This article is dedicated to one of the main characters of fishing equipment - the fishing hook, as an ancient, irreplaceable accessory that occupies one of the leading places in all fishing equipment.
The correct tactical use of the right hook can, even with small roughnesses in the equipment, please you with a catch. This article will help you figure out and understand what a fishing hook is, what parts it consists of, what is its feature, what types of hooks are there, how to properly tie them to a fishing line, store them, and much more.
Content
- 1. What is a fishing hook
- 2. What parts does a fishing hook consist of?
- 2.1 Fishing hook head and its function
- 2.2 Fishing hook forearm and its purpose
- 2.3 Prying a fishing hook
- 2.4 Fish hook tip
- 2.5 Function of the beard
- 5.1 Separation of hooks by type
- 5.2 Separation of hooks by fish species
- 5.3 Separation of hooks according to fishing conditions
- 6.1 How to correctly read sizing information on packaging
What types of hooks are there?
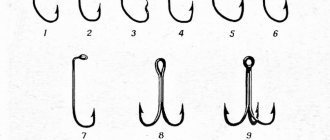
Basically, fishing hooks differ from each other in their shape, material and color. Well, and the size, of course. But the shape of the hook is probably their most important difference. To make it easier for you to understand how hooks are distinguished by shape, I made a visual drawing. It indicated the names of the main parts of a fishing hook. This is the ABC for a fisherman. Look and read in picture No. 1.
While my drawing of the hook parts looms before your eyes, I want to briefly talk about the classification of hooks by numbers. It is customary for us to represent the distance from the forearm to the tip in millimeters as the hook number. Let’s say if this distance is 5mm, then the number of such a hook will be No. 5. Everything is so simple and clear. For imported hooks, everything is a little different. The distance between the forearm and the sting of 5 mm for an imported hook, according to the international scale, will correspond approximately to hook No. 10. For clarity, I made a table of domestic and international hook standards. Look, compare, remember - the table is above.
Hook shapes
As I said before, fish hooks come in different shapes. From all the variety, three most common forms of hooks can be distinguished. These three forms have their own names: “Kirby”, “crystal” and the most universal form with a rounded tip - “Aberdeen”. There is another hook shape that is a cross between a crystal and a kirby. This form is called "limerick". Again, it’s better to look at the picture here.
Each of these three shapes has its own standard handguard size. But, in addition to the standard length, hooks with elongated and shortened shanks are also made. For different fishing conditions. For example, hooks with an extended shank are used to catch fish with small mouths, but with long baits. Suitable for catching ruffs with a worm. There are also so-called “bleak” hooks. These are small hooks with an extended shank. In this case, the long shank helps to hold the small hook with your fingers.
Hooks with a short shank are used for catching strong, powerful fish with small bait. Suitable for catching bream with bloodworms or carp with corn and boilies.
Some hooks have one or more barbs on the shank. These barbs serve to hold the bait more firmly on the hook. The worm will not slide down such a fore-end to the very bottom, and will not hang there as a lifeless thread at the very sting. And the dough holds better on such a hook.
Fly fishing hooks are presented as a separate group. These are hooks for flies and streamers. Most often these are hooks with a round bend and shod. The ring of these hooks is usually bent inward. This position of the ring is necessary to hold the fishing line along the axis of the hook shank. Fly fishing hooks come with regular and extended shanks. For tying flies, hooks with a regular shank are used. Hooks with an elongated shank are used for making streamers. Such hooks are also successfully used for float rigs when catching large fish.
Personally, when I catch non-predatory fish with float tackle, I successfully use hooks from No. 14 to No. 24 white with a round bend and a standard shank. At the end of the fore-end there is a spatula.
What parts does a fishing hook consist of?
2.1 Fishing hook head and its function
“Head” is the part of the hook that serves as the attachment point for the hook to the fishing line (for example, monofilament or braided fishing line) or other material.
The head is:
- ring-shaped;
- oval;
- without everything.
Below are the available head options
Hook with ring is used:
- with large diameter monofilaments;
- with braided lines;
- metal leashes.
A hook with a spatula is used with a monofilament line of small diameter, for catching small peaceful fish.
Both hook head designs are reliable and allow you to tie the desired fishing line with reliable knots; you can read about options and methods for tying the most reliable knots in this article
.
The third option is attached to the thread due to notches located on the top of the hook shank. This option is suitable for attaching fishing lines with a diameter of no more than 0.1 mm, and the entire structure looks like a single element of the equipment.
