In the fresh water bodies of Russia and the bays of the seas, the princess pike, beloved by fishermen, lives; the predator prefers weak or moderate currents, quiet backwaters, thickets of reeds and algae.
Find out how common pike grows and reproduces in nature and during home breeding, which one grows in a year, and how many offspring it bears. Do you like pike dishes?
- Yes 86%, 4074 votes
4074 votes 86%4074 votes - 86% of all votes
- No 10%, 495 votes
495 votes 10%
495 votes - 10% of all votes
- I don't eat fish 3%, 159 votes
159 votes 3%
159 votes - 3% of all votes
Total votes: 4728
18.06.2020
- Yes 86%, 4074 votes
4074 votes 86%4074 votes - 86% of all votes
- No 10%, 495 votes
495 votes 10%
495 votes - 10% of all votes
- I don't eat fish 3%, 159 votes
159 votes 3%
159 votes - 3% of all votes
Total votes: 4728
18.06.2020
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Ordinary
Typical, most numerous variety. It lives in most fresh water bodies of Europe, North America, and is found in the Aral Sea basin and water bodies of Siberia. The length of a representative of this species reaches 1.5 meters , and the average weight is 8 kg . There are 2 subspecies: grass and deep.
The color of the fish can vary depending on its habitat : from grayish-green and brown to gray-yellow shades of scales. Prefers to lead a solitary lifestyle in the coastal zone of water bodies , where there are thickets and slow currents. This predator lies in wait for its prey and plays the role orderly .
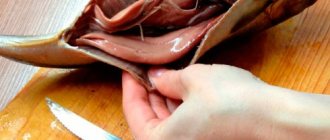
More about it: everything about the predator, how to clean a pike, at what pressure it bites, yawn, attractants for pike.
Vertical migration
The issue of vertical migration of pikes remained unstudied for a long time. From the very first description of the species, it was determined that pike is a shallow-water species. Well, that's all. And a little later they came up with the preferred depths for pikes, although this also did not answer the question. However, vertical migrations turn out to be so important that each individual pike changes depth a couple of times a day, every day throughout the year. And this only became clear in 2021.
Sunbathing
The study revealed two behavior patterns: pike staying in surface waters during the day and moving to the depths at night, or the same in reverse order. The occurrence of this behavior varied both among pikes and across seasons. It has been hypothesized that this is related to thermoregulation. For example, pike rose to the upper layers to increase their body temperature relative to the water temperature.
And we know that pike is a mesothermic animal (an average between warm-blooded and cold-blooded) and a higher body temperature relative to water temperature helps to hunt more successfully. However, in winter, wild pikes had a body temperature close to 0°C and this did not prevent them from feeding successfully. Nevertheless, the hypothesis put forward looks very plausible. What’s especially good is that this behavior was confirmed both for wild pike in field studies and for laboratory specimens.
In addition, pike demonstrated consistency in their use of vertical migrations throughout the season. Some pikes went to the depths in the morning and rose to the surface by night, while others did the opposite. Interestingly, all observed fish were consistent in their preferred migratory order throughout the season, but switched to the opposite pattern between seasons. For example, a particular pike rises to the surface during the day in the summer and goes to the depths at night, and by winter it switches to rising to the surface at night and going to the depths during the day.
The graph shows that the switching coincided with dawn and sunset hours. By the way, these same switchings repeat the peaks of pike activity, morning and evening. However, vertical migration is often not associated with feeding activity. That is, pike can rise to the surface simply to sunbathe and nothing more.
Another interesting paradox was when pike avoided warm water in October and November. However, here, most likely, the answer lies in the internal processes of the pike body. At this time, gametogenesis begins in pikes - the formation of germ cells. Caviar, to put it simply. This process is activated as a result of a drop in water temperature and a reduction in daylight hours []. And higher temperatures can disrupt normal cell formation [].
Preferred depth and temperature for young and adult pike
We have long had at our disposal average principles for the distribution of pike by depth and water temperature. Typically, this distribution is taken to be linear: the larger the pike, the greater the depth and the lower the temperature it prefers. In general, most observations confirm this.
