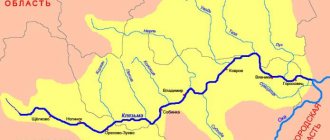
Volkhov basin and Lake Ilmen
| Name | Shelon |
| Length | 248 |
| Pool area | 9710 km2 |
| Pool | Ilmen/Volkhov/Lake Ladoga/Neva/Gulf of Finland/Baltic Sea |
| Water consumption | 43.6 m3/s |
| Measurement location | 59 km from the mouth |
| Source | Sudom Hills |
| Source location | Dedovichsky district of Pskov region |
| Source height | 85 |
| Source coordinates | 57°0′0″ S w. 30°0′0″w. d. |
| Estuary | Ilmen |
| Mouth location | Shimsky district of Novgorod region |
| Mouth coordinates | 58°13′39″ S w. 30°53′59″ W d. |
Shelon
(or
Shalon
) is a medium river in the Pskov and Novgorod regions of Russia. The length of the river is 248 km, the area of its drainage basin is 9710 km². The average annual water flow 59 km from the mouth is 43.6 m³/s. Belongs to the Baltic Sea basin.
On the river are the cities of Porkhov, Soltsy, as well as large villages - Dedovichi and Shimsk.
Large tributaries are Mshaga, Sitnya, Udokha, Uza, Sudoma, Ilzna (left), Koloshka, Lemenka, Lyuta, Shilinka, Polonka, Belka, Severa (right).
Mineral springs are often found in the river basin. The river is navigable in the lower reaches, from the city of Soltsy to the mouth.
Description
Shelon begins in large swamps located near the border with the Novgorod region to the southeast of the village of Dedovichi near the village of Novaya Sloboda.
The first meters are a small stream; beyond the mouth of the right tributary of the Severa River, the channel widens due to the support of a dam located just above Dedovichi. Behind the village, near which the large left tributary of the Sudom flows into the Shelon, the width of the river is about 30 meters. Further, the Shelon flows along the plain, sometimes accelerating on small rocky rapids (there are more than 40 rapids on the Shelon), the banks are low, the depth is small - 1.5-2 meters.
Beyond the confluence of the right tributary of the Belka into the Shelon, the Kholomki estate is located - the former estate of the rector of the St. Petersburg Polytechnic Institute A.G. Gagarin.
In front of the city of Porkhov and behind it, the banks of the river rise and are covered with pine forests. The width of the river in the city of Porkhov is about 40 meters, however, actively collecting water from many rivers flowing from the Sudomskaya and Luga uplands to the west of Ilmen, Shelon quickly expands and in the city of Soltsy its width already reaches 70 meters, in Shimsk - about 300 meters , and near the mouth it spreads over several kilometers. Between the border of the Novgorod region and Soltsy there is a series of small rapids on the river. Below Soltsov the river calms down and becomes accessible to ships.
Shelon flows into Lake Ilmen in its western part, forming a delta with an area of 10 km².
On the left bank of the Shelon, not far from the village of Velebitsy, Soletsky district, Novgorod region, on July 14, 1471, a battle took place between Moscow troops and the Novgorod militia, which went down in history as the Battle of Shelon.
Shelon
Shelon is a river flowing in the middle-eastern and north-eastern parts of the Pskov region and in the western part of the Novgorod region of Russia. Refers to the Baltic Sea basin, Lake Ilmen basin and the Neva and Volkhov river basin.
The Shelon River is very winding. The general direction of the current from the source to Porkhov is first north-east, then north, then west and after the village of Pionerny north-west. From Porkhov to the mouth - north-eastern.
The source of the Shelon emerges from the swamps on the border of the Bezhanitsky and Dedovicheskiy districts of the Pskov region, 2.5 km southeast of the village of Novaya Sloboda. The river flows into Lake Ilmen 3 km northwest of the village of Uspolon in the Shimsky district of the Novgorod region, forming a delta with an area of 10 km².
Settlements. The Shelon River flows in six districts of two regions of Russia. In the Pskov region: in Bezhanitsky, Dedovichesky, Prokhorovsky, and Dnovsky districts. In the Novgorod region: in Soletsky and Shimsky districts.
Along the banks of the river from source to mouth there are many villages, villages and towns. Large settlements - town. Dedovichi and town. Shimsk. The entire list of settlements located on the banks of the Shelon River can be found here >>…
There are also two administrative centers near the river. In the middle reaches of the river in the Prokhorovsky district of the Pskov region is the city of Porkhov. In the lower reaches of the river in the Soletsky district of the Novgorod region is the city of Soltsy.
The city of Porkhov was founded in 1239. The city's population is 10,608 as of 2010. Located in the Shelonskaya Lowland, 88 km east of Pskov. The main attractions are the ancient Russian fortress with four towers and the Church of St. Nicholas inside. The fortress functions as a museum.
The city of Soltsy was first mentioned in 1390. The city since 1914. The city's population is 10,317 as of 2010. Located 80 km southwest of the city of Veliky Novgorod, on the left bank of the Shelon River. The city is unique in its historical buildings that have survived to this day with merchant shops and mansions, as well as buildings: the wooden Church of the Intercession of the 18th century, the Old Believer chapel and the current Ilyinsky Cathedral, built in 1824-1825 in the style of classicism.