2.2 Fishing hook forearm and its purpose
“Forend” is a section (straight or in the form of a step for some types of offset hooks) running from the head to the hook. The size of the bait and future prey depends on the length of this section. For example, fishing hooks of medium or short length are designed for fishing medium-sized peaceful fish. Suitable for such bait as: leech, maggot, that is, having a compact shape in its dimensions.
With an elongated fore-end - in sea water, as they are aimed at large-sized bait and prey, with a powerful mouth and in order to protect the fishing thread from the sharp teeth of marine life. Also, hooks with an extended part of the fore-end can have additional beards, which gives an advantage in holding prey on the hook. Colorful worms (dung worms, sea worms, dendrobena worms, sandworms) are attached to such hooks. For fishing in Israel, you will need hooks with an extended shank.
There are hooks with a spring, the shank of which acts as a feeder into which the bait is placed. Otherwise, it is no different from its classic representative.
Thus, to determine the forearm length you need, first of all, you should decide on the type of future prey, its size and the dimensions of the bait used.
2.3 Prying a fishing hook
“Prying” is a rounded section that has the occipital part and the forehead, running from the forearm to the sting. The method and manner of rounding the hook determines the purpose of the fishing hook, for example, hooks for catching carp have an angular design, which is associated with the specifics of catching this fish.
Read more about the peculiarities of hooking carp hooks here
2.4 Fish hook tip
The “sting” is the tip of the hook, consisting of a sharp end and a barb; it is this that pierces the lip of the fish. It is very important to monitor the degree of sharpness of this element, since this factor affects the quality of the hook.
Basically, this element of the hooks is located parallel to the fore-end, but there are hooks with a sting curved inwards, reminiscent of an eagle's claw, their fore-end is short, such hooks are often used in carp fishing.
Why such a sting has become popular in this type of freshwater fishing, read here
Let's take a closer look at the sting options:
- “Knife edge” - perfectly penetrates the soft tissues of the fish and holds it well;
- “Needle” is less “penetrating”, but copes quite well with the process of retaining prey due to a small puncture, which does not increase during fishing;
- “Micro bard” - used in the smallest hooks intended for small fish, including trout;
- “Short” - on this sting the beard is located closer than provided for in the classic version;
- “Kirbed” or “reversed” - in such hooks the sting is deflected to the right and, accordingly, to the left, which is done for better hooking of fish.
2.5 Function of the beard
The main purpose of this part of the hook tip is to hold bait and prey during the fishing process. Location – internal or external part of the sting.
The thickness of the beard depends on the diameter of the material (wire) and the size of the barbed accessory and mainly constitutes a third of the thickness of the fishing sting. It is noteworthy that with small hooks this ratio may be smaller, which is associated with catching medium-sized fish with little resistance.
The sharp edge of the beard allows you to gently and easily pierce the tissues of the prey, and extraction requires some effort. Barbless hooks are designed for sports, such as feeder or float gear. Sports fishermen operate on the “catch a fish and release it” principle; in this case, barbless hooks will be suitable for this type of fishing, as they cause the least damage to the fish. The tip of such hooks is directed into the inner part of the hook structure, which prevents the bait from slipping and the fisherman from hooking the fish.
There are advantages and disadvantages to both hooks, with and without a beard. So, if barbless hooks hook better, but are not so reliable when fishing, then hooks with a barb, on the contrary, hook worse, but significantly reduce the chance of the fish coming off the hook.
Review of some models on the modern fishing tackle market
We can say that circle hooks with a self-cutting tip are universal. Among those available on the market, you can choose the best option for use both with natural baits and lures, and for fishing with artificial baits, such as silicone or spinners, and success is obvious even when fishing on the “track” (tension is created by the mass of the spinner).
Among the options available on the European market, there are three main manufacturers of self-cutting fishing hooks, among which the angler must definitely find the type and model that fully satisfies his needs.
- Rapala VMC Corporation. As a striking example of the described type of hooks, we can cite the VMC MYSTIC® MATCH Pellet Feeder model. These are single, reinforced hooks, produced under numbers 10, 12, 14 and 16, aimed at feeder and match fishing. The unsurpassed sharpness of the sting ensures instant hooking of fish. It has a high quality coating and is focused on the use of baits of plant and animal origin. The price for a package of 10 pieces is very affordable and is about 190 rubles.