However, even in this case, pikes exhibit individuality when individual fish do not do what they “should” do. Sometimes we can find exceptions in some reservoirs at the level of an entire population. For example, we can observe the opposite pattern, where large pikes sit at shallow depths, and small ones at depth.
General provisions
If the reservoir is a standard-type place where there are shallow waters with grass and open deep spaces, the distribution of pikes will be the most familiar: young fish sit mostly in the grass, and adults go into open water. But at the same time, when the reservoir turns out to be non-standard, we can observe both the inverse distribution and something in between.
For example, in “naked” reservoirs, young pikes can go to depth and thus avoid predation by adult fish. At the same time, large pike remain in shallow waters. We can observe the middle option most often in such reservoirs where the bottom is completely covered with grass and/or in these reservoirs there is no pronounced division into shallow water and open water. As a rule, this is a common story in various types of quarries, where sometimes the division into zones can be very arbitrary and very far-fetched. Here, pike of different age groups choose similar places. Even in cases where the risk of cannibalism is high.
Black
Also called striped . Despite the external resemblance to the northern common pike, it differs in the form of a dark stripe above the eyes , and on the sides of its body there is a characteristic mosaic pattern.
Due to slow growth, the fish has a short snout. In adulthood, its length reaches 60 cm, and its weight is 2 kg . The largest known specimen weighed slightly more than 4 kg. Comfortable habitat - dammed areas of fresh water bodies with abundant vegetation in the eastern part of North America.
This species has a very peaceful disposition; its diet mostly consists of invertebrates .
Pike in cooking
Since ancient times, among all freshwater fish, pike has always been considered a delicacy. No luxurious feast could be complete without one or more pike dishes.
Even medieval doctors assured that this is one of the best fish, because it has enormous health benefits. Over the past centuries, the opinion of doctors on this matter has not changed significantly, but has only found additional scientific justification. Pike meat contains many B vitamins (have a beneficial effect on the nervous system), potassium (normalizes blood pressure), magnesium (good for the heart), phosphorus (affects brain function) and other substances.
Like any fish, pike is a dietary product. It contains only one percent fat, but as much as 18% protein. The energy value of pike meat does not exceed 84 kcal per 100 g. Thus, pike is ideal for those who are watching their figure.
This fish has dry, but tender flesh. Moreover, experts assure that the larger the pike, the more pleasant the taste of meat is. However, very large fish is quite dry, so it is cooked in such a way as to saturate it with moisture. For example, they are stewed with vegetables, stuffed with lard, meat and vegetables, fish soup is prepared, etc.
In general, the variety of pike dishes is quite large, and the culinary tradition of preparing this fish goes back hundreds of years. Pike is baked, fried, stewed, boiled, stuffed, used in soup, made into cutlets, pates, etc. The only drawback of pike, for which many people do not like it, is its bonyness.
Amurskaya
Individuals of this species are characterized by small scales of silver or golden color with a green tint. In general, its color resembles taimen , due to the numerous dark spots located over the entire surface of the body.
The sizes are inferior to the common pike: the largest representatives of the species reach 115 cm and weigh 20 kg . Life expectancy is about 14 years. Habitat: Amur , also found in some reservoirs of Sakhalin .
Pike breeding
Under natural conditions, females of this species begin to reproduce at the age of two to three years, males at four years.
Spawning starts soon after the ice melts, when the water temperature does not exceed 3-6 °C. Females retreat to shallow water (depth up to one meter), where they begin to splash noisily and actively move within the spawning area. Each female is accompanied by several males.
The female is capable of laying from 17 to 215 thousand eggs. Pike have them quite large - 3 mm in diameter - and in the first days they are quite sticky, so they often stick to aquatic vegetation. But then most of them roll to the bottom, where their further development occurs.
Since the eggs end up in shallow water from the very beginning, when the water level in the reservoir drops significantly, most of the eggs die. This, for example, is typical for reservoirs, the water level in which is regulated by humans and is therefore very variable.
The larvae hatch from eggs during the entire second week after spawning and begin to feed independently, eating microscopic crustaceans. Having reached a length of 12-15 mm, young pike move onto carp larvae, which spawn after the pike. Five-centimeter young pike finally switch to fish.