Between the border of the Novgorod region and the city of Soltsy there are several small rapids on the river. Below the city of Soltsy, the river calms down and becomes accessible to passenger water transport to the very mouth.
Main tributaries. The largest tributaries of the Shelon River are the following: - Mshaga River - length 106 km; width 15-20 m; drainage area 1540 km²; located 19 km from the mouth of the Shelon River; left tributary. It flows through the territory of the Soletsky and Shimsky districts of the Novgorod region.
— Sitnya River – length 117 km; width 7-10 m; drainage area 1020 km²; located 64 km from the mouth of the Shelon River; left tributary. It flows in the Strugokrasnensky, Porkhovsky districts of the Pskov region and in the Soletsky district of the Novgorod region.
Information about other tributaries of the Shelon River can be found here >>…
In the Novgorod region: the river flows in the Priilmenskaya lowland to the very mouth. The lowland with wide steps (terraces) descends to Lake Ilmen. The Ilmen lowland is a tectonic depression, which in post-glacial times was filled with water from the periglacial basin and filled with moraine, sands and banded clays. The Ilmenskaya lowland is extremely flat. Altitudes range from 18 to 50 m above sea level. Its central part, where Lake Ilmen is located, is lower.
Soils: On the Sudom Upland there are soddy-slightly podzolic (soddy-brown podzolic - their classification is currently being discussed) soils with the local name poddubitsy. They formed under oak and spruce-oak forests on zvontsy-ridges, on lacustrine-glacial clays underlain by carbonate moraine. Due to significant deforestation, poddubitsa are included in the arable fund or are used for pastures and hayfields.
The Khilovskaya lowland in the area of the city of Porkhov is represented by soils of soddy-weak and soddy-medium podzolic soils, formed on terminal moraine and hydroglacial deposits.
The surface of the Priilmenskaya lowland is very swampy. The Priilmenskaya lowland is dominated by soddy-alluvial podzolic-marsh and swamp soils, the formation of which is caused by excessive waterlogging.
Vegetation. The Sudom Upland belongs to the Eastern European subtaiga zone. This is a zone of mixed and broad-leaved forests, but there are no broad-leaved trees here for a long time, and in coniferous and small-leaved forests - oak and linden are found sporadically. For a long time, the broad-leaved and coniferous-deciduous forests located in these places were converted into agricultural land. In the 50s, gray alder dominated everywhere. Aspen, birch and coniferous forests were much less common. There were more pine ones.
The Khilovskaya lowland is also represented by a mixed type of forest - coniferous and coniferous-deciduous. In addition to spruce, pine, aspen, and birch grow. The ground cover is dominated by “green” (hypnum) mosses. On moist soils, sorrel, blueberries, and lingonberries grow; on dry soils, lingonberries grow.
The Ilmen lowland is located mainly in the subzone of mixed forests. It is largely plowed for agricultural needs. The vegetation cover is dominated by mosses. Cassandra, heather and poisonous wild rosemary grow from the shrubs. There are a lot of cloudberries, cranberries, lingonberries, blueberries, and blueberries in the swamps. Trees grow rarely in swamps, they are stunted and are represented by pine and birch.
Hydrological regime. The length of the Shelon River is 248 km. The drainage basin area is 9710 km². The height of the source is 85 m. The water flow 59 km from the mouth is 43.6 m³/s. The bottom is hard limestone, pebbly, sandy and pitty in places. The diet is mixed, with a predominance of snow. The river freezes in November - December. High water occurs from April to May, and in the fall there are rain floods.
At the source, the Shelon River is a small stream flowing from the Sudom Hills, after the right tributary - the Severa River, the Shelon riverbed widens due to the backwater of a dam located just above the village of Dedovichi. Behind the village, near which the left tributary, the Sudoma River, flows into Shelon, the width of Shelon is about 30 meters. Further, the Shelon flows along the plain, sometimes accelerating on small rocky rapids. There are about 40 rapids on the river in total. The banks of the river are low, the depth is small, about 1.5-2 meters. Before and after the city of Porkhov, the banks of the river rise and are covered with pine forests. The width of the river within the city of Porkhov is about 40 meters. Further, actively collecting water from many rivers and streams flowing from the Sudomskaya and Luga uplands, the Sheloni channel expands and in the city of Soltsy its width reaches 70 meters, in the village of Shimsk - about 300 meters, and near the mouth the river spills over several kilometers.
Ichthyofauna. The Shelon River is rich in fish. Among the fish species that live in the river are: pike, perch, silver bream, white bream, bream, burbot, roach, etc.
Sights, tourism and recreation. In the Shelon River basin, Solets mineral water springs are often found. Soletskaya mineral water belongs to the group of North Caucasian Narzans. The village of Uspolon is also unique. The water from this village is sold all over Russia. This mineral water was called “Uspolon”. The river is popular for rafting and fishing. Mushrooms are collected in forested areas, and berries are collected in wet places and swamps.