- Gamakatsu Fishing Hooks. A Japanese brand, among whose models a prominent representative is the single hook Gamakatsu LS-3513F. This series is aimed at catching carp fish and is made of high-quality steel with the use of chemical sharpening of the tip. Like most hooks of this type, the axis of the hook is directed towards the attachment point. This ensures instant and reliable hooking of the fish, while causing minimal injury to it. One of the indicators of the quality of this company's products is that many European bait manufacturers use Gamakatsu hooks. The LS-3513F model comes in a package of 13 pieces, the cost of which is about 130 rubles.
- Eagle Claw. Hooks made in the USA, the name of which speaks for itself and translates as “eagle claw”. A traditional representative of the non-classical type of self-cutting hooks. The manufacturer offers many options for both single and double hooks. However, they are all united by reliability, American quality workmanship, as well as versatility in relation to catching various types of fish. However, the price corresponds to the positioning. Thus, the Eagle Claw L2004G model in a package of 5 pieces will cost about 400 rubles, and you can’t buy it in all Russian stores.
Recommended reading: What gear do you need for carp fishing?
What are fishing hooks made of?
The main material is metal wire, combining three types of steel, which affect the diameter of the future product and its quality characteristics. Only a few factories around the world are engaged in the manufacture of this element of equipment; other companies only purchase hooks and deliver them to consumers in colorful packaging.
“Hi-carbon steel” (high-carbon metal) - used for the manufacture of most budget products. This is a high-tech material, amenable to many types of mechanical and thermal treatment at various stages of production, which allows the wire to be plastic, elastic and have the desired shape. The main disadvantage of hooks made of this type of metal is corrosion. To prevent the occurrence of this “disease,” hooks need a special protective coating.
“Vanadium steel” (carbon steel) requires a high melting temperature of steel (1750 C), which makes it one of the refractory metals, but just 1% of this steel can increase the strength of the future product by 30%, which is a significant advantage over high-carbon steel. The surface of the hooks is resistant to oxidative reactions, but requires a protective coating to be applied to the surface. Hooks for catching carp and predators are usually made from this metal.
“Stainless steel” (stainless steel) is an expensive, technologically advanced material, which contains metals such as chromium, nickel and other additives. This material does not rust and is the basis for the manufacture of sea fishing hooks and hooks for hunting trophy specimens.
Sharpening methods:
- chemical sharpening or cut point;
- mechanical or cone cut;
- pressed or needle cone.
As for the thickness of the wire, first you need to decide on the load that your “barbed” friend must handle. So, for powerful predatory fish and peaceful, strong representatives (barbel, carp), it is better to use hooks made of wire of a larger diameter. If you intend to hook a wary individual by offering it a delicate dinner, then it is better to use hooks made of thin wire. It is reasonable to install such hooks in rigs with small and expensive spinning baits, wobblers, and silicone baits, since if a hook occurs, it will break and thereby save your expensive bait.
A short video from the Fredda king channel about the production of hooks
Structure of a fishing hook
Fishing hook - hereinafter referred to as RK.
For a detailed study of the Republic of Kazakhstan, it is convenient to divide it into zones.
Zone I "Head"
Serves to attach a hook to a fishing line or cord.
Different head configurations are justified by the convenience of connecting the RC with fishing lines and cords of various sections.
- Ring.
- Cone ring.
- A loop.
- Needle eye.
For fishing lines and cords with a cross-section from 0.08 to 0.8 mm.
This head shape is considered more reliable than a ring. For fishing lines and cords with a cross-section from 0.08 to 1 mm.
For thick lines and cords with a diameter >0.8 mm.
- on single hooks used for fastening thin fishing lines 0.029 - 0.04 mm;
- for attaching several RCs to a ring made of thin wire;
- for tees.
- Spatula.
- Without a head with serrations on the forend.
- direct;
- curved;
- with a step.
For thin lines with a cross section of 0.04-0.4 mm.
For thin lines <0.1mm.
Heads in relation to the axis of the forearm
1- Straight circular. 2- Inwardly curved ring. 3- Outward curved ring. 4- Flat. 5- Looped.
Zone II "Forend"
The handguard is:
The configuration of the forend determines the choice of bait.
A RC with a straight fore-end is used for putting on traditional bait (worms, small animals, cereals, cereals) when float fishing, as well as for putting on live bait or soft artificial bait when catching predatory fish.
Curved forend. The enlarged throat of the receptacle is convenient for putting on large baits when catching large peaceful and predatory fish.
With a step. The step is used on offset hooks with straight and curved shanks to hold soft, most often silicone baits.