It is interesting that pike river fish often spawn in swimming lakes, which quickly lose connection with the river after the end of the spring flood. When there is a shortage of food in such reservoirs, hatched fry grow extremely unevenly. Representatives of one generation can differ in size by 2 or more times. In such conditions, the food chain is built on the basis of cannibalism, when very small pike feed on plankton, and young animals feed on fry, while themselves becoming prey for last year’s and older pike. This happens especially often in Yakutia and northern Canada, where similar pike lakes exist on a permanent basis.
American (redfin)
It has a short snout and cannot boast of impressive size, so this aquatic inhabitant can hardly be called a large fish. This species is divided into 2 subspecies :
- northern redfin;
- southern (herbal).
Both subspecies have a short snout and very modest sizes: the length of an adult reaches 30-45 cm and weighs 1 kg . The only difference is that southern pike do not have the orange color of their fins.
The lifespan of these fish does not exceed 10 years. A comfortable habitat is dammed reservoirs and lakes in eastern North America .
Pike behavior
Pike is a species of fish that hunts and is not at all interested in plant foods. It lives in flowing lakes and rivers with a calm current, but is not found in small stagnant ponds and fast rocky rivers with cold water.
Pike prefers to hide near underwater thickets, where it can easily ambush small fish and its other victims. The basis of the pike diet consists of species such as roach, silver bream, gudgeon, perch, ruffe, bream, etc. At the same time, pikes do not disdain eating young animals of their own species. In spring and early summer, this predator hunts frogs and young crayfish. Large pike can grab ducklings and small mammals (rats, squirrels, etc.) that find themselves in the water for one reason or another. There are known cases of pikes attacking adult ducks.
In general, pikes are not at all afraid of hunting large prey. Quite often the victim of this predator is a fish whose size is 50% and even 60% of the size of the pike itself. However, medium-sized pike, that is, about half a meter, feed mainly on numerous “trash” fish, so this species is invariably used in fisheries to exterminate small ruff and perch.
Like many other predatory fish, pike hunt from ambush, hiding in thickets of algae, from where they rush at their prey. If the ambush is unsuccessful, the pike almost never gives chase. She always swallows caught prey from the head, turning it in the right direction if necessary. In hunting, the pike is helped not only by its vision, but also by its very sensitive lateral line.
Muskinong
This gigantic fish owes its name to the Indians, who called it maashkinoozhe, which means “ugly pike.” It is rightly considered the rarest and largest representative of the pike family in the reservoirs of America.
Some specimens grow up to 1.8 and reach a weight of 40 kg . However, much more often caught individuals of this species weigh no more than 20 kg .
The transition to carnivorous feeding occurs in the first year of life; up to the age of 10 years, growth increases very rapidly , then its pace slows down , while the fish continues to gain weight .
Females reach sexual maturity at the age of 5 years , their length at that time is 60 - 80 cm with a weight of 2.5 - 4 kg. The duration of the life cycle is about 30 years . The muskellunge bears some external resemblance to the common and American pike. A distinctive feature is more than 7 sensory points on the lower jaw .
This giant can have a silver , brown or green color, and vertical stripes are scattered on the sides of its body, sometimes turning into spots .
In cases where the fish lives in turbid waters, stripes and spots may be completely absent . Based on color, there are 3 types of muskellunge:
- striped (common);
- spotted;
- clean (naked).
Reference. By crossing the muskie with the common pike, a hybrid form was developed - the tiger muskie. A hybrid individual cannot reproduce in nature, so their independent populations do not exist.
The most popular lures for catching pike
When going fishing with any gear, you need to carefully prepare; one form with a reel and fishing line will not be enough. An important element on which the outcome of fishing directly depends is the bait; without it, the capture will definitely not happen.
Spinning lures for pike are divided into several types, and each of them can attract the attention of a predator no worse than the others. The choice is influenced by various indicators, among which the important ones will be:
- test indicators of the form;
- reservoir criteria;
- weather;
- season;
- the size of the predator living in the reservoir.
