagger. Chagger is a type of popper. At the front end of the body, the chagger has a depression. Thanks to it, the chugger has a special character of play and makes special smacking and squelching sounds. When at rest, the chugger hangs in the water at an angle with its head and mouth facing upward. If you pull the fishing line, the chugger dives, capturing an air bubble with a characteristic sound and then, having traveled the desired distance at depth, it emerges to the surface. Posting must be accompanied by pauses. The bait is designed for perch and pike.
Crawler is another type of popper - floating, surface bait. The shape imitates various insects. It works on the principle of poppers, creating gurgling, squelching sounds. Simulates an insect that has fallen into the water. Wiring with jerks and jerks. Crawlers are good at seducing trout, ide, chub, and asp. The shapes and body structure of crawlers are sometimes very intricate. The given classification is very conditional. The variety of body shapes of wobblers is so great that many occupy intermediate positions or can be classified into several categories at once. Some models cannot be classified at all, because they have a completely original form, play and application.
How to fish with a wobbler from the shore and boat
Pike fishing with wobblers requires a certain rod. As a rule, this is a stick of medium action with a dough from 10 to 45 g. The amplitude of the bait reflects the frequency of oscillations at the tip of the spinning rod, so working with a fast blank is uncomfortable. The predator prefers uniform wiring, so the “twitch” technique is effective - animation using short twitches to the side.
To fish from the shore, take a medium-sized rod up to 2.4 m tall. It is difficult to cast with a taller model, because shrubs, grass and trees grow along the banks of reservoirs. Fishing from a boat does not require long poles; you can swim to any promising point. Returning to the question of the price of baits, we note that when fishing on the shore there are more losses; it is not always possible to unhook an expensive wobbler from a branch on the opposite bank or remove it from a snag in the middle of the reservoir.
It is better to take a reel with a size of 2000-3000 units; such a spool is enough for long casts and fighting large trophies. The cord should have a greater margin of strength than when fishing with a jig. Instead of thick fluorocarbon leaders or tungsten, spinners use metal twists.
You will need a spinning rod with a fast or medium-fast action with a blank length of 2.1 - 2.4 m. With such a spinning rod it will be convenient to cast the bait and control its presence in the water. With dough for baits up to 14-16 grams.
How to properly fish with a wobbler
And then many may disagree with me. Every fisherman believes that his school is the best. This is true, just like the fact that we learn individually. Everyone has their own “tricks”.
When my friend and I were learning to fish with wobblers, there were no arguments. I won’t be mistaken if I say that at that time we were the only fishermen in our village who used a wobbler. We learned from videos. You can't argue with the authors. However, usually standing ten meters from each other and periodically peeking, trying to repeat the teachings of the video guru, everyone developed their skills.
I’ll try to briefly describe below how to develop skills and learn how to fish with a wobbler. At least this is the view of a person with some experience.
We fishermen are all different. Temperament and anatomical proportions make the bait move differently. Plus, there are differences in the set of spinning rod, reel, and cord.
Something like that. I hope that the note will be of some help to the novice wobbler lover. Believe me, learning to fish with a wobbler is no more difficult than with any other bait. You just need desire and patience.
The variety of models can confuse any inexperienced fisherman. Of course, you can catch fish even with a simple homemade wobbler, or a cheap Chinese one. Many fishermen prefer inexpensive ones, because the bait may be lost forever during fishing. But there are some models of wobblers that have earned the respect of fishermen and won prestigious awards:
Wobbler operating horizon
Conventional symbols are also used to indicate the operating horizon of the wobbler (different manufacturers may have the same symbols corresponding to different ranges of working depths).
SSR - Super Shallow Runner - extra shallow wobbler. (Anyone get it? I don't.) SR - Shallow Runner - surface-mounted wobbler. DD - Deep Diver - deep model. DR - Deep Runner - same as DD. SDR - Super Deep Runner - the same as DD, only with slightly greater diving depths. XDD - Extra Deep Diver - extremely deep wobblers with a diving depth of 7+ m.
As you can see, the keywords are Shallow, meaning surface baits, and Deep, meaning deep ones. The prefixes Extra and Super indicate only the degree of these properties. With minimal knowledge of English it is quite easy to understand.
Which wobblers are the most catchy?
The variety of models can confuse any inexperienced fisherman. Of course, you can catch fish even with a simple homemade wobbler, or a cheap Chinese one. Many fishermen prefer inexpensive ones, because the bait may be lost forever during fishing. But there are some models of wobblers that have earned the respect of fishermen and won prestigious awards:
| № | Photo | Name | Characteristics |
| 1 | Zip Baits Khamsin-SR 70 | This seven-centimeter bladed wobbler is equipped with two tees and a magnetic system that allows you to cast it very accurately. It performs well both in still water and in currents. | |
| 2 | Imakatsu Power Bill Minnow 115SP | The Minnow is 115 mm long, equipped with three hooks, has realistic animation and a set of balls in an empty body, thus, when wired, it spreads sound waves. | |
| 3 | Tsuribito Hard Minnow 95F | This bait is famous for its realistic animation, which will not leave any pike indifferent. | |
| 4 | Yo Zury L-Minnow 66 | Perfect for depths of 1-1.5 meters, the choice of many sports fishermen. | |
| 5 | Rapala X-Rap 10 | An excellent suspender, known for its performance. Due to its significant weight, it can be cast over a long distance and is good for fishing from the shore. |
The depth of the wobbler when retrieved is determined by the size and angle of the nose blade . The smaller it is and the closer the angle of location is to a straight line, the shallower the depth the wobbler goes. Accordingly, the following models are distinguished:
Types of wobbler wiring
There are actually several options for wiring a volber. The countless variations used by many successful anglers are usually variations of the basic types.