Zone III "Prying"
The underhook zone is characterized by a bend (or bend) of the hook, and zone III a “Back of the head” and zone III b “Forehead” (Figure 1) can have bends of various shapes.
The nature of the bend determines the direction of attack of the hook.
There are three main forms of prying:
- TIEMCO.
- SPROAT.
- ABERDEEN.
The smooth bend of the hook and the straight tip are convenient not only for classic float fishing, but also for tying dry flies.
SPROAT with a regular hook is ideal for fly fishing, with an extended hook it is convenient for putting on bulky lures.
The round shape of the hook is used for various baits. Often used in sea fishing.
IV zone "Sting"
Determines the point of attack of the hook.
The sting can be straight or bent .
The straight tip lies in the same plane as the fore-end.
Bent:
- Kirbed – the plane is tilted to the left in relation to the forend;
- Reversed – the plane is deviated to the right.
In this zone there is a “barb” - a pointed wedge-shaped protrusion on the hook for fixing the bait and holding the caught fish.
The barbed sting forms various forms that are subject to standardization:
- Spear-shaped standard. The beard is straight.
- Sunken. The beard is concave, easily penetrating the soft tissues of fish.
- Beak. The sting is located on the same axis of the fishing line due to the fact that the tip of the sting is directed towards the head. Reduces hook pressure.
- Needle. Sharp sting with rounded edges.
- Blade of knife. Straight beard with mutually sharpened edges for catching large specimens.
There are 4 types of stings common in sport fishing:
- Beaked. The chemically sharpened, curved, sharp sting easily penetrates the fish's mouth.
- Falkus outbarb. The beard located on the outside of the tee makes it easier to release the fish.
- Hollow point. Confidently breaks through the mouth and keeps the fish on the hook.
- No goatee. The bare tip is used for high-speed fishing of peaceful fish.
Important characteristic. Pharynx (or pharynx). Characteristics of the hook, describing the distance between the forearm and the sting (Figure 1). Large mouth for putting on bulky bait and holding large fish.
Finish and color of fishing hooks
The paint color of a fishing hook has two meanings:
- Masking an equipment element.
- Protective function against the influence of natural factors (especially for hooks made of carbon material).
Bronzing is one of the ways to protect the hook from oxidation. Plus, manufacturers apply a paint and varnish composition consisting of polymers in order to give the product the desired color.
Nickel plating is a method of coating a product in colors from silver to dark (black). This coating is more resistant to external factors, durable and, accordingly, more expensive.
Tinning is one of the most expensive coating options and is used in the production of products intended for sea fishing (for example, in the Mediterranean Sea).
Surface colors are designated by the following English abbreviations:
- BK - black;
- BN - black nickel;
- BZ - bronze;
- GO - gold;
- NI - stainless steel;
- PS – red or pewter.
Material for production
High carbon steel (Hi-carbon steel). Raw steel is ductile and easy to machine. Steel that has undergone a certain heat treatment acquires hardness and strength. Products made from this steel are cheap, but susceptible to corrosion.
The cheapest fishing hooks are made from uncoated high-carbon steel. Such hooks are subject to rapid rusting and failure.
To reduce corrosion, special coatings are applied to the RC made of this material, which at the same time increases the cost of the products.
Vanadium steel . High-carbon steel, alloyed with 0.08-0.15% vanadium, increases refractoriness to 17500C and increases strength by 25-30%. This steel is resistant to oxidation, but is susceptible to aggressive environments. For use in sea fishing, steel also needs a protective coating.
Durable vanadium steel hooks are designed for catching predators. Carp hooks are also made from it.
Protection of carbon steel products from oxidation and exposure to aggressive environments is carried out mainly in three ways:
- Bronzing.
- Nickel plating.
- Tinning with tin.
Stainless steel . Such high-strength RCs are not subject to corrosion and exposure to aggressive environments. They have the highest cost. Mainly used for sea fishing.
Color
To paint the fish pen in certain colors that camouflage the hook or attract fish, polymer paints are added to the protective coating.
For example, the red color of a tee does not scare off a predator, but on the contrary, the color of blood additionally attracts fish. In addition, it is believed that carp love the color red, and often carp hooks are painted red.
The color designations for the surface of the hooks are as follows:
- PS – red or tin;
- GO - gold;
- BZ - bronze;
- BK - black;
- BN - black nickel;
- NI - stainless steel.
What are the sizes (numbers) of fishing hooks?