It is also worth taking into account the personal preferences of the fisherman; some prefer to fish only with silicone, while others only bite with a wobbler.
A novice spinning angler needs to try all the baits and only then independently choose the one he likes.
It’s very difficult for a beginner to decide on his own; the store shelves with gear amaze with their variety. That is why it is necessary to take a mentor with you or study the range of products on your own before going on a trip. We will try to help you a little with your choice; to do this, we will study in more detail the most catchy spinning lures for pike.
Wobblers
This type of bait for pike is very popular. It is the wobbler that is most similar to real fish, and not only visually. It is made in such a way that, when placed in water, it imitates aquatic inhabitants as much as possible; most often, wobblers imitate a dead fish or a very fast fry.
But this is not all the information about the bait; wobblers are divided according to body shape; for pike they are most often used:
- cranks;
- minnow;
- poppers;
- jerky.
The wiring for this type of bait can be varied, in most cases it all depends on the shape and characteristics of the reservoir. Twitch, uniform and uneven wiring will give you catchability. In this case, it often happens that the fisherman himself must choose the most suitable one, and sometimes combine several at once.
It is worth understanding that this bait for pike is also divided by buoyancy. There are:
- drowning;
- floating;
- with neutral buoyancy.
It is also necessary to distinguish a wobbler by its depth; for this you need to carefully examine the shovel, it will be the correct indicator of immersion. The larger the size, the deeper the wobbler will go when moving it through the water column.
It’s worth paying attention to the colors; a real spinning fisher’s arsenal should include both bright acid baits and lures with a more natural body color.
It is better to select a larger size for pike if you want to get a trophy specimen of the predator.
Spinner
One of the most popular for pike is a spinner. It often happens that a toothy resident of a pond does not respond to any of the proposed baits, but it is the spinner that attracts its attention and forces it to attack.
Experienced fishermen recommend always having several types of spinners in your box; the most catchy ones are considered to be:
- Aglia;
- Aglia long;
- Black Fury;
Spinner baits of this type are the most catchy from Mepps; Blue Fox produces excellent quality and a specific shaped core; those who use large-sized Ponton 21 also get good results.
Many craftsmen make such lures on their own; their products are often even superior in catchability to branded ones.
The color of the petal of a spinner is of great importance; its choice should be taken responsibly. It is advisable to have all the basic ones without fail, but purchase an acid one as needed.
Oscillating spoon
Pike responds well to oscillators throughout the year; the main thing is to know how to use them in reservoirs. There are a lot of varieties of baits of this type; they are distinguished by shape, weight, and color.
The most popular are:
- Castmaster;
- Syclops;
- many models from Spinnex.
You should choose a bait of this type based on the time of year, the depth of the reservoir, and also take into account the size of the inhabitants of the river or lake. Models with a silver body are considered universal baits, but there is no need to remove gold and bronze from your arsenal at all.
Acid-colored pike baits are also popular with experienced fishermen; pike especially often react to cyclops with this coloring. Spinner baits from Spinex are no less popular; they are caught both on lakes and rivers in different regions.
The retrieve for such a spinner should be uniform, but fast. This is how the spinner can best imitate a quickly fleeing fish, and the predator will rush to catch up with it.
Stickers are equipped with ordinary hooks, often tees. But for wiring between water lilies or other bottom vegetation, it is better to install non-snagging hooks.
Silicone
Silicone baits are among the most budget-friendly ones; another advantage is that installation can be done in several ways.
Approaching a display case with silicone, even the most experienced spinning player will be confused. Today's stores can offer a wide variety of baits of this type. Spinning attachments for pike are distinguished by:
- size;
- color;
- body shape;
- tail shape.
Silicone from the edible series is included in a separate group; there is also plenty to choose from.
The same manufacturers have been the most popular for many years; their products always work in any weather. The best lures for pike are made by:
- Manss;
- Relax;
- Lucky John.
But the shape can be very diverse; vibrating tails are most often preferred, they are most similar to fish. Twisters can also attract the attention of pike; special attention should be paid to frogs made of silicone, worms, crustaceans, and leeches. Each of the above baits will be able to attract the attention of a pike and, with proper wiring, the predator will definitely be hooked.