Uniform wiring. Retrieving the wobbler by uniformly rotating the reel without jerking or moving the rod tip. In this mode, the wobbler, which has its own game, reaches the depth specified by its characteristics and plays as it should. Most wobblers work great when pulled evenly. The same wiring is used for rotating and oscillating spinners. There are slow and fast uniform wiring. The technical characteristics of wobblers usually indicate depth. For example, 0.5-1m. This means that with a slow retrieve, the wobbler will play steadily at a depth of 0.5 meters, and with a fast retrieve - 1 m. A slower retrieve is not recommended for it, as is a faster one: the action of the bait may be disrupted. Uniform wiring is one of the simplest and most undemanding. Any gear.
Trolling, track. A type of uniform retrieve in which the angler does not have to touch the rod at all until the bite occurs. In fact, it does not carry out wiring as such. A boat does this instead. On oars in case of track and outboard motor in case of trolling. The meaning of fishing is shifting towards the selection of baits and the choice of place and time of fishing. When trolling, a wobbler, evenly towed behind the boat, goes at a certain depth and plays only due to its own characteristics. This depth is usually the maximum specified in the characteristics of the wobbler. Those models that are designed for trolling can withstand it quite accurately. Universal wobblers can go deeper. Twitching wobblers that do not have their own game, small surface wobblers for trolling and tracks are not suitable.
Uneven wiring, wiring with accelerations. When the retrieve is uneven, the fisherman quite often changes the speed of the bait, using only the reel. He changes the reeling speed, leaving the spinning rod in the same position. They make a slow retrieve, barely rotating the reel handle, the wobbler floats up, then they speed up the rotation - the wobbler goes deeper and changes the game to a more intense one, then they change the intensity of the reeling again. This is how they entice a passive predator to grab it. Most conventional wobblers are suitable for uneven wiring.
Stop and go. (from English stop and go). A combination of uniform and uneven wiring techniques combined with pauses. The essence comes down to guiding the wobbler using steps or a ladder. When retrieving quickly (with a reel and rod), the wobbler quickly deepens. Then comes a stop, during which the wobbler floats up, sinks evenly, or simply hangs in the water. The calculation is that the intensive period of fishing will attract fish, and at the moment of a pause it will quickly overtake the bait. Also, in this way you can fish different depths from the surface to the bottom in one trip. Floating wobblers or suspenders are especially effective for such wiring. Stop and go fishing requires the selection of gear and bait. For example, you need to know that this wobbler goes deep to 1 m at 10 revolutions of the reel at a certain speed and floats to the surface in 5 seconds from a depth of 1 m. Accordingly, for a given model of wobbler and selected gear, the wiring should consist of 10 turns of the reel, a pause of 5 seconds, again 10 turns of the reel. In this case, the wobbler will go sawtooth to a depth of 1 m. You need to adapt again to other gear and fishing conditions. Typical wiring for jig fishing. Hence the term “jigging.”
Twitching. Unlike uneven retrieving where they work with a reel, when twitching the tip of the rod works, and the reel provides uniform reeling. The angler jerks the tip of the rod, causing the wobbler to make throws and pirouettes. Twitching is fished in the surface layers of water with small wobblers designed specifically for twitching. The most famous of these baits are poppers. Twitching wobblers often do not have their own game at all and do not work with even wiring. You can also twitch with regular wobblers. Twitching simulates a wounded fish. Jerking or Jerking. A forceful method of guiding large, heavy baits with large gear. As the name suggests, wobblers are used - jerkbaits and swimbaits. Often these are composite wobblers. A strong jerk makes the wobbler rush deeper and to the side, and the reel picks out the slack line. Strong jerks force the wobbler to change its usual game and imitate the fleeing prey. Sometimes the angler contributes to the deviation to the sides by changing the direction of the retrieve. Large active fish are caught in this way. Jerk wiring can also be carried out with conventional wobblers. Then it looks like aggressive twitching.
Rafting or vacation. Alloy wiring is used mainly on rivers with medium and strong currents. There are a lot of different variations. For example, a wobbler is thrown into one place and, using the action of a rod and reel, they ensure that it is carried by the current to the intended fish stop, they simply float the wobbler downstream to a considerable distance, inaccessible for casting in this place, in the rapids they lead the wobbler not towards themselves but away from themselves, so as in a very strong current the wobbler does not play. Such tricks allow you to fish in cramped conditions when accurate long-distance casting is not possible.
In conclusion, I would like to mention one more term - Casting. This is not exactly a method of guiding wader, but rather a method of casting with a spinning rod. He came from England, where casting competitions with a spinning rod with a multiplier reel have long been held: who can cast the farthest, who can cast more accurately, etc. However, the recommended type of wiring is often written on wobblers: casting, twitching. This means, as a rule, that the wobbler has good flight characteristics and is suitable for long-range accurate casting with a spinning rod.