Size is a parameter that fishing enthusiasts take into account when choosing the right hook. This parameter should be understood as this distance
For general understanding, special designations (numbers) of hooks are used in practice. For example, for the Russian system, which has existed since the times of the USSR, the size indicated the width between the tip of the sting and the fore-end and was measured in millimeters (hook No. 6 meant that the distance between these two parts was 6 mm). Understanding Soviet designations is not difficult, but how to read international designations?
The essence of foreign numbering is that, firstly, all the designations indicated on the packaging are approximate, and secondly, there is no uniform approach to numbering, therefore leading manufacturers use their own designation system. Why is that? Everything is tied to competition, in order to lead in which, manufacturers invent new sophisticated forms of forends, which are very difficult to systematize. It is important to remember that as the number increases, the hook size decreases. So, the smallest hook in size is designated by number 32, and the largest by 20/0.
Below is a table that will help you navigate and compare the hook numbers of a particular numbering system
Let's look at possible situations of using certain fishing hooks.
№2,5 — 3 – this size is used for catching small fish as future live bait. Such small miners are hooked to maggots, bloodworms, vegetable baits in the form of semolina, cereals, bread, fishmeal (kemah dagim), etc.
№3-4 – roach, bleak, rudd, silver bream.
№5 — 7- ide, crucian carp, bream.
№4 — 6 – standard option for float gear. These hooks can be used to hook medium-sized carp, crucian carp, white fish and other representatives.
№7 — 12 – lovers of bottom fishing have such hooks in their arsenal; as a rule, larger fish cling to them and large-sized baits are used, for example, a dendrobene worm, a dung worm.
And the largest sizes are intended for catching trophy catfish.
We also present a table in which you can get acquainted with Japanese and Finnish numberings and compare them with Russian and international ones
6.1 How to correctly read sizing information on packaging
The ability to decipher the inscription seen on the packaging is not an easy task for a beginner, but this information is important, as it tells us:
- thickness and length of the forend;
- the width of the fishing hook.
For example, take the following encryption I No. 6-0.3-12:
- I (Roman numeral 1) indicates that this is a single blade with a single bend;
- No. 6 – hook number;
- 0.3 – thickness of material (wire) in mm;
- 12 – forend length parameter.
What do Roman numerals mean:
- II - single with a ring and bend;
- III - single with a blade and 2 bends;
- IV - single with a ring and 2 bends.
Examples of gear used: self-cutting fishing hooks
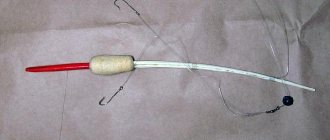
Roller-type equipment for pike fishing
Despite the fact that self-cutting hooks are more common when catching peaceful fish of the carp family, an example can be given of how to use them when catching a predator, such as pike, perch, pike perch or burbot. For this purpose, a “skating rink” type tackle is used.
The design of this fishing tool is simple and consists of the following elements:
- float-cylinder made of hard foam 18 cm in length and 6 cm in diameter and a cut for fastening the fishing line in the end part;
- fishing line of the required length, wound in the center of the float;
- olive shaped sinker;
- retractable leashes on carabiners, equipped with self-locking hooks.
We recommend reading: Zherlitsa
The principle of fishing with such gear is similar to fishing with mugs, but has the advantage that it works even in windy weather. The sinker creates enough tension so that with a sharp jerk the predator sits on the hook. After fishing, the leash with the fish is unfastened from the main fishing line, replaced with a new one, and fishing continues.
Feeder self-cutting tackle
There are three options for using self-cutting tackle together with a feeder, although they are only suitable for reservoirs with standing water.
First option. It is the most popular and is actually a paternoster equipped with a short leash, the difference being the sinker, which changes to a weighted swim feeder. In this design, the fishing gear works very effectively when hunting roach, practically eliminating empty bites. The length of the leash is about half a meter, and the weight of the feeder is 50 grams; it is filled with animal bait. After casting, the line is tightened and a heavy bite alarm is installed.
Second option. Unlike the first option, this equipment consists of more elements:
- main line with a size 18 feeder attached to it;
- a leash with a self-closing hook is fastened from the feeder at a distance of half a meter;
- at the very end of the tackle a bombard weighing 50 grams is installed.
It is important to remember that with such heavy equipment, hooking is not only not required, but is generally dangerous, since it can lead to breakage of the working line. Notching and fishing are done smoothly and slowly, slightly reeling in the line.