Wiring for this type of bait is used in different ways; uniform, twitch, and stop and go are suitable.
Pike can be caught using spinning rods and other baits, but these are the ones that are used most often and effectively.
Social structure and reproduction
Female pike become sexually mature around four years of age, and males at five years of age. The suitable temperature for starting spawning is from 3 to 6 degrees plus. Spawning occurs immediately after the ice melts, near the shore, where the water depth does not exceed one meter. At this time, pike can be seen in shallow water, where violent splashes are heard. Usually the small specimens begin to spawn first, then the heavier fish join them.
Despite the fact that pike is a solitary fish by nature, during the mating season these fish form small schools consisting of several males (from 3 to 5 pieces) and one female. The female, as the leader, swims in front, and the males follow her, clinging to her side or being above her back. Spawning pike can rub against snags, roots, reed and cattail stems, which is how they spawn. When the spawning process comes to an end, strong splashes are common, and some pikes make high jumps.
The fry develop from one to two weeks, and the young fish's menu includes small crustaceans, and a little later - fry of other fish.
One pike can lay from 17 to 215,000 sticky eggs, the diameter of which is about 3 mm. Their number directly depends on the size of the female. First they cling to aquatic plants. After a few days, the eggs cease to be sticky and sink to the bottom, detaching from the plants, where they continue to develop. If after spawning the water begins to rapidly subside, then the eggs mostly die.
It happens that the eggs stick to the paws of the birds that eat them, so they are transferred to other bodies of water where pike have not previously been observed.
It is worth noting that in those reservoirs where the food situation is difficult, pike fry, reaching sizes of only half a centimeter, begin to eat each other at such a young age.
What does pike eat?
Photo: Pike in the water
The usual feeding hours for pike are early in the morning and evening; during the day, the predator is engaged in digestion, resting in a secluded place. Pike eats three times a year, then it feeds around the clock. The first zhor occurs before spawning (usually in March-April), the second occurs after spawning (in May-June), and the third occurs in August-September, sometimes in October.
The menu of this avid sharp-toothed predator includes a huge variety of fish; pike feeds on:
It should not be surprising that this predatory fish happily eats its relatives. Cannibalism flourishes in the pike environment; a larger individual happily eats small pike, which is why these fish stay solitary and live apart from each other. In spring or at the very beginning of summer, pike can feast on both frogs and crayfish that are in the process of molting.
There have been cases when pike caught and pulled under the water small ducklings, rats, squirrels, mice, and waders swimming across the river.
Large pike individuals can attack ducks; this often happens when birds molt and cannot take off into the air. Also, large predators successfully catch fish whose size is half the size of the toothiest hunter or even a little more. Scientists studying the diet of pike have found that the menu of medium-sized pike consists mainly of fish, which are of no value and are numerous, so pike is very important for many fisheries, because it prevents the stocking of water bodies.
Natural enemies of pike
Photo: Animal pike
Despite the fact that the pike itself is very voracious, toothy and quite bloodthirsty, it has enemies who are not averse to feasting on it. Among the pike's detractors are otters and bald eagles, which love to eat all kinds of fish, including toothy pike. In Siberian rivers, pike compete with taimen, which copes excellently with predators of identical size, so in those places pike rarely reaches very large dimensions.
For pike living in southern waters, another enemy awaits them - large catfish. If large fish have enemies, then it is even more difficult for fry and young fish to survive; they often become prey for perches, rotans, and large pike perch. We should not forget that the pike itself eats its fellows, paying absolutely no attention to family ties.
In some northern lakes, pike cannibalism flourishes, where pikes feed only on their own kind. The food chain in those places looks like this: the fry eat small crustaceans, the fry are eaten by medium-sized relatives, and the latter become a snack for their heavier relatives.
Humans can also be considered the enemies of this toothy predator, because it is an honorable trophy for many fishermen who hunt for it. In some regions, pike fishing is not controlled in any way and is often massive. In addition, many fish die due to winter death, which usually occurs in small bodies of water.