In the city of Soltsy (lower reaches of the Shelon River) there are: • Church of Elijah the Prophet, built in 1825. • The wooden Church of the Intercession of the Blessed Virgin Mary in the village of Mussy on the outskirts of Soltsy, built in 1750-90. • Soletsk Local Lore Museum.
In the vicinity of the Shelon River there are famous estates: Alexandrovo, Volyshevo, Vyazye, Goromulino, Knyazhi Gorki, Nikandrovskaya Pustyn, Khilovo, Kholomki.
Reference Information.
Length: 248 km. Basin area: 9710 km². Swimming pool: Baltic Sea, Lake Ilmen. River basin: Volkhov and Neva. Source: Sudom Upland Location: 2.5 km southeast of the village of Novaya Sloboda, Dedovicheskiy district, Pskov region of Russia. Coordinates: 57°21′53.74″ N. latitude, 30°14′44.31″ e. Ustye village: western part of Lake Ilmen. Location: 3 km northwest of the village of Uspolon in the Shimsky district of the Novgorod region of Russia. Coordinates: 58°12′59.8″ N. latitude, 30°48′36.23″ e. d.
Story
Hanseatic documents of the 15th century repeatedly report on the so-called Luga Route, which connected Novgorod with the Gulf of Finland. One of its sections passed along Shelon: Volkhov—Ilmen—Shelon—Mshaga—Kiba—drag to the river. Luga and further along Luga to the Gulf of Finland. The Luga route was the most important transport artery and was actively used when the traditional Volkhov-Ladoga-Neva route was blocked for some reason.
In 1471, on the banks of the Sheloni River, in the area of the current villages of Skirino and Velebitsy (Vybitskoye rural settlement), the Battle of Shelon took place, which determined the end of the Novgorod Republic.
Shelonskaya Pyatina was also named after the river.
Physiographic characteristics[ | ]
The basin of the Volkhov and Lake Ilmen
Shelon begins in large swamps, 23 km southeast of the village of Dedovichi, in particular, 1 km southeast of Lake Selezen near the tract (former village) Novaya Sloboda (near the village of Gorodovik, Sosonsky volost ) Dedovichsky district near the border with the Bezhanitsky district of the Pskov region and in general not far from the border with the Novgorod region[4].
The first kilometers are a small stream; at Bolotnaya the riverbed enters an extended reservoir at the confluence with the riverbed. Bolotki. The width of the reservoir reaches 400-450 meters in some places. Just above Dedovichi, near Pionerny there is a dam and a state district power station. Behind the dam, the river is about 30 meters wide. Further, the Shelon flows along the plain, sometimes accelerating on small rocky rapids (there are more than 40 rapids on the Shelon), the banks are low, the depth is small - 1.5-2 meters.
Beyond the confluence of the right tributary of the Belka into the Shelon, the Kholomki estate is located - the former estate of the rector of the St. Petersburg Polytechnic Institute A.G. Gagarin.
In front of the city of Porkhov and behind it, the banks of the river rise and are covered with pine forests. The width of the river in the city of Porkhov is about 40 meters, however, actively collecting water from many rivers flowing from the Sudomskaya and Luga uplands to the west of Ilmen, Shelon quickly expands and in the city of Soltsy its width already reaches 70 meters, in Shimsk - about 300 meters , and near the mouth it spreads over several kilometers. Between the border of the Novgorod region and Soltsy there is a series of small rapids on the river. Below Soltsov the river calms down and becomes accessible to ships.
Shelon flows into Lake Ilmen in its western part, forming a delta with an area of 10 km².
Water register data
Tributaries (km from mouth)
- 9 km: Veksha River (pr)
- 14 km: Uglyanka River (pr)
- 18 km: Strupenka river (lv)
- 19 km: Mshaga River (lv)
- 21 km: Sosenka River (pr)
- 32 km: Turyevsky stream (pr)
- 35 km: Koloshka River (pr)
- 42 km: Krutets River (lv)
- 48 km: Milits River (lv)
- 51 km: Borovenka River (pr)
- 57 km: Patcherka (Koleshovka) river (pr)
- 64 km: Sitnya river (lv)
- 71 km: Lemenka River (pr)
- 82 km: Lyuta River (pr)
- 93 km: Udokha River (lv)
- 103 km: Dryazhzhinka river (lv)
- 106 km: river Shchilinka (Krasukha) (pr)
- 112 km: Demyanka river (Tenyukha, Demyanka) (lv)
- 120 km: Uza River (lv)
- 125 km: Polonka River (pr)
- 145 km: Bakharevka stream (lv)
- 148 km: Belka River (pr)
- 151 km: Lyubava stream (lv)
- 153 km: Tishinka River (lv)
- 165 km: Dubechenok stream (pr)
- 178 km: Sudoma River (lv)
- 185 km: Ilzna River (lv)
- 200 km: Gorodyanka river (lv)
- 210 km: Severka River (Severa) (pr)
- 215 km: Gribkovsky stream (pr)
- 221 km: Bolotinka River (pr)
Add a comment
Comment
Send