Since the feeders have a considerable mass, to cast them, the tensile strength of the fishing line must be at least 3 kg. To protect the working leash with a strength of 1 kg, a spacer made of durable elastic material is used, which acts as a shock absorber.
Third option. This option is justified when fishing for carp. A large feeder feeder is attached to the end of the main line, and a self-cutting fishing hook is mounted just above it, on a very short leash.
The fishing technique is to fill the feeder with bait until a dense ball is formed. A hook is inserted into this ball, on which bait is pre-attached and camouflaged. The careful fish does not notice the line of the leash and begins to eat the bait with appetite, among which bait with a hook appears unnoticed. When the fish senses danger and suddenly swims to the side, it will hook itself. Using this method, the largest and most cautious carp are caught.
Do-it-yourself self-cutting tackle
- It is necessary to prepare diverting leashes with special hooks, a weight or feeder with a mass calculated from the mass of the expected fish caught, as well as accessories in the form of swivels, carabiners, shock absorbers and beads.
- The next step is to tie the swivel to the leash, and attach it to the main fishing line using a link from a carabiner with a bead and a shock-absorbing cambric.
- At the last stage, it is necessary to tie a feeder or a weight corresponding to the type of fishing to the end of the fishing line.
It should also be remembered that it is always necessary to adjust the drag on the reel if there is a lot of hiding place for fish in the reservoir. The rod must always be visible and within reach in order to exercise control over it. It is advisable to place it in your hand or a special holder, otherwise a large individual may drag it into the water with it, since a fish caught on a self-sustaining hook will no longer be able to get off it.
How to store fishing hooks
Basic storage rules:
- hooks should not come into contact with each other, as well as with other foreign objects.
- if you have a package with hooks, for example, in the amount of 10 pieces, then you can store them in this form.
Storage methods - on leashes in a leash, in plastic boxes, in a matchbox (and in order to prevent it from rusting, put a small piece of cloth soaked in vegetable oil in this box), in a box with a magnet, etc.
Life hack from Arthur Yakovlev, which will show you one of the simple ways to store hooks of the same size
In this video from the Siberia Fishing and Hunting channel you will learn many interesting facts, life hacks and tricks
Typification of fishing hooks
In order not to get lost in the ocean of fishing hooks, they are divided according to many parameters.
Type
- Single. Head -1. Forend and sting - 1 piece each.
- Double. Head -1. Forend and sting - 2 pieces each.
- Triples. Head -1. Forend and sting - 3 pieces each.
By type of fishing
- jig hooks;
- fly fishing hooks, etc.
By type of fish
- carp hooks;
- perch;
- catfish, etc.
Local
- sea fishing;
- freshwater
useful links
https://fish-rifle.ru/stat/rybalka/snasti-i-ekipirovka/?p=rybolovnye-kryuchki-zarubezhnaya-otechestvennaya-klassifikaciya - this article discusses in detail the constituent elements of a fishing hook;
https://rybamechty.com/snasti/snasti-snasti/kryuchki-rybolovnye-razmery1.html - the article is devoted to the types, features of fishing hooks, methods of tying and storing them;
https://rybalkaspoplavkom.ru/ryibolovnyiy-kryuchok/ - article about the design features and shapes of fishing hooks.
Fishing Hook Size Charts
Today, two main hook numbering systems have become firmly established among fishermen:
- Soviet (domestic)
- international (western).
It's easy for an inexperienced beginner to get confused. And while studying the store catalog, you buy absolutely the wrong hooks that are needed. However, Russian and international numberings do not exhaust the entire topic. Although for us they are closer and more convenient than all the others.
There are also Finnish and Japanese numbering. See the table with sizes and corresponding numbers for each classification below.
Types and shapes of fishing hooks
In addition, fishing hooks also differ in shape and purpose. It is clear that for catching bleak, single high-quality hooks are sufficient. In general, today the range of hooks in fishing stores is huge. Their terminology is also varied.
Single Fishing Hooks
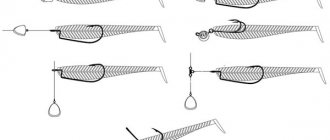
It is important not only to choose the right fishing hook, but also to tie it to the fishing line. Here is an example of using hooks of various shapes. And also the influence of proper knitting on the comfort and success of fishing.
Here are the types of the most popular hooks among fishermen.
These are all single hooks. There are also doubles (twins) and triples (trebles). They are used primarily for catching river predators: pike, asp, pike perch, perch, etc.